Guidelines for monitoring the progression of type 2 diabetes
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Currently, diabetes is increasing, leaving heavy consequences on the health and life expectancy of patients, increasing the burden of disease and social costs. Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90-95% of all patients with diabetes. Monitoring the progress of the disease helps patients prevent possible complications.
1. Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. Diabetes is caused by a defect in insulin secretion, or the action of insulin, or both. Prolonged chronic elevation of glucose will cause disturbances in the metabolism of protide, lipid, carbohydrate,... Then it leads to damage to various organs, especially blood vessels, nerves, heart, eyes, nerves. terrible.
Types of diabetes include:
Type 1 diabetes: Also known as insulin dependent diabetes, due to destruction of pancreatic beta cells leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes: Or non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, due to progressive decrease in pancreatic beta cell function against the background of insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes: Diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. Previously, the patient did not have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Diabetes caused by other causes: diabetes caused by medication, neonatal diabetes,... Of which, type 2 diabetes accounted for about 90. -95% in all forms of diabetes. Therefore, it is very important to guide the progression of type 2 diabetes for patients to help them self-treat at home and to prevent and detect possible complications early. .
Types of diabetes include:
Type 1 diabetes: Also known as insulin dependent diabetes, due to destruction of pancreatic beta cells leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes: Or non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, due to progressive decrease in pancreatic beta cell function against the background of insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes: Diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. Previously, the patient did not have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Diabetes caused by other causes: diabetes caused by medication, neonatal diabetes,... Of which, type 2 diabetes accounted for about 90. -95% in all forms of diabetes. Therefore, it is very important to guide the progression of type 2 diabetes for patients to help them self-treat at home and to prevent and detect possible complications early. .

Đái tháo đường tuýp 2 chiếm khoảng 90-95% trong các thể bệnh đái tháo đường
2. Identify risk factors and diagnose disease
2.1 Risk factors Risk factors for diabetes include:
BMI (weight/height^2) ≥ 23 kg/m2 Age ≥ 45 Blood pressure over 130/85 mmhg Family history diabetics. Women: and have a special maternity history such as: giving birth to a baby weighing more than 3600 grams, pre-diabetes, gestational diabetes, spontaneous abortion, stillbirth,... and having ovarian syndrome polycystic eggs. History of metabolic syndrome, pre-diabetes: impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasting blood sugar. Blood lipid disorders. Lack of physical activity Drink a lot of alcohol, smoke cigarettes 2.2 Diagnosing diabetes To diagnose diabetes is to do a blood sugar test. Patients will be tested for blood sugar in the morning, fasting without eating. Fasting is defined as not eating or drinking energy-dense foods for at least 8 hours prior. The test should be performed 2 times on 2 different days for sure:
Results if blood sugar ≥ 7.0 mmol/L (126mg/dL) is recorded as diabetes. Oral glucose tolerance test (give the patient 75g of glucose to drink, 2 hours after blood glucose measurement). A blood glucose result of ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) is recorded as diabetes. An HbA1C test result ≥ 6.5% in a patient with a normal hemoglobin status (no anemia, no blood loss, no polycythemia vera or other hemoglobin abnormalities) is recognized as diabetes. Patients with symptoms of diabetes (polyuria, increased appetite, heavy weight loss) and random blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) are recorded as diabetes.
