Is skin cancer hereditary? Genes and other factors
Skin cancer is a fairly common cancer that can develop by many different factors, including genetics and the environment. Skin cancer is divided into several types with varying degrees of severity. Taking preventive measures early can help reduce the risk of this disease.
1.Most common types of skin cancer
Skin cancer is classified based on the type of skin cells affected on your body. The most common types of skin cancer include:
1.1 Keratin cell carcinoma
This is the most common type of skin cancer and can be divided into 2 subtypes:
Basal cell carcinoma, which accounts for a large proportion (about 80%) of skin cancer cases. It tends to affect mainly the basal cells located in the outermost layer of the skin, also known as the epidermis. In general, basal cell carcinoma is usually the least life-threatening. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), usually begins in the squamous cells and is found in the epidermis just above the basal cells of the skin. In general, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are more likely to develop in locations that are regularly exposed to the sun's UV rays, such as the neck and head. Although these types of skin cancer can spread to other parts of the body, they are rare, especially if found and treated early.
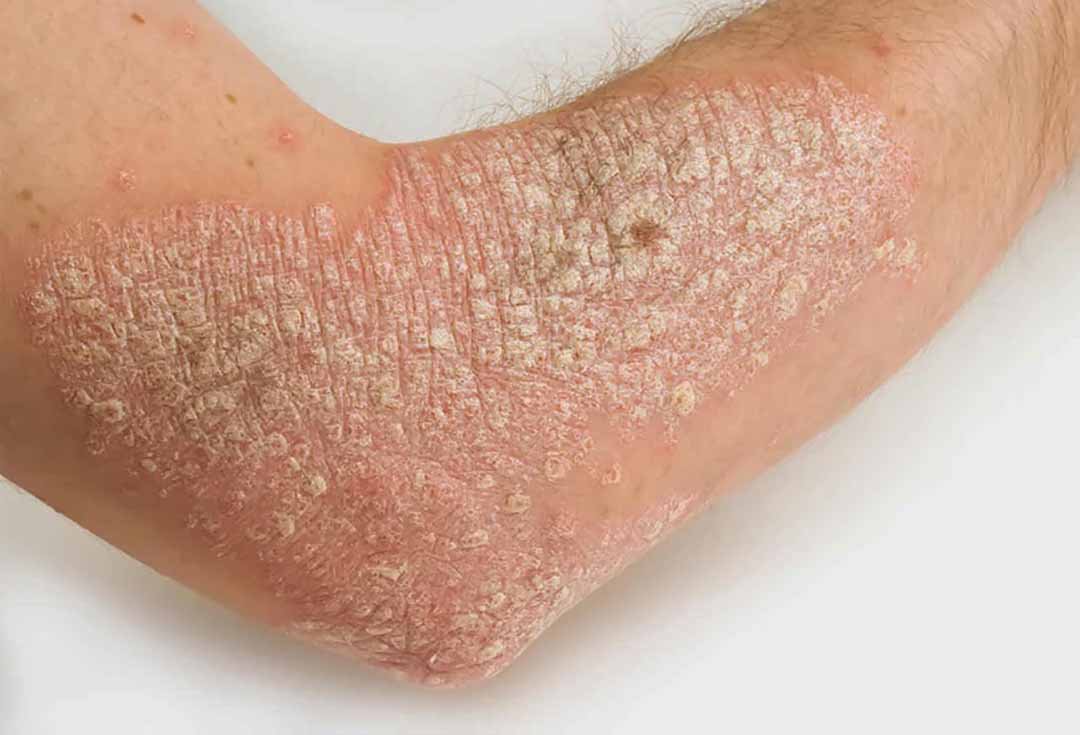
Ung thư da tế bào mô sưng kiến da trở nên khô và cứng
1.2 Melanoma cell cancer
It is a less common but more serious and dangerous type of skin cancer than other types. Melanoma is more likely to spread to other areas of the body if not detected and treated early.
1.3 Other less common types of skin cancer
Other types of skin cancer include:
Merkel cell carcinoma Skin T-cell lymphoma Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) Sebaceous adenocarcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma Skin T-cell lymphoma Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) Sebaceous adenocarcinoma
2. How is genetics related to skin cancer?
Many people wonder if skin cancer is hereditary? Although we know that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or tanning beds can increase the risk of skin cancer, it seems that genetics or family history may also be a factor. factor in the development of this disease.
According to researchers, about 10% of cases diagnosed with melanoma have a family member who has had this skin cancer at some point in their lives. surname. So, if you have a close relative, such as a parent, brother, or sister with melanoma, you have a higher risk of developing the disease.
