Can x-rays determine the severity of osteoarthritis?
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Luu Thi Bich Ngoc - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders, especially in the elderly. Although osteoarthritis is not life-threatening, it can affect a patient's quality of life. This disease is also known by other names such as osteoarthritis, wear-and-tear arthritis.
1. What is degenerative arthritis?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common chronic (long-lasting) joint damage. A joint is the place where two bones connect. The ends of these bones are covered with protective tissue called articular cartilage. With osteoarthritis, the cartilage in the joint breaks down, causing the ends of the bones in the joint to rub together. This can cause joint pain, stiffness, and other symptoms.
Degenerative arthritis most commonly occurs in older adults, although the condition can also occur in adults of any age. Degenerative arthritis is also known as degenerative joint disease, wear-and-tear arthritis. This condition is one of the leading causes of disability in the United States.
Degenerative arthritis most commonly occurs in older adults, although the condition can also occur in adults of any age. Degenerative arthritis is also known as degenerative joint disease, wear-and-tear arthritis. This condition is one of the leading causes of disability in the United States.
2. Causes of degenerative arthritis
Degenerative arthritis is a progressive condition in which joint damage occurs faster than the body's ability to repair itself. Degenerative arthritis occurs most commonly in adults over the age of 65 but can occur at almost any age.
Women have a higher risk of contracting this disease than men. While genetics is thought to play a part, degenerative arthritis is often caused by another problem that drives it. This is especially true in children with early-onset osteoarthritis caused by some other medical condition.
2.1. Age Degenerative arthritis occurs due to the aging process of the body and is common in people aged 50 years and over. At this age, the ability to regenerate and produce cartilage cells is reduced, causing the quality of joint cartilage to deteriorate.
At the same time, the body no longer secretes mucus to lubricate the joints. Over time, the joint cartilage loses its elasticity, becomes dry, cracked and worn away, causing pain and limitation of movement.
2.2. Poor posture in living and working People who do specific jobs, often have to sit, stand for a long time in one position or carry heavy objects are very susceptible to degenerative arthritis.
In addition, this disease can also appear due to sleeping with too high a pillow, sleeping only in a fixed position, ... This is also the cause of increasing osteoarthritis in young people.
Improper postures will put great pressure on the joint cartilage and discs, causing damage to the joint cartilage, over time the bones and joints will be weak and prone to degeneration.
2.3. Excessive exercise and sports When playing sports such as football, long jump, tennis, ... will put great pressure on joints. At the same time, there is a risk of causing injuries such as: broken ligaments, fractures, dislocations, ... These injuries make bones and joints degenerate faster.
Women have a higher risk of contracting this disease than men. While genetics is thought to play a part, degenerative arthritis is often caused by another problem that drives it. This is especially true in children with early-onset osteoarthritis caused by some other medical condition.
2.1. Age Degenerative arthritis occurs due to the aging process of the body and is common in people aged 50 years and over. At this age, the ability to regenerate and produce cartilage cells is reduced, causing the quality of joint cartilage to deteriorate.
At the same time, the body no longer secretes mucus to lubricate the joints. Over time, the joint cartilage loses its elasticity, becomes dry, cracked and worn away, causing pain and limitation of movement.
2.2. Poor posture in living and working People who do specific jobs, often have to sit, stand for a long time in one position or carry heavy objects are very susceptible to degenerative arthritis.
In addition, this disease can also appear due to sleeping with too high a pillow, sleeping only in a fixed position, ... This is also the cause of increasing osteoarthritis in young people.
Improper postures will put great pressure on the joint cartilage and discs, causing damage to the joint cartilage, over time the bones and joints will be weak and prone to degeneration.
2.3. Excessive exercise and sports When playing sports such as football, long jump, tennis, ... will put great pressure on joints. At the same time, there is a risk of causing injuries such as: broken ligaments, fractures, dislocations, ... These injuries make bones and joints degenerate faster.

