Dementia in head trauma
Dementia following head trauma is an important public health problem. Young people are more prone to head injuries than older people. Head trauma is the third most common cause of dementia. It is behind infections and alcoholism.
1. Characteristics and causes of dementia in head trauma
The nature of dementia in people with head trauma varies widely according to the type and location of the injury and the person's characteristics prior to the head injury. Older adults with head injuries are more likely to develop complications such as dementia and, in children, the likelihood of more severe complications. Men, especially younger men, are more likely to have a head injury than women.
Post-head trauma dementia is different from other types of dementia. Many types of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease, get worse over time, but head injury dementia does not usually get worse over time and may even improve somewhat over time. time. However, improvement is often slow and takes months or years.
The most common causes of head injury:
Falls (40%); Injury due to unintentional (15%). Motor vehicle accidents (14%); Attack (11%); Unknown cause (19%); Use of alcohol or other substances is a factor in about half of these injuries.

Bản chất của chứng sa sút trí tuệ ở những người bị chấn thương đầu rất khác nhau tùy theo loại
2. Symptoms of dementia in head trauma
Symptoms associated with dementia in head trauma include those that affect thinking and concentration, memory, communication, personality, interactions with others, mood and behavior . These symptoms appear depending on the head injury, the force of the blow, the extent of the injury, and the personality of the person before the injury. Some symptoms may appear quickly, while others develop more slowly. In most cases, symptoms began to appear within the first month after the injury.
Symptoms of dementia in people with a head injury include:
Problems thinking; Lost memory ; Poor concentration; The thought process slows down; Irritability, easily frustrated; Impulsive behavior; Mood swings; Restlessness or agitation; Insomnia ; Aggression, war or hostility; Headache ; Tired; Ambiguous physical symptoms; Some people have seizures after a head injury. These are not part of dementia, but they can further complicate the diagnosis and treatment of dementia.

Các triệu chứng liên quan đến sa sút trí tuệ trong chấn thương đầu bao gồm những triệu chứng ảnh hưởng đến suy nghĩ và sự tập trung
Major psychiatric disorders can develop after head trauma. A person may have 2 or more of these symptoms:
Depression, sadness, quick tears, lethargy, withdrawal, loss of interest in activities that used to be enjoyed, insomnia or sleeping too much, weight gain or loss; Excessive anxiety or fear that disrupts daily activities or relationships; Physical signs such as restlessness or extreme fatigue, muscle tension, trouble sleeping; Extreme excitement, restlessness, hyperactivity, insomnia, rapid speech, impulsivity, poor judgment; Mental disorder, inability to think realistically; symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, paranoia and lack of clear thinking; If severe, behavior is severely disrupted, and if mild, behavior tends to be bizarre or suspicious; Obsessive-compulsive symptoms; The development of obsessions and compulsions appears; lack of flexibility or ability to change; Risk of suicide. Feeling worthless or life not worth living or the world would be better without them, raising suicidal thoughts, making suicide plans.
3. Examination and screening for dementia after a head injury
In most cases, the appearance of dementia symptoms is clearly related to a known head injury. The doctor will ask the injured person to detail the onset of symptoms. They must include the following:
Determine the exact nature of the injury and how it occurred; The first aid and medical care given immediately after the injury; Your status since injury; Any prescription or over-the-counter medications, which you are taking Describe all symptoms, their duration and severity Details of all treatment undergone since love. In addition, the doctor will also ask details of all current and previous medical problems, all medications and other therapies, family medical history, work history, habits and your lifestyle. In most cases, a parent, spouse, adult child, or other relative or close friend must be present to provide information that the injured person cannot.
At any point during this evaluation, the doctor may refer the injured person to a neurologist.
A thorough physical examination will also be performed to identify neurological, cognitive, mental or social functioning problems and abnormal appearance, behavior or mood. injury.

Trong hầu hết các trường hợp, sự xuất hiện của các triệu chứng sa sút trí tuệ rõ ràng có liên quan đến một chấn thương đầu đã biết
4. Imaging for head trauma, dementia
Head trauma also requires a brain CT scan to determine if any brain structures are physically abnormal.
A CT scan is a test that uses X-rays to show details of the brain. This is the standard test in someone who has had a head injury. Scans performed 1 to 3 months after injury can detect lesions that are not visible immediately after injury. MRI is more sensitive than CT scan in identifying some types of lesions.
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) may be better than CT scan or MRI at detecting functional problems in the brain for certain types of dementia or other brain disorders. SPECT is only available at select major medical centers. An electroencephalogram (EEG) can also be used to diagnose seizures or an abnormally slow brain activity rate.
5. Treatment of dementia after a head injury
A person with a head injury that has become dementia will need treatment for the following:
Behavior modification; Cognitive rehabilitation; Medicines for specific symptoms; The family or network intervenes; Social services. One goal of these interventions is to help people with head injuries adapt to their injuries cognitively and emotionally. Another way is to help the person master skills and behaviors that will help them achieve their personal goals. These interventions also help family members learn about ways they can help the person with the head injury and themselves cope with the challenges that head trauma presents. These interventions can be especially important in setting realistic expectations for outcomes and rates of improvement.
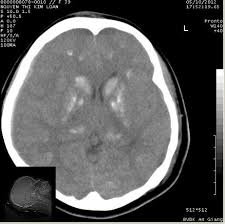
Chấn thương đầu cũng cần phải chụp cắt lớp não để xác định xem có cấu trúc não nào có biểu hiện bất thường về thể chất hay không
6. Head Injury Prevention
Head injury and the complications it causes are very preventable.
Use protective gear when playing contact sports, hard hats and workplace safety equipment if available; Fasten seat belts and wear bicycle and motorcycle helmets; For older adults, changing surroundings to reduce the risk of falls is important; A person who has experienced a head injury is at risk for additional head injuries. Reduce risk by being aware of risk factors; Some patients with head trauma have suicidal thoughts. These people need immediate medical attention. In many cases, suicide can be prevented with depression treatment, counseling, and other therapies; Athletes should not return to competition until they have been cleared by a doctor. The outlook for people with dementia after a head injury is difficult to predict with certainty. Some people fully recover from severe injuries, but others remain disabled for long periods of time after much milder injuries. Dementia caused by head trauma does not usually get worse over time and may even improve over time.
Patients need to go to a reputable hospital to conduct examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of dementia after a head injury. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR portable X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 128 rows and 1 16 arrays), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla and 1 1.5 Tesla), 1 room for 2 levels of interventional angiography and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in diagnosis and detection. early signs of abnormality in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Reference source: webmd.com
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






