How to read the results of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical spine
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Dinh Hung and MSc.BS Doan Xuan Sinh, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Initial evaluation of the cervical spine must begin with a general morphological assessment. What is the general or total condition of the spine, as seen on the sagittal, coronal images.
1. The parameters included in the results of magnetic resonance of the cervical spine
Curvature of the spine, the ligaments. Structure of the cervical vertebrae. Neck marrow. Spinal canal, synaptic foramen, lateral joint block. Organize live edge software.
2. How to read statements, analyze indicators
Initial evaluation of the cervical spine must begin with a general morphological assessment. What is the general or total condition of the spine, as seen on the sagittal, coronal images.
Need to quickly identify any gross evidence of recent or metastatic trauma or evidence of diffuse myelopathy, considering the presence of a tumor or infection; or if the case is simple it is necessary to define the type of degeneration (which is the most common condition).
As part of the initial general morphological assessment, a general idea of disease severity can be formed. May start with T2W or STIR sagittal imaging (Figure 1 shows normal spine anatomy).
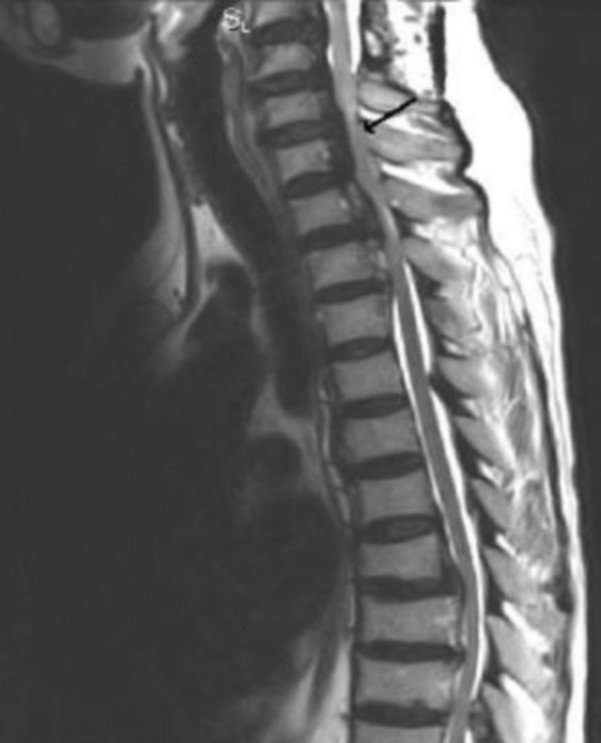
Hình ảnh sagittal T2W
2.1 Assessment of spinal/ligament straightness Immediately after general morphology assessment, spinal straightness can be assessed. All vertebral bodies maintain a normal relationship with the adjacent vertebral body and whether the vertebral bodies are properly aligned (i.e. the posterior, anterior and lateral contiguous cortex are axially aligned).
In the case of a new injury, an indication of misalignment should exclude an associated fracture. In the absence of acute trauma, the most common cause of abnormal vertebral alignment or vertebral subluxation is degenerative slip.
2.2 Evaluation of Vertebral Structures Bone marrow-containing structures need to be evaluated with proper signal features. These signaling features vary with the amount of hematopoietic components compared with the amount of bone marrow fat. Usually, in elderly patients with adipocyte-rich bone marrow, the picture is relatively uniform with sometimes mottled areas of heterogeneity due to the presence of more hematopoietic bone marrow cells.
After examining the vertebral body, remember to consider the other parts of the vertebrae, including the pedicle, the vertebral plate, the superior and inferior articular processes, the transverse processes, and the spinous processes.
This assessment is to detect focal lesions. The most common benign lesion is a vertebral hemangioma (typically as high-intensity as or higher than adjacent bone marrow on T1-weighted images and high-intense on T2-weighted images), low-intense inversion on all pulse sequences, and borderline margins. Characteristic brushing is not always seen on MRI. Normal variations such as marginal vertebrae may also be noted. The vertebral body is bordered by a triangular separation of the apophysis, which may be traumatic or congenital and may involve anterior or posterior vertebral margins.

Các cấu trúc đốt sống cổ trên phim cộng hưởng từ
Finally, check for any evidence of bone marrow fat infiltration (eg, Leukemia, lymphoma, Gaucher disease, eosinophilic granulomatosis, or mucopolysaccharidosis) or if myeloid deficiency , where adipocytes replace hematopoietic components (as seen in aplastic anemia, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy). The vertebral column and waist regions, in particular, should be evaluated in relation to tumors or fractures. MRI has an advantage over CT in the evaluation of cancellous bone, where it is possible to show intraosseous edema following compression injury, which often precedes a marked waist fracture. Detect this early for early treatment.