Luyện tập thể thao quá độ có thể tăng nguy cơ gây viêm xương khớp
2.4. Genetic factors If someone in your family has osteoarthritis, your risk of developing the disease is also higher than normal.
2.5. Congenital malformations of the spine Scoliosis curvature partially changes the morphology and normal compression of the spine, gradually causing the spine to degenerate faster than normal.
2.6. Other diseases Osteoarthritis is also a consequence of a number of diseases such as: Osteoporosis, diabetes, gout, ...
2.7. Lack of nutrients Diet lack of nutrients, especially calcium deficiency, chondroitin - these are necessary substances to help keep bones strong - is also one of the causes of accelerating the process of osteoarthritis.
2.8. Overweight Uncontrolled weight gain leads to obesity, which puts more pressure on the spine as well as the entire musculoskeletal system. This long-term condition will lead to damage to the joint cartilage and the bone below the cartilage, causing osteoarthritis.
2.9. Other causes Postpartum women or in perimenopause, menopause are susceptible to degenerative arthritis due to a large amount of calcium deficiency that cannot be compensated in time. In addition, people who have to use antibiotics for a long time can also develop spondylolisthesis earlier than normal.
2.5. Congenital malformations of the spine Scoliosis curvature partially changes the morphology and normal compression of the spine, gradually causing the spine to degenerate faster than normal.
2.6. Other diseases Osteoarthritis is also a consequence of a number of diseases such as: Osteoporosis, diabetes, gout, ...
2.7. Lack of nutrients Diet lack of nutrients, especially calcium deficiency, chondroitin - these are necessary substances to help keep bones strong - is also one of the causes of accelerating the process of osteoarthritis.
2.8. Overweight Uncontrolled weight gain leads to obesity, which puts more pressure on the spine as well as the entire musculoskeletal system. This long-term condition will lead to damage to the joint cartilage and the bone below the cartilage, causing osteoarthritis.
2.9. Other causes Postpartum women or in perimenopause, menopause are susceptible to degenerative arthritis due to a large amount of calcium deficiency that cannot be compensated in time. In addition, people who have to use antibiotics for a long time can also develop spondylolisthesis earlier than normal.
3. Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Patients with degenerative arthritis will experience many persistent and long-lasting symptoms, limiting movement, making the patient always in a state of fatigue and weakness. Below are the common symptoms of osteoarthritis.
3.1. Arthritis pain Symptoms appear in degenerative joints, the pain is often dull, pain increases in the early morning, at night or when moving the joint. There is a crunching sound in the joints during movement. When the weather changes, especially when the cold air comes in, the pain will become more severe.
3.2. Stiffness Joint stiffness in the morning right after waking up is also one of the symptoms of degenerative arthritis.
Because during sleep, the patient often does not move, causing the joints to gradually stiffen. When waking up, the patient cannot perform joint movements as usual. However, the symptoms of stiffness will gradually decrease after a few minutes of massage and movement.
3.3. Limitation of movement Patients with degenerative arthritis will have difficulty in performing joint movements, leading to limitations in daily activities such as: walking, lifting legs, standing up and sitting down, climbing stairs, turning neck,... In the severe stage, the patient also loses balance and falls easily when walking.
3.4. Joint deformity Joint deformity occurs when the disease has entered the severe stage of osteoarthritis, the cartilage is severely damaged, and bone spurs appear. The joints become enlarged and deformed by this condition. Patients will face the risk of disability, if not treated promptly and properly.
3.1. Arthritis pain Symptoms appear in degenerative joints, the pain is often dull, pain increases in the early morning, at night or when moving the joint. There is a crunching sound in the joints during movement. When the weather changes, especially when the cold air comes in, the pain will become more severe.
3.2. Stiffness Joint stiffness in the morning right after waking up is also one of the symptoms of degenerative arthritis.
Because during sleep, the patient often does not move, causing the joints to gradually stiffen. When waking up, the patient cannot perform joint movements as usual. However, the symptoms of stiffness will gradually decrease after a few minutes of massage and movement.