In addition to the cancer gene, you can also get skin cancer if you have many unusual or atypical moles, including the following:
Asymmetrical moles Moles with serrated edges or not even
According to researchers, about 10% of cases diagnosed with melanoma have a family member who has had this skin cancer at some point in their lives. surname. So, if you have a close relative, such as a parent, brother, or sister with melanoma, you have a higher risk of developing the disease.
In addition to the cancer gene, you can also get skin cancer if you have many unusual or atypical moles, including the following:
Asymmetrical moles Moles with serrated edges or not even
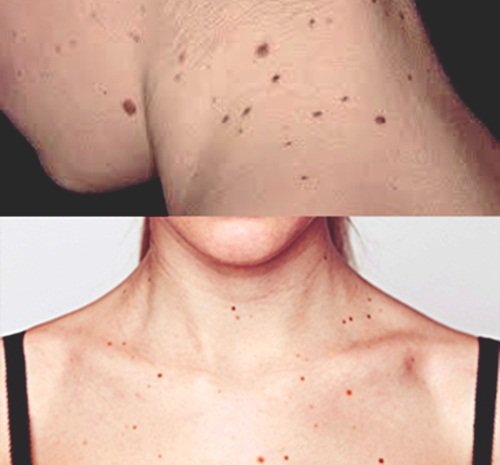
Nổi các nốt ruồi bất thường là dấu hiệu của bệnh ung thư da
Moles of different shades, such as tan, brown, black or red The diameter of the mole is larger than 1⁄4 inch The size, color, shape and thickness of the mole have changed significantly In addition, people with the gene for skin cancer, also known as familial atypical multiple mole syndrome (FAMMM) have a 17.3 times higher risk of developing melanoma compared with those who do not. others. Studies have also shown that certain defective genes can be inherited and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
DNA changes in tumor suppressor genes, such as BAP1 and CDKN2A, may increase the risk of melanoma, say researchers. If these genes are damaged by UV radiation, they can stop doing their job of controlling cell growth, thereby contributing to the formation of cancer cells in the skin. .
On the other hand, white or light-skinned people seem to have a higher risk of skin cancer than other people. This is because of the physical characteristics they inherit from their parents. People who are born with the following characteristics have a higher risk of developing skin cancer at some point in their lives:
Red or yellow hair Fair and freckled-prone skin Light eye color
3. Some other factors contribute to the development of skin cancer
Many cancers can result from a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Although genes play a role in increasing the risk of skin cancer, the environment seems to have a larger impact.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun is considered the main cause of skin cancer. In addition, UV rays from ultraviolet lamps or tanning beds can also harm your skin.
Although the sun can cause bad effects on your skin from an early age, many cases of skin cancer appear only after the age of 50. UV rays from the sun can change or damage the DNA structure of skin cells, causing cancer cells to grow and multiply rapidly. People who live in areas with high levels of UV radiation from the sun have a higher risk of skin cancer than other people.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun is considered the main cause of skin cancer. In addition, UV rays from ultraviolet lamps or tanning beds can also harm your skin.
Although the sun can cause bad effects on your skin from an early age, many cases of skin cancer appear only after the age of 50. UV rays from the sun can change or damage the DNA structure of skin cells, causing cancer cells to grow and multiply rapidly. People who live in areas with high levels of UV radiation from the sun have a higher risk of skin cancer than other people.
4. How to prevent skin cancer?
Even if you have a cancer gene or other high risk factors for skin cancer, it's important to take precautions to protect your skin from UV damage.
If skin cancer runs in the family or you have fair skin, it's best to pay attention to protect your skin from the sun. Here are some skin cancer prevention measures to take:
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen: Include sunscreens that block both UVA and UVB rays. Use a high SPF sunscreen: Dermatologists recommend that everyone wear a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Reapply Sunscreen Regularly: Remember to reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, or even more often if you sweat a lot, after exercising or swimming.

Bảo vệ làn da khỏi tác động của ánh mặt trời giúp ngăn ngừa ung thư da
Limit direct sun exposure: If you have to go outside, you should try to find places with shade, especially from 10 am to 3 pm - when UV rays are most active best. Wear a wide-brimmed hat: Provides extra protection for the face, head, ears, and neck. Wear sun-protective clothing: Choose light and loose-fitting sun-protective clothing to avoid clogging your skin. Get regular skin checkups: You should try to get your skin checked every year at a dermatology clinic. Tell your doctor if you have a family history of melanoma or other types of skin cancer. Early diagnosis for timely treatment helps increase the likelihood of recovery for skin cancer patients. A skin biopsy is one of the methods used to diagnose skin cancer. At Vinmec International General Hospital, the skin biopsy technique is currently being applied in a sterile environment. The doctor performing the procedure is experienced and highly qualified, professional medical examination and treatment services.