BMI (weight/height^2) ≥ 23 kg/m2 Age ≥ 45 Blood pressure over 130/85 mmhg Family history diabetics. Women: and have a special maternity history such as: giving birth to a baby weighing more than 3600 grams, pre-diabetes, gestational diabetes, spontaneous abortion, stillbirth,... and having ovarian syndrome polycystic eggs. History of metabolic syndrome, pre-diabetes: impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasting blood sugar. Blood lipid disorders. Lack of physical activity Drink a lot of alcohol, smoke cigarettes 2.2 Diagnosing diabetes To diagnose diabetes is to do a blood sugar test. Patients will be tested for blood sugar in the morning, fasting without eating. Fasting is defined as not eating or drinking energy-dense foods for at least 8 hours prior. The test should be performed 2 times on 2 different days for sure:
Results if blood sugar ≥ 7.0 mmol/L (126mg/dL) is recorded as diabetes. Oral glucose tolerance test (give the patient 75g of glucose to drink, 2 hours after blood glucose measurement). A blood glucose result of ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) is recorded as diabetes. An HbA1C test result ≥ 6.5% in a patient with a normal hemoglobin status (no anemia, no blood loss, no polycythemia vera or other hemoglobin abnormalities) is recognized as diabetes. Patients with symptoms of diabetes (polyuria, increased appetite, heavy weight loss) and random blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) are recorded as diabetes.
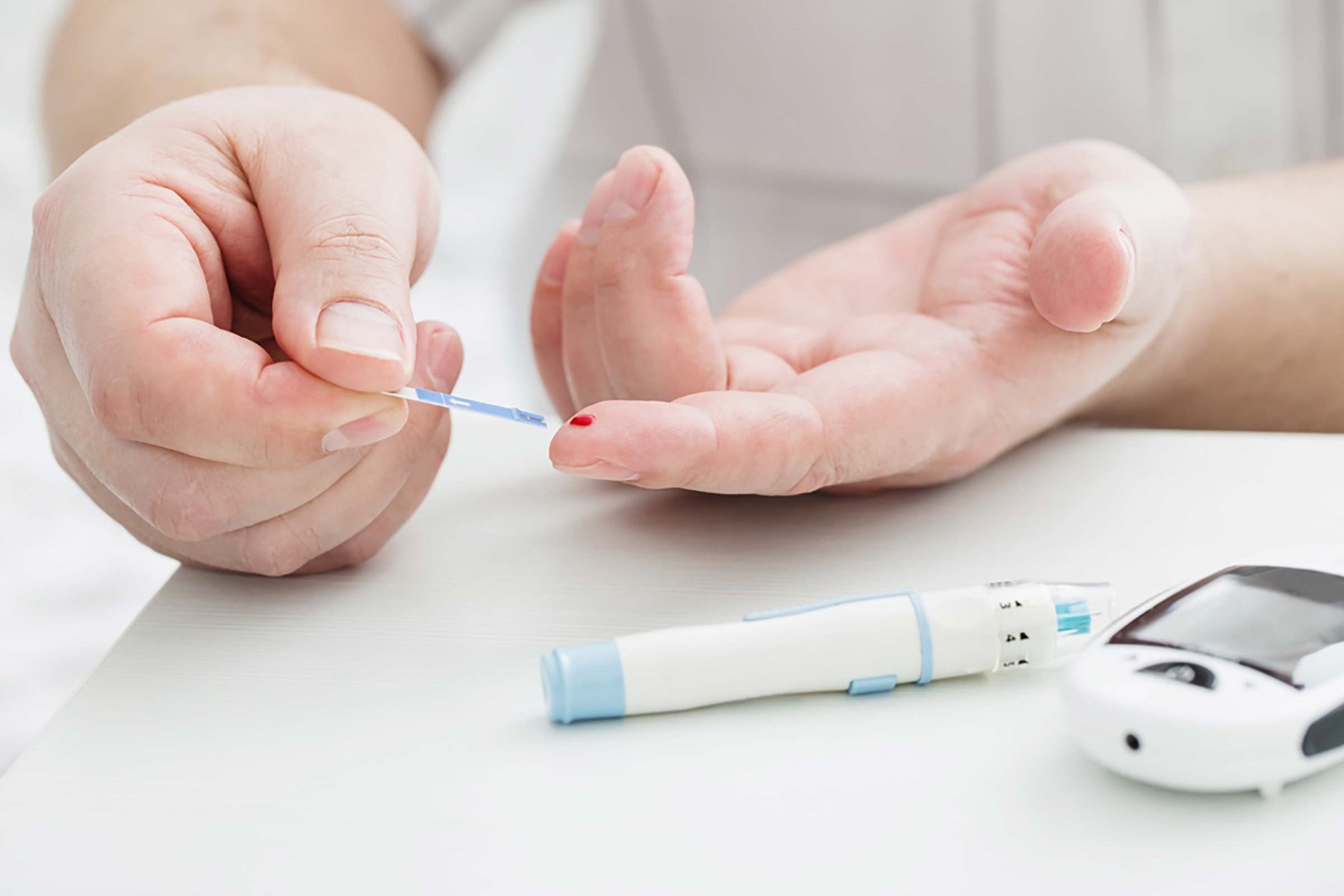
Bệnh nhân được chẩn đoán bệnh đái tháo đường thông qua xét nghiệm máu
3. Managing and monitoring diabetes progression
3.1 Diet and activities Guidelines on living and nutritional regimens for patients to help them lead a healthy lifestyle include:
Increase the intake of green vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Limit starches, and foods of animal origin. Can be replaced with plant-based foods such as beans, peanuts, etc. Do not eat foods that provide fast sugar for example: sweet foods, confectionery, soft drinks. ,... Sweet fruits contain a lot of sugar such as na, jackfruit, mango, pineapple... Chemical sweeteners can be used to replace normal sugar such as saccharin. Note weight loss if you are obese or overweight on a reduced-calorie diet. For people who are not overweight or obese, do not over-diet. Ensure adequate vitamins, especially vitamin B group. Increase physical exercise such as walking, running, swimming. Increase exercise in daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, avoid using motorbikes when not absolutely necessary,... Keep clean to prevent infection: clean body, teeth and treat right away the scratches on the limbs,... Live in moderation, avoid alcohol, and quit smoking. 