9 important functions of protein for the body
Protein is a very important nutrient for health. Proteins are made up of amino acids, linked together to form long chains. Proteins are involved in most cellular functions and perform many different tasks. So what does protein do?
1. Growth and maintenance of tissues
The body needs protein to function in growth and maintenance of tissues. However, protein in the body is always in a state of constant change.
Normally, the body breaks down certain amounts of protein to build and repair tissues. But sometimes protein is also used more than usual, causing the body's need for additional protein to increase.
This condition is common in people who are sick, pregnant and lactating women. In addition, people recovering from injury or surgery, the elderly, and athletes also need more protein. These subjects often need the effect of whey protein to supplement protein.

Whey protein giúp bổ sung protein
2. Create a biochemical reaction
Proteins make enzymes, involved in supporting thousands of biochemical reactions that take place inside and outside cells. The structure of an enzyme that combines with other molecules inside the cell - called a substrate, to catalyze reactions necessary for metabolism.
Some enzymes also work outside of cells, including digestive enzymes such as lactase (which helps break down the milk sugar lactose) and sucrase (which helps hydrolyze sugar). Some enzymes will promote other molecules, such as vitamins or minerals, to make the reaction happen.
The functions of the body that depend on enzymes include:
Digestion; Energy production; Coagulation; Muscle spasm. An enzyme deficiency or an enzyme that doesn't work properly can lead to a number of conditions.
3. Support signal transmission
Chemically, some proteins are hormones, which aid in communication between cells, tissues, and organs. Endocrine tissues or glands produce hormones, which are then transported by the bloodstream to target tissues or organs. Here the hormone will bind to protein receptors on the cell surface.
Hormones are grouped into 3 main categories:
Proteins and peptides: Made from a few to hundreds of amino acids, linked in a chain; Steroids: Produced by fatty cholesterol. The sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen) are both steroid-based; Amines: Made from the individual amino acids tryptophan or tyrosine, which help form hormones related to sleep and metabolism. Proteins and polypeptides are a group of hormones that make up most of the body, including:
Insulin : Signals for glucose uptake into cells; Glucagon : Signal to break down glucose stored in the liver; hGH (human growth hormone): Stimulates growth of tissues, including bones; ADH (anti-diuretic hormone): Signals the kidneys to reabsorb water; ACTH (adrenal cortex hormone): Stimulates the release of cortisol - a key factor in metabolism.
4. Shaping the tissue structure
Some protein structures are fibrous, giving strength to tissues and cells. These proteins include:
Keratin: A structural protein found in skin, hair and nails; Collagen: The most abundant protein structure in the body, making up bones, tendons, ligaments and skin; Elastin: Several hundred times more flexible than collagen. The high elasticity allows many tissues in the body to return to their original shape after being stretched or contracted, such as the uterus, lungs, and arteries.
5. Maintain proper pH
Protein plays an important role in regulating acid and base levels in the blood and other body fluids. The balance between acids and bases is measured using the pH scale. The scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the strongest acid, 7 being neutral, and 14 being the strongest alkaline.
Examples of pH values of some common substances are:
pH 2: Stomach acid; pH 4: Tomato juice; pH 5: Black coffee; pH 7.4: Human blood; pH 10: Milk of magnesia; pH 12: soapy water; Many buffer systems help body fluids maintain a normal pH range. This is necessary because even a small change in pH can be harmful or potentially fatal.
Some proteins are also involved in pH regulation, such as hemoglobin - a protein that makes up red blood cells. Hemoglobin will bind with a small amount of acid, helping to maintain the normal pH value of human blood.
Other buffer systems in the body include phosphate and bicarbonate.
6. Fluid balance
Protein regulates body processes to maintain fluid balance. For example, albumin and globulin are proteins in the blood that help maintain fluid balance by capturing and retaining water.
If you don't get enough protein, the albumin and globulin levels in the body will gradually decrease. As a result, blood cannot stay in the vessels and fluid accumulates in the spaces between the cells. At this time, there will be swelling or edema, especially in the stomach.
This is a severe form of protein malnutrition, known as Kwashiorkor edematous malnutrition. This condition occurs when a person consumes enough calories but lacks protein. Kwashiorkor is rare in developed parts of the world, but is common in poverty-stricken areas. Patients may need the effects of whey protein to supplement protein.