3.3. Limitation of movement Patients with degenerative arthritis will have difficulty in performing joint movements, leading to limitations in daily activities such as: walking, lifting legs, standing up and sitting down, climbing stairs, turning neck,... In the severe stage, the patient also loses balance and falls easily when walking.
3.4. Joint deformity Joint deformity occurs when the disease has entered the severe stage of osteoarthritis, the cartilage is severely damaged, and bone spurs appear. The joints become enlarged and deformed by this condition. Patients will face the risk of disability, if not treated promptly and properly.
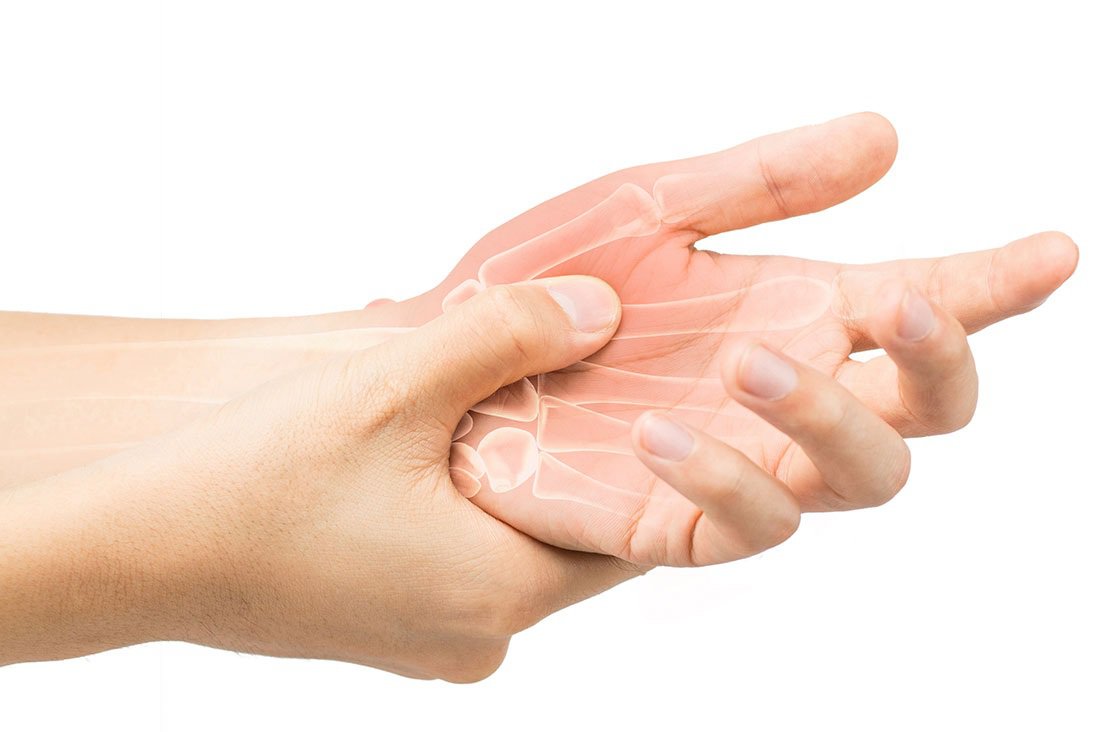
Đau cứng khớp là triệu chứng điển hình của viêm khớp thoái hóa
4. Stages of osteoarthritis
The disease usually goes through 4 stages:
4.1. Stage 1: The manifestation is not clear At this stage, the patient does not feel clear symptoms of the disease, if there is only a transient pain when working too much because the joint cartilage is still slightly affected. At this point, no abnormality in the joint will be detected when the patient has X-ray
4.2. Stage 2: Mild manifestations At this stage, although small bone spurs have begun to form, touching the tissues in the joint, the cartilage layer of the joint has not been damaged much. When waking up or it is cold, the patient will feel that the joints are stiff and painful. The condition where the cartilage begins to wear down, there are bone spurs and the joint space narrows will be detected when performing an X-ray.