3.2 Antidiabetic drugs In the initiation of treatment, depending on the level of the baseline diabetes index, cardiovascular risk stratification that considers the choice of different drug combinations. It is common to initiate metformin in conjunction with aggressive lifestyle changes. Particularly in patients with one or more of the following characteristics:
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Very high cardiovascular risk Chronic kidney disease Heart failure In addition to using Metformin in combination with lifestyle changes, consider the use of SGTL2i drugs (Inhibitors of SGTL2 channels in the renal tubules) drugs such as: Empaliflozin (Jardiance), Dapagliflozin ( Forxiga)
In other patients, after 3 months of Metformin therapy in combination with lifestyle changes, the treatment goal had not been achieved (HbA1C target: tight < 6.5%, mean < 7.0%) , loose < 8.0%), then consider the individual characteristics of the patient and choose the combination drug group:
Want to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia: DPP-4i group of drugs such as Sitagliptin (Januvia, Janumet), Sitagliptin (Januvia, Janumet), Vildagliiptin, Linagliptin (Trajenta) or SGLT2i group Want not to gain weight or want to lose weight: SGLT2i group Want to save money: SU group drugs such as Gliclazide MR (Diamicron 30.60), Gliclazide MR (Diamicron) 30,60), Gliclazide MR (Diamicron 30,60).. Patients are usually examined once every 3 months, to adjust the drug according to the target HbA1C. Cases that do not respond to the maximum tolerable dose should be considered in addition to other drug classes, including insulin.
Characteristics of some drugs commonly used in the treatment of diabetes include:
Metformin: Metformin: the cornerstone drug for diabetes treatment. It should be used at the beginning of treatment. Mechanism of action: reduce glucose synthesis in the liver, increase insulin sensitivity in tissues, increase glucose utilization in muscle, reduce glucose absorption in the intestine, inhibit lipid synthesis (triglycerides, cholesterol), create a feeling of loss of appetite. The drug does not cause hypoglycemia Common side effects of the drug are diarrhea, nausea, lactic acidosis (rare), B12 deficiency (peripheral neurological manifestations, anemia). Start with a dose of 500mg x 2 times / day, the maximum dose is usually 1000mg x 2 times / day, gradually increase the dose to avoid side effects. The drug is in the form of delayed release (XR) used once a day (evening). Drink with or after meals.
