Treatment of acute intussusception in children
This article is professionally consulted by Resident Doctor Resident Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Acute intussusception is an acute illness in children in which part of the anterior intestine slides into the lumen of the intestine in the subsequent passage. This condition often blocks food or fluid from passing through the intussusception or cuts off blood supply to the affected portion of the intestine leading to intestinal perforation, infection and necrosis of intestinal tissue.
1. Symptoms of children with intussusception
Because acute intussusception in children is an acute disease, in case you think your child may have intussusception, go to a medical facility immediately for timely diagnosis and treatment. Each child may have different symptoms. The most common symptom is sudden abdominal pain, the baby crying very loudly even though the baby was previously healthy.
At first parents may think the baby is fussy but then the infant raises his knees high, acts very irritable and cries loudly. Children may feel better and play in the midst of pain. Or the baby may become tired and exhausted from crying a lot.
Other symptoms include:
Vomiting profuse bloody stools. Fever Fatigue or lethargy Diarrhea Sweating Dehydration Stomach bloating. A hard lump can be seen on the abdomen. Not every child has all of the symptoms. Some babies have no obvious pain and some have no blood or a hard mass in the abdomen. Some older children may have only colic but no other symptoms.

2. Causes of acute intussusception in children
Currently, doctors have not found the exact cause of acute intussusception in children. It usually occurs in the fall and winter, and because many children have flu-like symptoms of acute intussusception, some experts suspect a virus may play a role in the cause of acute intussusception. In some cases, it can happen after a child has had gastroenteritis or stomach flu (Stomach Flu). A bacterial or viral gastrointestinal infection can cause swelling of the infection-fighting lymph node tissues in the intestinal tract and lead to one part of the intestine slipping into the next.
In children less than 3 months of age or older than 5 years, acute intussusception is more likely to be related to certain physical conditions such as enlarged lymph nodes, tumors, or problems with blood vessels in the intestines.
3. Treatment of acute intussusception in children
Treatment will depend on the symptoms and severity of the intussusception, the age and general condition of the child. Occasionally, intussusception can resolve spontaneously when the child has a barium-enhanced gastrointestinal x-ray. In many other cases, the doctor will treat it by placing a small tube into the child's rectum under the guidance of an ultrasound or X-ray (fluorescent) machine to help put the tube in place and pump air or water. salt. Injecting air will help the intestines move back to its normal position. But if the child has complications such as an abdominal infection or other problems, the doctor will have to perform surgery.
For surgery, the child will be anesthetized and the surgeon will open the abdomen to push the intestines back to their original position and check for other problems in the abdomen. If there is a section of intestine that has become necrotic, then the doctor will have to remove and connect the two ends of the healthy intestine together.
After treatment, the child will stay in the hospital and receive parenteral nutrition until bowel function returns to normal and the child can eat. Doctors will keep a close eye on the baby to make sure the intussusception doesn't come back. In addition, some children must take extra antibiotics to prevent infection.
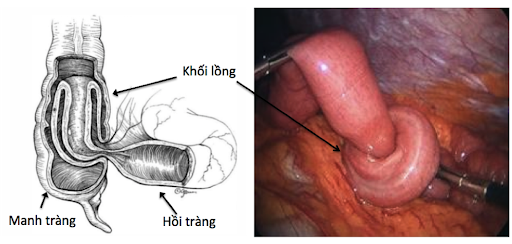
4. Complications of acute intussusception
Acute intussusception can cut off the blood supply to the posterior part of the intussusception, causing the intestine to become necrotic due to lack of nourishment. Intestinal necrosis can lead to intestinal perforation and an infection of the lining of the abdominal cavity known as peritonitis.
Peritonitis is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Signs and symptoms of peritonitis include:
Abdominal pain Abdominal bloating Fever Fever Peritonitis can send a child into shock. Signs and symptoms of shock include:
Cold, wet, pale, or gray skin and limbs Weak and rapid pulse Abnormal breathing rate that may be slow and shallow or very rapid Worrying or agitated face Child in shock may be conscious or unconscious. If you suspect your child is in shock, take them to a medical facility for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
For detailed advice, please come directly to Vinmec Health System or book online
References: stanfordchildrens.org, mayoclinic.org