4.3. Stage 3: Moderate expression At this stage, cartilage damage is increasing, many medium-sized bone spurs appear, which can deform the subchondral joint surface. Over time, inflammation builds up in the joint tissues, causing swelling. When operating, the patient will feel pain and discomfort.
4.4. Stage 4: Severe manifestations At this stage, the symptoms of the disease begin to appear more clearly, the bone spurs are large, the ends of the bones and joints are completely worn away or there is very little remaining, the mucus surrounding the joints decreases. forward. Stiffness, inflammation, pain, difficulty walking will occur for patients at this stage.
4.1. Stage 1: The manifestation is not clear At this stage, the patient does not feel clear symptoms of the disease, if there is only a transient pain when working too much because the joint cartilage is still slightly affected. At this point, no abnormality in the joint will be detected when the patient has X-ray
4.2. Stage 2: Mild manifestations At this stage, although small bone spurs have begun to form, touching the tissues in the joint, the cartilage layer of the joint has not been damaged much. When waking up or it is cold, the patient will feel that the joints are stiff and painful. The condition where the cartilage begins to wear down, there are bone spurs and the joint space narrows will be detected when performing an X-ray.
4.3. Stage 3: Moderate expression At this stage, cartilage damage is increasing, many medium-sized bone spurs appear, which can deform the subchondral joint surface. Over time, inflammation builds up in the joint tissues, causing swelling. When operating, the patient will feel pain and discomfort.
4.4. Stage 4: Severe manifestations At this stage, the symptoms of the disease begin to appear more clearly, the bone spurs are large, the ends of the bones and joints are completely worn away or there is very little remaining, the mucus surrounding the joints decreases. forward. Stiffness, inflammation, pain, difficulty walking will occur for patients at this stage.
5. How is OA diagnosed?
Based on the physical examination of the patient's symptoms and medical history, a diagnosis of osteoarthritis can reasonably be made. To confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the disease, X-rays can be used.
Joint space stenosis, growth of bone spurs are typical findings on radiographs. At the same time, this is also an overgrowth of bone, also known as subchondral sclerosis or subchondral bone defects.
X-rays help doctors detect the degree of joint deterioration including joint narrowing, thinning or erosion of the ends of bones, fluid accumulation in the joints, bone spurs as well as other abnormal features. Thanks to this method, the doctor can distinguish the different forms of arthritis.
For most cases, no other form of diagnosis is needed. However, a doctor may order a patient to have a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan if a medical condition is suspected. In imaging soft tissues, this method is more effective.
Joint space stenosis, growth of bone spurs are typical findings on radiographs. At the same time, this is also an overgrowth of bone, also known as subchondral sclerosis or subchondral bone defects.
X-rays help doctors detect the degree of joint deterioration including joint narrowing, thinning or erosion of the ends of bones, fluid accumulation in the joints, bone spurs as well as other abnormal features. Thanks to this method, the doctor can distinguish the different forms of arthritis.
For most cases, no other form of diagnosis is needed. However, a doctor may order a patient to have a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan if a medical condition is suspected. In imaging soft tissues, this method is more effective.
6. Differential diagnosis
Joint pain has many causes, and osteoarthritis is just one of more than 100 different types of arthritis. Infections are one of them, and others are triggered by autoimmune disorders. In it, cells are attacked by the body.
Degenerative arthritis is not an infection. This is the main difference between osteoarthritis and all other causes. Although, the result of overtraining or joint activity will lead to inflammation. However, the main feature as well as defining osteoarthritis is not due to this cause.
Autoimmune forms of arthritis can also be distinguished from osteoarthritis. Later on, autoimmune arthritis can involve specific joints and develop bilaterally (on the same joint on both sides of the body). In addition, even when external symptoms are under control, persistent inflammation characterizes autoimmune forms.
