Learn about peritoneal tube disease in children
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Tran Van Trong - Specialist in Pediatric Surgery, Plastic Surgery - Aesthetics - Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Danang International Hospital
The process of incomplete sealing of the peritoneal canal in children will cause congenital pathologies such as inguinal hernia, hydrocele, spermatic cyst... If not treated promptly, the child can lead to complications of septic shock due to damage to the digestive tract, high risk of death.
1. What is the peritoneal tube?
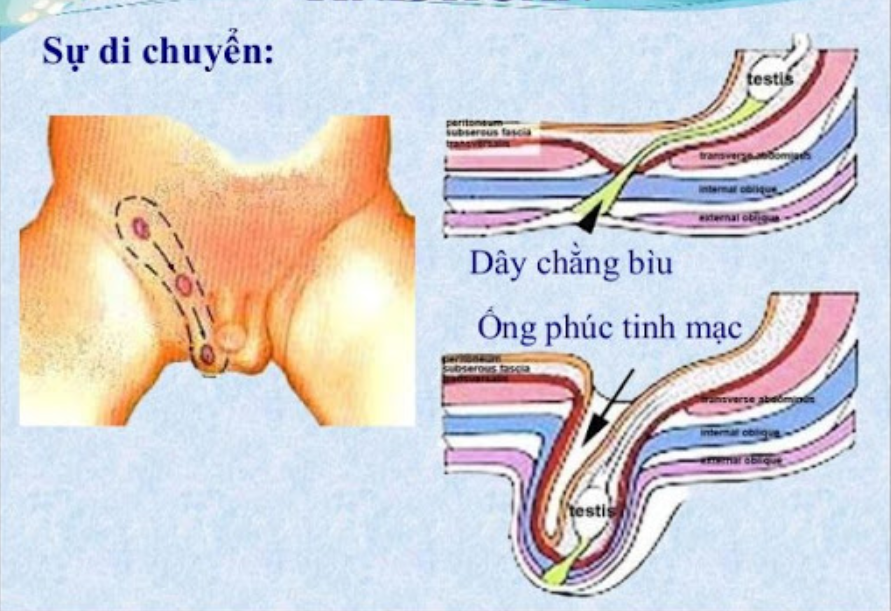
In boys, the peritoneal tube is an extension of the peritoneal tube to the scrotum, located in the inguinal canal and forming the spermatic cord. The spermatic cord consists of the vas deferens and the vas deferens, both of which lie against the wall of the peritoneal duct. When a boy is born, the peritoneal peritoneal tube will fibrosis and the last part of the tube will form a "cap" that covers three-quarters of the testicle - the testicle. In girls, the peritoneal tube is located above the labia majora and forms the Nuck duct.
2. What is peritoneal tube disease?
Normally, at the end of pregnancy, the peritoneal tube will automatically atrophy and form fibrous fibers. In boys, the bottom part forms the testicle, but if for some reason the peritoneal tube is not working as it should, there will be some pathologies of the peritoneal tube in congenital boys such as:
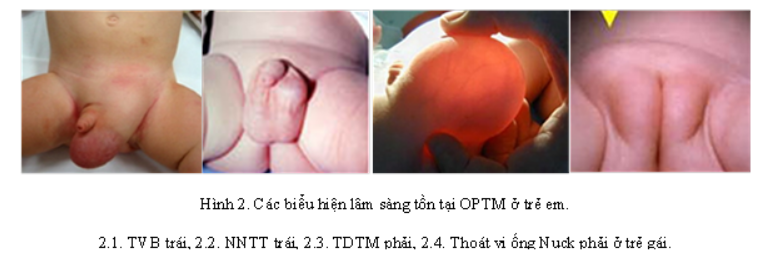
The peritoneal canal is enlarged, so the intestines and abdominal organs can move down into the inguinal-scrotal area and cause a congenital inguinal hernia. The atrophy of the peritoneal canal and segmental fibrosis will cause fluid retention along the spermatic cord to create spermatic cord cysts. The peritoneal tube is atrophied, but there is still a small tube that causes fluid in the abdomen to drain into the scrotum, then the capsule of the testicle is filled with water, causing congenital hydrocele. In girls, the peritoneal tube can cause a Nuck tube hernia (inguinal hernia in girls).
Bệnh lý ống phúc tinh mạc
3. Management of congenital peritoneal tubules
3.1. Congenital inguinal hernia in boys An inguinal hernia can be unilateral or bilateral and presents as a soft mass located above the groin. This tumor can change volume: when the baby is lying down it will shrink and it will expand when the child runs, jumps or cries. Congenital inguinal hernia in boys can lead to complications of strangulation. The symptom to detect a strangulated inguinal hernia is that the hernia can be painful and cannot be pushed up. If treated late, it can lead to intestinal obstruction.
Management of congenital inguinal hernia in boys can happen in two directions:
In case of inguinal hernia is not strangled: parents should take the child to a pediatrician and have an early surgery plan. as possible to avoid complications of strangulation in the future. The doctor may surgically suture the neck of the peritoneal canal close to the deep inguinal ring. The contralateral peritoneal canal can then be examined to avoid missing lesions. In case of strangulated inguinal hernia: The doctor will appoint emergency surgery to release the hernia viscera and sew the neck of the hernia sac. In this case, the hernia sac is not removed because it is easy to tear.
Thoát vị bẹn bẩm sinh
3.2. Management of congenital inguinal hernia in girls Congenital inguinal hernia in girls (Nuck duct hernia) is less common than boys, but this is a matter of great concern in treatment because it is a hernia. Combined ovarian taste - extremely rare.
In case of Nuck tube hernia, after pushing the bowel up, the ovary can be palpated along with a small mass rolling under the finger and cannot be pushed up. For this situation, the doctor will recommend early surgery. For inguinal hernia in girls, the neck can be ligated with the round ligament, the inguinal hole is completely closed, so the recurrence rate is very low.
3.3. Congenital spermatic cord cysts Congenital spermatic cord cysts are round or oval masses of variable volume (1-5cm) located in the path of the spermatic cord. Cysts are usually smooth, painless, and do not shrink when manipulated. In cases of congenital spermatic cysts, the doctor will prescribe surgery to remove the spermatic cord cyst.

Cha mẹ có thể đưa trẻ đến Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec để được thăm khám
3.4. Management of congenital hydroceles Hydroceles may appear soon after birth or some time later. Symptoms of the disease showed that the scrotum was moderately stretched, but there was no pain, and the testicle was not palpable. When viewed through light, it is possible to see how the volume of the scrotum changes at different times of the day: it can enlarge when moving around a lot and shrink when the baby is sleeping.
For cases of congenital hydrocele, the doctor will appoint surgery when the child is after two years of age. The testicle capsule will be opened, followed by suturing the peritoneal canal and opening the epididymal window.
Parents can bring their children to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination, diagnosis and treatment of peritoneal tube disease. Vinmec has a team of well-trained pediatricians, highly qualified and experienced in examining and treating diseases of infants, children and children under 16 years old. Vinmec is equipped with a system of modern and advanced medical supplies and professional service quality that will support high efficiency in diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.