Increase the intake of green vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Limit starches, and foods of animal origin. Can be replaced with plant-based foods such as beans, peanuts, etc. Do not eat foods that provide fast sugar for example: sweet foods, confectionery, soft drinks. ,... Sweet fruits contain a lot of sugar such as na, jackfruit, mango, pineapple... Chemical sweeteners can be used to replace normal sugar such as saccharin. Note weight loss if you are obese or overweight on a reduced-calorie diet. For people who are not overweight or obese, do not over-diet. Ensure adequate vitamins, especially vitamin B group. Increase physical exercise such as walking, running, swimming. Increase exercise in daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, avoid using motorbikes when not absolutely necessary,... Keep clean to prevent infection: clean body, teeth and treat right away the scratches on the limbs,... Live in moderation, avoid alcohol, and quit smoking. 3.2 Antidiabetic drugs In the initiation of treatment, depending on the level of the baseline diabetes index, cardiovascular risk stratification that considers the choice of different drug combinations. It is common to initiate metformin in conjunction with aggressive lifestyle changes. Particularly in patients with one or more of the following characteristics:
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Very high cardiovascular risk Chronic kidney disease Heart failure In addition to using Metformin in combination with lifestyle changes, consider the use of SGTL2i drugs (Inhibitors of SGTL2 channels in the renal tubules) drugs such as: Empaliflozin (Jardiance), Dapagliflozin ( Forxiga)
In other patients, after 3 months of Metformin therapy in combination with lifestyle changes, the treatment goal had not been achieved (HbA1C target: tight < 6.5%, mean < 7.0%) , loose < 8.0%), then consider the individual characteristics of the patient and choose the combination drug group:
Want to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia: DPP-4i group of drugs such as Sitagliptin (Januvia, Janumet), Sitagliptin (Januvia, Janumet), Vildagliiptin, Linagliptin (Trajenta) or SGLT2i group Want not to gain weight or want to lose weight: SGLT2i group Want to save money: SU group drugs such as Gliclazide MR (Diamicron 30.60), Gliclazide MR (Diamicron) 30,60), Gliclazide MR (Diamicron 30,60).. Patients are usually examined once every 3 months, to adjust the drug according to the target HbA1C. Cases that do not respond to the maximum tolerable dose should be considered in addition to other drug classes, including insulin.
Characteristics of some drugs commonly used in the treatment of diabetes include:
Metformin: Metformin: the cornerstone drug for diabetes treatment. It should be used at the beginning of treatment. Mechanism of action: reduce glucose synthesis in the liver, increase insulin sensitivity in tissues, increase glucose utilization in muscle, reduce glucose absorption in the intestine, inhibit lipid synthesis (triglycerides, cholesterol), create a feeling of loss of appetite. The drug does not cause hypoglycemia Common side effects of the drug are diarrhea, nausea, lactic acidosis (rare), B12 deficiency (peripheral neurological manifestations, anemia). Start with a dose of 500mg x 2 times / day, the maximum dose is usually 1000mg x 2 times / day, gradually increase the dose to avoid side effects. The drug is in the form of delayed release (XR) used once a day (evening). Drink with or after meals.