Osteoarthritis can be differentiated from other diseases based on a number of features, including:
Ankylosing spondylitis, mainly involving the spine Gout, involving the big toe Inflammation Juvenile idiopathic arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Psoriatic arthritis Infective arthritis (also known as septic arthritis). Osteoarthritis can be differentiated from other conditions by assessing joint space for fluid. An elevated white blood cell count is a clear indicator of infectious or autoimmune causes. That is a sign of inflammation. The number of white blood cells in the joint fluid is not elevated in patients with degenerative arthritis. Blood tests may be used to rule out infectious or autoimmune causes.
Degenerative arthritis is not an infection. This is the main difference between osteoarthritis and all other causes. Although, the result of overtraining or joint activity will lead to inflammation. However, the main feature as well as defining osteoarthritis is not due to this cause.
Autoimmune forms of arthritis can also be distinguished from osteoarthritis. Later on, autoimmune arthritis can involve specific joints and develop bilaterally (on the same joint on both sides of the body). In addition, even when external symptoms are under control, persistent inflammation characterizes autoimmune forms.
Osteoarthritis can be differentiated from other diseases based on a number of features, including:
Ankylosing spondylitis, mainly involving the spine Gout, involving the big toe Inflammation Juvenile idiopathic arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Psoriatic arthritis Infective arthritis (also known as septic arthritis). Osteoarthritis can be differentiated from other conditions by assessing joint space for fluid. An elevated white blood cell count is a clear indicator of infectious or autoimmune causes. That is a sign of inflammation. The number of white blood cells in the joint fluid is not elevated in patients with degenerative arthritis. Blood tests may be used to rule out infectious or autoimmune causes.
Cần phân biệt viêm khớp thoái hóa với các tình trạng khác như: Viêm khớp vảy nến, viêm cột sống dính khớp,...
7. How is degenerative arthritis treated?
Based on each specific case, the notes when treating osteoarthritis are determined. Each case of degenerative arthritis will apply appropriate treatment, mainly including drug treatment, treatment by lifestyle changes, treatment with physical therapy and treatment through surgery. .
7.1. Drug treatment Drugs used to treat OA include topical creams, Acetaminophen, NSAIDs, Glucosamine, opioid pain relievers, and corticosteroid injections. Depending on certain factors, your doctor will prescribe these medications for you, including the current medications you're taking and your pain level.
7.2. Lifestyle changes Losing weight and exercising regularly is a way of making lifestyle changes to make living with osteoarthritis easier. Your doctor will advise you on what to change in your daily activities.
7.3. Physical therapy Through physical therapy exercises, the muscles around the affected joint will be strengthened. In addition, through the use of walking aids or techniques such as splints, physical therapy also involves helping patients with osteoarthritis learn how to cope with the disease, find ways to put extra pressure on the joints. Arthritis patients will also participate in pain management and stress management classes.
7.4. Surgery Pain relief is the primary goal of surgical treatment and, when possible, helps prevent progressive weakness and deformity. There are three types of surgery for joints affected by arthritis, including:
Fusion (arthrodesis): This is a procedure that helps the bones on each side of the joint to grow together. For joints that are stiff and painful, crooked or unstable, this combination can be very helpful. Joint reconstruction or arthroplasty: The basal joint of the thumb and the small joints of the fingers have been developed by artificial joints. A reasonable alternative to primary fusion is a transplant. In some cases, this method can be used to restore motion to the fused joint. Osteotomy: This involves cutting the bones for the purpose of rearranging them in a way that is beneficial to the patient. painless movement. Body modification can reduce the wear and tear of damaged cartilage in patients with osteoarthritis.
7.1. Drug treatment Drugs used to treat OA include topical creams, Acetaminophen, NSAIDs, Glucosamine, opioid pain relievers, and corticosteroid injections. Depending on certain factors, your doctor will prescribe these medications for you, including the current medications you're taking and your pain level.