Nếu cơ thể không có đủ protein sẽ dẫn đến suy dinh dưỡng protein
7. Immune Health
Protein helps form immunoglobulins, or antibodies, to fight infection. Antibodies are proteins in the blood that help protect the body from harmful "invaders" such as bacteria and viruses.
When foreign factors enter the cells, the body creates antibodies to destroy them. Without these antibodies, bacteria and viruses would freely multiply and overwhelm the body, causing infections.
Once antibodies against a particular bacteria or virus have been created, the cells automatically memorize this mechanism. As a result, the antibodies will react faster when an old pathogen enters your body again. Therefore, the body has an immunity to fight off diseases it has been exposed to.
8. Transport and storage of nutrients
Through the bloodstream, proteins transport nutrients in and out of cells, such as vitamins or minerals, glucose, cholesterol, and oxygen.
For example, hemoglobin (hemoglobin) is a protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to body tissues. Glucose transporter (GLUT) carries sugar to cells, as well as lipoproteins that transport cholesterol and other fats in the blood.
Each carrier protein is specific, binding only to specific substances. In other words, a glucose transport protein would not be able to move cholesterol.
In addition, proteins also have a storage role, for example ferritin helps to store iron. Another type of storage protein is casein, which is mainly present in milk and helps babies grow.
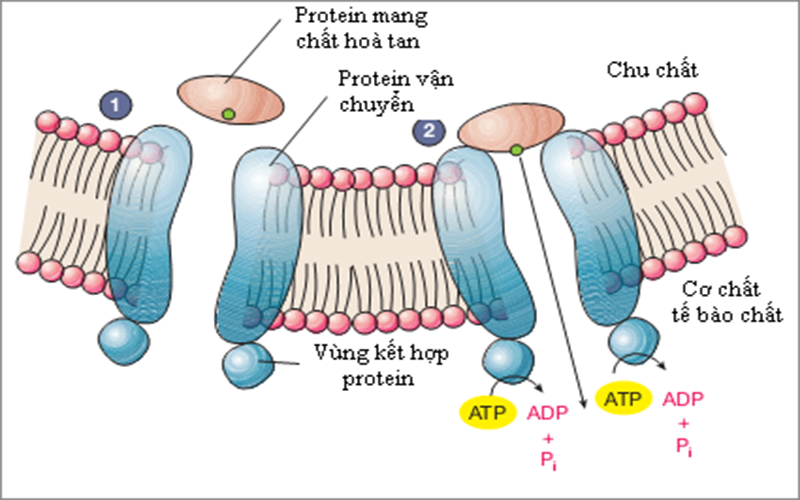
Protein giúp vận chuyển các chất dinh dưỡng vào tế bào
9. Power Supply
Protein can also provide energy for the body. Each gram of protein contains 4 calories, equivalent to the amount of energy that carbs provide. Meanwhile fat provides the most energy, at 9 calories per gram.
However, protein is the last substance the body wants to use for energy. This is because protein has to participate in many other functions throughout the body. Therefore, the body will prioritize storing carbs and fats to use as fuel, creating an active energy source. Furthermore, trans fats and carbs are also more efficient than protein.
In fact, protein provides the body with very little energy under normal circumstances. However, during a fasting state (18 - 48 hours without carbs and fat), the body breaks down skeletal muscle so that amino acids can provide energy instead.
The body also uses amino acids from skeletal muscle if carbohydrate stores are low. This phenomenon occurs after you exercise at a high intensity or when you do not consume enough calories.
Protein plays many roles in the body, helping to repair and build tissues, as well as promote metabolic reactions. In addition to providing the body's structural framework, protein also maintains proper pH and fluid balance. Finally, the protein structure keeps the immune system strong, helps transport and store nutrients, and even becomes an emergency source of energy when the body needs it. All these functions make protein very important for health.
In order to improve the quality of examination and treatment services, Vinmec International General Hospital has put a system of modern facilities and standard equipment into operation for medical examination and treatment processes. Especially at Vinmec, there is always a team of doctors and nurses ready to listen, advise and treat diseases as well as advise on nutrition and good food for children, adults and the elderly.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Reference source: healthline.com
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.