Metformin - thuốc nền tảng trong điều trị đái tháo đường
Gliclazide MR (Diamicron 30mg and 60mg) belongs to the SU group: The drug has the effect of increasing insulin secretion, for the heart, it also reduces the formation of blood clots. Initial dose: 30mg/day, maximum dose is used 120mg/day. Medicines that can cause hypoglycemia Take the medicine before meals to avoid hypoglycemia. Empaliflozin (Jardiance) belongs to the SGLT2i group: The drug works to remove excess glucose through the kidneys by blocking its reabsorption through blocking the SGTL2 channel in the renal tubules, thereby reducing blood sugar. Initial dose: 10mg/day, the maximum dose used is 25mg/day. The drug has some side effects such as: urogenital infections, dehydration (frequent urination, thirst, constipation, renal failure, low blood pressure), bone fractures, bladder cancer, ketoacidosis that glucose normal blood. Increased risk of hypoglycemia when used with insulin or SU groups. Do not use if glomerular filtration rate < 30 ml/min/1.73 m2. Dapagliflozin (Forexiga 10mg) belongs to the same group of SGLT2i: Mechanism of action and side effects are similar to Empaliflozin. Initial dose: 5mg/day, maximum dose used 10mg/day. Do not use if glomerular filtration rate < 45 ml/min/1.73 m2. Other drugs when used will be consulted by a doctor.
3.3 Detect complications Some clinical signs to detect complications early, and need to take the patient to a medical facility immediately for treatment:
Hyperglycemia: Increased thirst, frequent urination Hyperglycaemic coma: Slow consciousness or coma. Hypoglycemia: Sweating, shaking limbs. Hyperglycemia: Abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea Neurological complications: Numbness of limbs Foot ulcer complications: Leg ulcers Persistent cough Infection: Persistent fever Thrombophlebitis, arterial thrombosis: Leg pain when walking Complications Renal: edema 3.4 Complications of hypoglycemia Some signs of hypoglycemia and its management include:
Symptoms of hypoglycemia are sweating, hunger, tremors, which, if severe, can lead to coma. It usually occurs when a patient takes an overdose of the drug, or skips a meal while still taking the medication. The patient should immediately drink a glass of water with sugar 10 - 15 grams of sugar or eat something sweet such as cake, candy, banana, ... or a glass of sweet fruit juice. After the symptoms are gone, the patient should go to the doctor to adjust the dose of the drug. To avoid complications of hypoglycemia, the patient should eat on time, do not skip meals and take antidiabetic drugs before meals.
3.3 Detect complications Some clinical signs to detect complications early, and need to take the patient to a medical facility immediately for treatment:
Hyperglycemia: Increased thirst, frequent urination Hyperglycaemic coma: Slow consciousness or coma. Hypoglycemia: Sweating, shaking limbs. Hyperglycemia: Abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea Neurological complications: Numbness of limbs Foot ulcer complications: Leg ulcers Persistent cough Infection: Persistent fever Thrombophlebitis, arterial thrombosis: Leg pain when walking Complications Renal: edema 3.4 Complications of hypoglycemia Some signs of hypoglycemia and its management include:
Symptoms of hypoglycemia are sweating, hunger, tremors, which, if severe, can lead to coma. It usually occurs when a patient takes an overdose of the drug, or skips a meal while still taking the medication. The patient should immediately drink a glass of water with sugar 10 - 15 grams of sugar or eat something sweet such as cake, candy, banana, ... or a glass of sweet fruit juice. After the symptoms are gone, the patient should go to the doctor to adjust the dose of the drug. To avoid complications of hypoglycemia, the patient should eat on time, do not skip meals and take antidiabetic drugs before meals.

Người bị hạ đường huyết có triệu chứng vã mồ hôi, lả, run tay
3.5 Assessment of results and goals of glycemic control in non-pregnant type 2 diabetics Capillary glucose before meals: 4.4 - 7.2 mmol/L (80-130mg/dL) Capillary glucose 1-2 hours after meals : <10.0 mmol/L (<180mg/dL) HbA1C: tight < 6.5%, moderate < 7%, loose < 8%. In summary, diabetes is on the rise, leaving heavy consequences on the health and life expectancy of patients, increasing the burden of disease and social costs. Educating patients to monitor the progress of type 2 diabetes can help patients self-treat at home, reduce hospital costs, and detect abnormal signs early and promptly go to medical facilities to prevent dangerous complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the nationwide health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the nationwide health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.






