5 causes of pain in the ovary, diagnosis, treatment
The ovaries are an important part of the female reproductive system with two main functions: (1) producing egg cells and (2) producing the hormones estrogen and progesterone and triggering menstruation. There are many causes of ovarian pain, from cysts to tumors.
1. Ovarian cyst
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in the ovaries. This disease is very common in women, especially of reproductive age. Usually cysts form during ovulation because the egg is not released or after the egg is released, the follicle sac does not disappear, the sac swells and contains fluid inside. Ovarian cysts usually cause no symptoms and go away on their own. However, they can produce a dull ache or sharp pain if the cyst is large and ruptures.
Other symptoms of ovarian cysts
Irregular menstrual cycles Pain during intercourse or bowel movements Nausea or vomiting Feeling full quickly after eating Bloating How an ovarian cyst is diagnosed?
Pelvic exam to detect tumors. An ultrasound uses sound waves to create an image of the ovaries and help your doctor determine the size and location of the cyst. Ovarian cyst treatment
Waiting. Most ovarian cysts will go away on their own. If you don't have any unpleasant symptoms, especially if you haven't reached menopause. Instead of no treatment, your doctor will recommend regular physicals to monitor for any changes in your cyst or your overall health. Endoscopic surgery. This is a technique that uses a small incision and a small camera on the tip of the device that is inserted into the abdomen to help the doctor see inside the pelvis and remove small cysts. Larger cysts may require a larger incision in the abdomen. Birth control pills. Birth control pills that prevent ovulation should reduce the chance of new cysts forming.
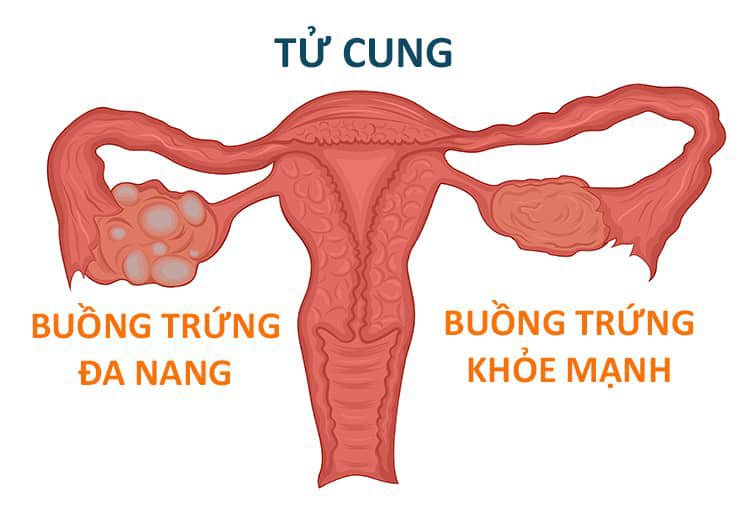
Phẫu thuật nội soi là phương pháp điều trị u nang buồng trứng hiệu quả
2. Ovarian tumor
Tumors can form in the ovaries, just like in other parts of the body. The tumor may be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant), and the tumor may cause right ovarian pain or left or bilateral ovarian pain.
In addition to pain, other symptoms of an ovarian tumor include:
Bloating or a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen Urinating Indigestion Diarrhea or constipation Loss of appetite, or feeling of fullness Unknown weight loss causes or enlargement of the abdomen How is an ovarian tumor diagnosed?
Computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). These are diagnostic techniques that produce detailed images that help the doctor find the tumor in the ovary and whether the ovarian tumor has spread and, if so, where. CA-125 . This is a blood test that looks for a protein that tends to be higher in women with ovarian cancer. CA-125 is not used to screen for ovarian cancer, but it can be done in women who have symptoms of ovarian cancer. Ovarian tumor treatment
Laparoscopic surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. If the tumor is cancerous and has spread, the surgeon may also remove the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, fatty deposits on the waist where the omentum is located, and nearby lymph nodes. Valence . Chemotherapy includes drugs that are given through a vein or orally to kill cancer cells. Radiotherapy . This treatment uses high-energy X-rays to kill or shrink cancer cells. Radiation is given from outside the body or placed directly near the site of a tumor on the inside of the body.
3. Ovarian pain due to endometriosis
Normally, the uterine cavity is covered with a layer of lining called the endometrium. Every month, this lining grows so that at the end of the menstrual cycle, if the egg is not fertilized, this lining will shed to form menstruation. Normally only the uterine cavity has a layer of endometrium, but if this layer occurs outside the uterus, it is called endometriosis.
Other symptoms of endometriosis include:
Pain in the pelvic area during menstruation and increasing pain Pain during intercourse More bleeding than usual Vaginal dryness Pain during bowel movements How is endometriosis diagnosed?