In addition to evaluating the pedicle within the tumor, the pedicle can be rapidly evaluated on coronal images (if available) and on Axial images to evaluate interpeduncular stenosis. This type of stenosis is often seen on axial images in cases of cartilage aplasia, in which the transverse interpedicular distance is reduced; and on sagittal images in patients with short arches (anteroposterior). Interstitial stenosis should be noted in both the anteroposterior and medial lateral dimensions as this reduction is consistent with the diagnosis of congenital spinal stenosis (as opposed to degenerative stenosis). When there is a large pedicle, the possibility of Paget's disease should be considered. Enlargement of the pedicle may cause lateral recess or foramen constriction. Finally, the presence of bone marrow edema is a clue to trauma, anemia, infection, and adjacent neoplasms. If such causes are absent, then idiopathic edema may be considered.
2.3 Evaluation of the cervical pulp Accurately assess the morphological structures of the pulp to ensure the absence of tumors or other signal abnormalities, in pathologies, marrow infarction, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory myelitis.
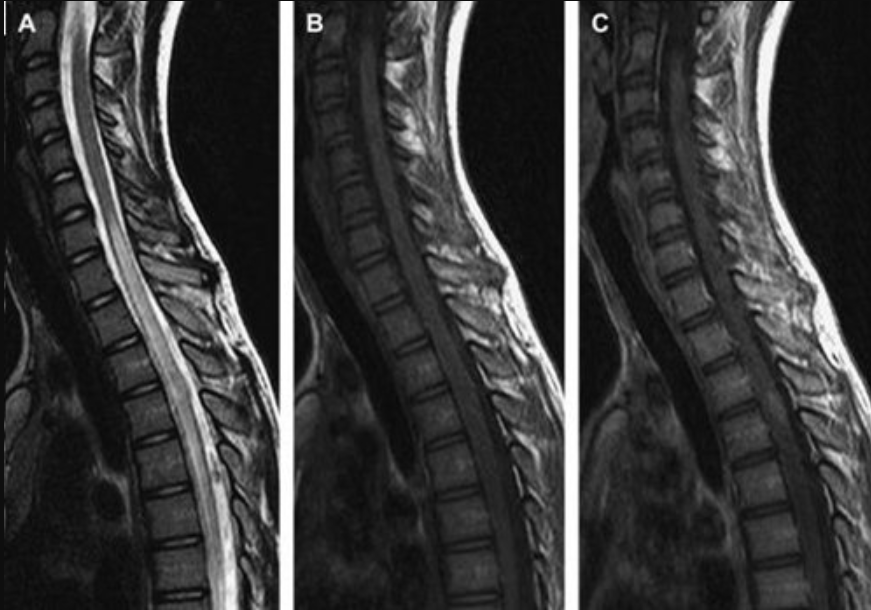
Hình sagittal T2W thấy bất thường tín hiệu kéo dài từ T7 đến L2.
2.4 Review of joints, central and lateral recess Joints, central spinal canal, and lateral recess require careful consideration, including evaluation for posterior interphalangeal (dynamic) and disc spondyloarthropathy buffer (semi-dynamic joint). The posterior interphalangeal joints and the vertebral-cushioned joints form the three-joint complex of the intervertebral joints.
The normal posterior tarsal joint resembles another normal movable joint, showing smooth cortical margins and smooth uniform cartilage and no significant fluid and bony proliferation. The normal yellow ligament is thin and low signal. When the yellow ligament is normal, it is an indistinct structure located along the medial margin of the vertebral plate. Degenerative thickening of the yellow ligament is one of the major causes of central and lateral canal stenosis.
2.5 Examine paravertebral soft tissue and other bony components Paravertebral soft tissue lesions such as paravertebral abscesses, paravertebral soft tissue cyst lesions.
3. What to do with normal spinal indexes
Radiologists synthesize abnormal indicators into groups of symptoms related to certain diseases, coordinate clinical symptoms with clinicians to make diagnoses and give advice to patients. patient.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Reference article:
Textbook of the Cervical Spine E-Book
Spine Magnetic Resonance – MSc Le Van Phuoc
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