7.2. Lifestyle changes Losing weight and exercising regularly is a way of making lifestyle changes to make living with osteoarthritis easier. Your doctor will advise you on what to change in your daily activities.
7.3. Physical therapy Through physical therapy exercises, the muscles around the affected joint will be strengthened. In addition, through the use of walking aids or techniques such as splints, physical therapy also involves helping patients with osteoarthritis learn how to cope with the disease, find ways to put extra pressure on the joints. Arthritis patients will also participate in pain management and stress management classes.
7.4. Surgery Pain relief is the primary goal of surgical treatment and, when possible, helps prevent progressive weakness and deformity. There are three types of surgery for joints affected by arthritis, including:
Fusion (arthrodesis): This is a procedure that helps the bones on each side of the joint to grow together. For joints that are stiff and painful, crooked or unstable, this combination can be very helpful. Joint reconstruction or arthroplasty: The basal joint of the thumb and the small joints of the fingers have been developed by artificial joints. A reasonable alternative to primary fusion is a transplant. In some cases, this method can be used to restore motion to the fused joint. Osteotomy: This involves cutting the bones for the purpose of rearranging them in a way that is beneficial to the patient. painless movement. Body modification can reduce the wear and tear of damaged cartilage in patients with osteoarthritis.
8. Diet for patients with degenerative arthritis
Diet and nutrition play a huge role if you have arthritis. First of all, to put unnecessary stress on your joints, you need to keep your weight in the normal range. There are many studies that suggest that a diet high in flavonoids is helpful for certain types of arthritis. This nutrient is found in fruits and vegetables. Besides, many fruits and vegetables also contain antioxidants, which help fight free radicals caused by inflammation. Free radicals are molecules that can damage cells.
By following a high-quality diet, patients with degenerative arthritis can experience relief from their arthritis symptoms by reducing inflammation and swelling. Consuming some of the following foods high in vitamins and minerals may be helpful for patients with degenerative arthritis, such as:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Vitamin C Vitamin D Calcium Beta-carotene Unmodifiable treatment of patients with complete recovery of degenerative arthritis because it is a chronic condition. However, the outlook is good with early treatment. Don't be subjective and ignore the symptoms of chronic joint pain and stiffness. If the patient is diagnosed early and treated promptly, the patient's condition will improve significantly.
Currently, X-ray is a diagnostic imaging method performed routinely at Vinmec International General Hospital, including bone and joint X-ray techniques to determine the extent of degenerative arthritis. . The X-ray procedure at Vinmec is carried out methodically under the guidance of the medical team of the Department of Diagnostic Imaging. In addition, Vinmec is now equipped with the most modern X-ray machine, meeting international standards for true and clear images, helping doctors to accurately diagnose the disease and the stage of the disease, from It has an effective treatment direction, creating a sense of safety for the patient.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please register for an online examination on the Website for the best service.
By following a high-quality diet, patients with degenerative arthritis can experience relief from their arthritis symptoms by reducing inflammation and swelling. Consuming some of the following foods high in vitamins and minerals may be helpful for patients with degenerative arthritis, such as:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Vitamin C Vitamin D Calcium Beta-carotene Unmodifiable treatment of patients with complete recovery of degenerative arthritis because it is a chronic condition. However, the outlook is good with early treatment. Don't be subjective and ignore the symptoms of chronic joint pain and stiffness. If the patient is diagnosed early and treated promptly, the patient's condition will improve significantly.
Currently, X-ray is a diagnostic imaging method performed routinely at Vinmec International General Hospital, including bone and joint X-ray techniques to determine the extent of degenerative arthritis. . The X-ray procedure at Vinmec is carried out methodically under the guidance of the medical team of the Department of Diagnostic Imaging. In addition, Vinmec is now equipped with the most modern X-ray machine, meeting international standards for true and clear images, helping doctors to accurately diagnose the disease and the stage of the disease, from It has an effective treatment direction, creating a sense of safety for the patient.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please register for an online examination on the Website for the best service.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.