Based on medical history and physical exam Ultrasound and MRI scan to help the doctor detect the location of endometriosis. Abdominal endoscopy. Treatment of endometriosis
Painkiller. Medications like ibuprofen can help relieve some of the uncomfortable symptoms of endometriosis. Birth control pills, which prevent the monthly growth of endometrial tissue on the ovaries and elsewhere, help reduce endometriosis symptoms and make menstrual cycles lighter. GnRH-agonists (GnRH agonists). This is a group of drugs that reduce the amount of estrogen hormone in the body, so it will slow the development of endometriosis and limit its symptoms. Laparoscopic surgery to remove endometriosis on the ovaries and elsewhere. If endometriosis is extensive, your doctor may recommend removal of the uterus and sometimes the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
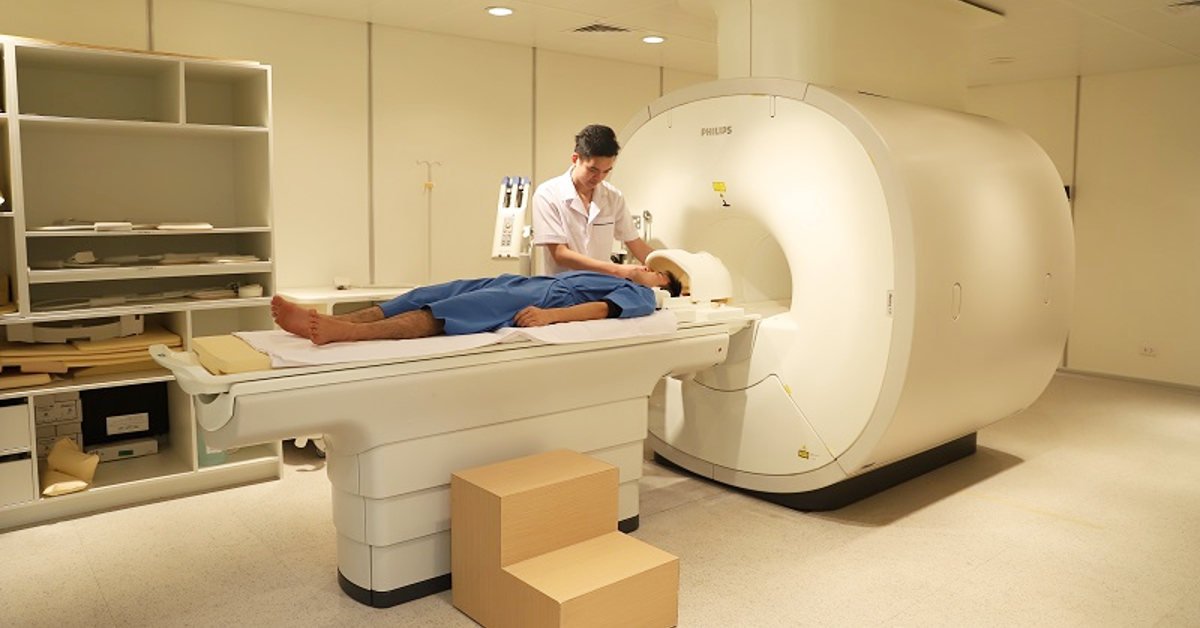
Siêu âm và chụp MRI để giúp bác sĩ phát hiện vị trí của lạc nội mạc tử cung.
4. Pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is an infection of the ovaries, uterus or fallopian tubes. It is caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea or chlamydia. It is one of the most common causes of pelvic pain in women.
Other symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease include:
Pain during intercourse Fever Vaginal discharge with an unusual odor Irregular menstrual bleeding Diarrhea Vomiting Fatigue Difficulty urinating How is pelvic inflammatory disease diagnosed?
Pelvic exam to have your doctor look for any lumps, unusual discharge, or pain in the pelvis. Blood and urine tests to identify infection. Pelvic ultrasound. Abdominal endoscopy. Pelvic inflammatory disease treatment
Antibiotics by mouth or by infusion/intravenous to kill the bacteria that cause pelvic inflammatory disease. If you are taking antibiotics for treatment, your sexual partner should also be treated, as there is a high chance that you have passed on a sexually transmitted infection to others or vice versa.
5. Pieces left after ovarian surgery
After surgery to remove the uterus and ovaries, in rare cases, a small piece of the ovary may be accidentally left behind. This remnant can develop into painful cysts in the abdomen.
Other symptoms include:
Pain during intercourse Difficulty urinating Diagnosis
The doctor will perform an ultrasound, CT scan and MRI scan to locate any remaining tissue in the abdomen.
Treatment
Usually, the doctor will perform laparoscopic surgery to remove the pieces left in the ovaries or laparoscopic surgery to remove these pieces in the abdomen.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Articles refer to sources: webmd.com, healthline.com
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






