How would you feel if your blood sugar was too high?
Blood sugar that is too high or too low can increase your risk of developing a diabetic coma. This is a serious, life-threatening health problem if not treated promptly. Therefore, strict implementation of measures to control blood sugar is an important step in the prevention of diabetic coma.
1. Overview of diabetic coma
Diabetic coma is a life-threatening diabetic complication that causes unconsciousness. If you have diabetes, your blood sugar will either go high (hyperglycemia) or low (hypoglycemia). At dangerous levels, it can lead to a diabetic coma.
If you fall into a diabetic coma, you will not be able to wake up or be able to respond purposefully to sounds, images or other stimuli. If not treated early, a diabetic coma can lead to death.
Diabetic comas, although quite dangerous, can be prevented by following a diabetes treatment plan prescribed by your doctor, combined with a healthier lifestyle .
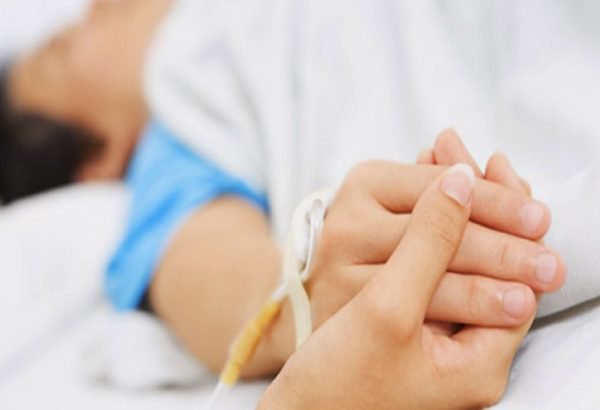
Nếu lượng đường trong máu của bạn quá cao hay quá thấp, nó có thể dẫn đến hôn mê do tiểu đường
2. Symptoms of Diabetic Coma
Before developing a diabetic coma, you may experience some signs and symptoms of high blood sugar or low blood sugar. Specifically:
*High blood sugar (hyperglycemia): If your blood sugar is too high, you will have the following symptoms:
Increased thirst Fatigue Urinating more often Nausea and vomiting Vomiting Abdominal pain Shortness of breath Very dry mouth Fruity breath Tachycardia *Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia): Some of the signs and symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
Anxiety and trembling Weakness Fatigue Feeling very hungry Sweating Dizziness or lightheadedness Nausea Difficulty speaking Confusion For some people, especially those who have had diabetes for a long time, it can develop a condition known as hypoglycemia unawareness. This condition will not have specific warning signs when your blood sugar drops.
If you experience any symptoms of high or low blood sugar, you should have your blood sugar checked and follow the diabetes treatment plan prescribed by your doctor based on the results. test results.
3. Causes of diabetic coma
Blood sugar levels that are too high or too low for a long period of time can cause many different serious health conditions, all of which can lead to a diabetic coma, including:
Ketoacidosis Diabetes: If your muscle cells are starved for energy, your body responds by breaking down your fat stores. This process forms toxic acids, also known as ketones. If ketone levels (measured in blood or urine) and blood sugar are high, the condition is called diabetic ketoacidosis. If not treated promptly, it can lead to a diabetic coma. Diabetic ketoacidosis most commonly occurs in patients with type 1 diabetes, but can also occasionally occur in type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes. Diabetic Hyperosmolar Syndrome (Hyperosmolar): If your blood sugar exceeds 600 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 33.3 millimoles per liter (mmol/L), the condition will known as diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome. Severely high blood sugar can cause your blood to become thick and syrupy. The excess sugar moves from your blood into your urine, triggering filtration to draw large amounts of fluid out of your body. Without early treatment, this can lead to dehydration, which is life-threatening and causes a diabetic coma. According to research, about 25 to 50% of people with diabetic osmotic syndrome are at risk of developing a diabetic coma. Hypoglycemia: Normally, our brain will need a certain amount of glucose to be able to function effectively. In some severe cases, low blood sugar can cause you to become unconscious. Hypoglycemia occurs because your body has too much insulin or doesn't eat enough food. In addition, intense exercise or drinking too much alcohol can also cause low blood sugar.
4. Risk factors for diabetic coma
Anyone with diabetes is at high risk of developing a diabetic coma, however the following factors are considered top risk factors for this condition, including:
Problems with insulin delivery : If you are using an insulin pump, you need to check your blood sugar often. The insulin delivery may stop if the pump fails or the catheter becomes twisted or falls out of place. A lack of insulin can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Illness, injury, or surgery: When your body gets sick or suffers an injury, your blood sugar tends to spike suddenly. This can cause diabetic ketoacidosis if you have type 1 diabetes and don't increase your insulin dose to make up for the shortfall. Certain other health conditions, such as kidney disease or congestive heart failure, can also increase your risk of diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome (hyperosmolar). Poorly controlled diabetes: If you don't regularly monitor your blood sugar or take medications not as directed by your doctor, you're at increased risk for long-term diabetes complications, even death. diabetic coma. Intentionally skipping meals or not taking insulin: Sometimes people with diabetes who may also have an eating disorder choose not to use insulin as directed in the hope of possibly losing weight. This is a rather dangerous, life-threatening act and increases the risk of a diabetic coma. Drink a lot of alcohol: Alcohol is one of the factors that can have a difficult effect on your blood sugar. The sedative effects of alcohol can make it difficult to tell when you're experiencing symptoms of low blood sugar. This will also increase the risk of a diabetic coma. Using illegal drugs: Certain banned drugs, such as cocaine or ecstasy, can increase the risk of severely high blood sugar and other marriage-related conditions. diabetic coma.
5. Complications of Diabetic Coma
If not treated early, diabetic coma can lead to the following dangerous complications:
Permanent brain damage Death

Tổn thương não, thậm chí tử vong là những biến chứng nguy hiểm của hôn mê do tiểu đường
6. Prevention of diabetic coma
Good control of your diabetes every day can help you effectively prevent a diabetic coma. To achieve this, you can follow some simple methods below:
Plan your meals accordingly: Making a specific plan and coming up with a consistent eating schedule (all meals) Meals and snacks) will help you keep your blood sugar under control. Regularly monitor blood sugar: Regular blood sugar testing is a way to help you know if your blood sugar level is normal or not, thereby providing an early warning of dangerous high or low blood sugar levels. dangerous. In addition, people with exercise habits also need to check their blood sugar regularly, as exercise sessions can lower blood sugar levels in just a few hours. Take medication as directed by your doctor: If you regularly have high or low blood sugar, you should talk to your doctor to help adjust the dose and duration of medication that is right for you. Manage diabetes on sick days: Illnesses can cause sudden swings in your blood sugar. If you are sick and cannot eat and drink as usual, there is a risk that your blood sugar will drop (hypoglycemia). Therefore, when you are sick, you should talk to your doctor about the best way to manage or control your blood glucose levels. Test for ketones when blood sugar is high: You should have a urine test about 2 times in a row to check for ketones when your blood sugar is above 250 mg/dL (or 14 mmol/L), most is when you are sick. If the results show higher than normal levels of ketones, you should see your doctor immediately as high ketone levels can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis – a leading factor in diabetic coma. Street. Have glucagon and fast-acting sources of sugar on hand: If you're using insulin to treat diabetes, you should have glucagon and quick-acting sources of sugar on hand. such as glucose tablets or orange juice, which provide quick treatment and support for cases of hypoglycemia. Use a continuous blood glucose monitor (CGM): This special device will help you monitor your blood glucose level even if you are having trouble maintaining a steady blood sugar or not feeling it. have any symptoms of hypoglycemia. A CGM is a device that uses a small sensor, mounted underneath the skin, to monitor your blood sugar and transmit the received information to a wireless device. These devices can warn you when your blood sugar is dangerously low or it is dropping too quickly. However, you will still need to check your blood sugar with a glucometer even if you are using a CGM. Although CGMs are more expensive than other conventional methods of blood glucose monitoring, they often give you better control of your blood sugar. Use caution with alcohol: Alcohol can have a big effect on your blood sugar, so it's a good idea to have a snack or a meal while drinking. To actively control diabetes, you should have regular health checkups on schedule. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Standard 2020 VIP general health checkup package 2020 General health checkup package Special 2020 Patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
If you have a need for a general health check at Vinmec, please register directly at the website or contact the hotline system for detailed advice.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Reference source: mayoclinic.org






