Digital imaging with background erasure and percutaneous intraluminal biopsies
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
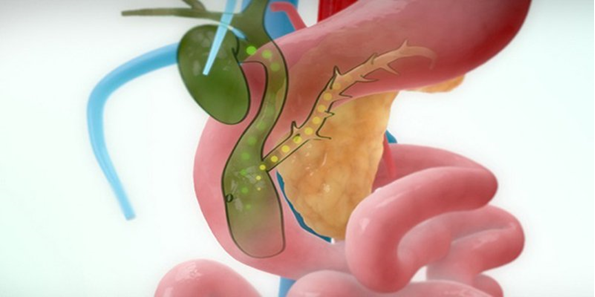
Biopsy of the biliary lumen under the guidance of digital background erasure is one of the modern techniques. This method helps doctors to directly intervene the damage in the biliary tract to diagnose and treat the disease, limiting dangerous complications.
1. Overview
The pathologies related to the intra or extrahepatic biliary tract are quite diverse and complex, especially if they are diffuse and cause biliary obstruction. Determining the histopathological organization of the lesion and providing the appropriate treatment is one of the important goals for clinical practice.
Endoscopic duodenal biopsies play a major role in diseases of the ampulla of Vater and the lower part of the common bile duct. However, there are many cases of severe narrowing or lesions located high in the liver hilum, making the endoscope inaccessible.
Percutaneous intrahepatic biliary biopsy was first introduced in 1980, so far has been widely used worldwide. This technique is performed by inserting a biopsy instrument into the biliary tract through the liver parenchyma. The rate of obtaining successful specimens is quite high, helping to supplement those cases that cannot be biopsied through endoscopic or transhepatic.
Meanwhile, the system of digital subtraction angiography (DSA - abbreviated as "Digital Subtraction Angiography") is an imaging method. Background erasing digital angiography technique combines X-ray and digital image processing, which helps to capture the vascular system in the body and intervene in treatment. The outstanding advantage of this method is that it is minimally invasive and does not require open surgery.
Endoscopic duodenal biopsies play a major role in diseases of the ampulla of Vater and the lower part of the common bile duct. However, there are many cases of severe narrowing or lesions located high in the liver hilum, making the endoscope inaccessible.
Percutaneous intrahepatic biliary biopsy was first introduced in 1980, so far has been widely used worldwide. This technique is performed by inserting a biopsy instrument into the biliary tract through the liver parenchyma. The rate of obtaining successful specimens is quite high, helping to supplement those cases that cannot be biopsied through endoscopic or transhepatic.
Meanwhile, the system of digital subtraction angiography (DSA - abbreviated as "Digital Subtraction Angiography") is an imaging method. Background erasing digital angiography technique combines X-ray and digital image processing, which helps to capture the vascular system in the body and intervene in treatment. The outstanding advantage of this method is that it is minimally invasive and does not require open surgery.

Chụp số hóa xóa nền giúp chẩn đoán hình ảnh chính xác
2. When is an intraluminal biopsy necessary?
2.1. Point
This technique is often performed in cases of benign or malignant biliary obstruction of any cause, and the diagnosis cannot be confirmed by endoscopic or transhepatic biopsy. Specifically:
Intra-/extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, primary/recurrent; Cancer of the stomach, pancreas, or gallbladder with invasion of the biliary tract; Cancer metastatic biliary tract, including: Cancer of the cervix, cancer of the lymphatic system, bronchi; Chronic sclerosing cholangitis; Primary biliary fibrosis.
Intra-/extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, primary/recurrent; Cancer of the stomach, pancreas, or gallbladder with invasion of the biliary tract; Cancer metastatic biliary tract, including: Cancer of the cervix, cancer of the lymphatic system, bronchi; Chronic sclerosing cholangitis; Primary biliary fibrosis.
2.2. Contraindications
Biopsy should not be performed in the biliary lumen under the guidance of digital background scanning if the patient has severe coagulopathy, the following indicators:
Coagulation time INR > 1.5; Platelet count < 50 G/l (need platelet transfusion before intervention); Coagulation factor Prothrombin < 50% (fresh plasma infusion before intervention). Other contraindications include:
Acute liver and biliary tract infections (liver or biliary tract abscess); Bile duct bleeding.
Coagulation time INR > 1.5; Platelet count < 50 G/l (need platelet transfusion before intervention); Coagulation factor Prothrombin < 50% (fresh plasma infusion before intervention). Other contraindications include:
Acute liver and biliary tract infections (liver or biliary tract abscess); Bile duct bleeding.
3. Prepare
3.1. Executor
Specialist; Physician support; Electro-optical technician; Nursing staff; Anesthesiologist/technologist (if patient cannot cooperate).
3.2. Vehicle
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA); Film, film printers, and image storage systems; Lead vest and apron to shield X-rays.
3.3. Medicine
Local anesthetic or general anesthetic depending on indication; Water-soluble Iodine Contrast; Antiseptic solution for skin and mucous membranes.
3.4. General medical supplies
5ml and 10ml syringes; Distilled water, physiological saline; Gloves, gowns, caps and surgical masks; Aseptic intervention kit: Knife, scissors, tongs, 4 metal bowls, bean tray and tool holder; Gauze, cotton, surgical tape; Medicines and first aid equipment if there is a contrast agent accident.
3.5. Special medical supplies
Needs to tease Chiba; Set of tubes into the vessel lumen; Standard conductor 0.035 inch; Hard conductor 0.035inch, length 260-300cm; Cobra 4-5F angiography catheter; 6-12F pigtail drain; Endoscopic biopsy forceps (Forceps); Leather stitches.
3.6. Patient
The procedure is explained carefully to cooperate well with the doctor; Need to fast and drink before 6 hours can drink less than 50ml of water; If there is a coagulopathy, vitamin K supplementation is needed; Intravenous prophylactic antibiotic injection 6 hours before intervention; In the intervention room: The patient lies on his back, with a machine to monitor vital indicators. Disinfect the skin, then cover with a sterile towel with holes; In case the patient is too agitated and refuses to lie still, give sedatives...

Cần bổ sung vitamin K cho bệnh nhân có rối loạn đông máu
3.7. Test form
Medical records for inpatient treatment; There is an approved order to carry out the procedure; Films, computed tomography, X-ray, MRI ... if available.
4. Procedure
4.1. Percutaneous cholangiography
Use contrast medium to check percutaneous biliary drainage; Insert the guide wire, then remove the biliary catheter; Proceed to insert the catheter into the biliary tract through the wire; Conduct digital scan to clear the biliary tree background through the catheter; Determine the expected site for the biopsy.
4.2. Biopsy
Withdraw the catheter; Insert the intravascular catheter into the biliary tract through a guide wire; Withdraw the lead wire; Insertion of the endoscopic biopsy forceps into the biliary tract through the intravascular catheter; Using pliers for endoscopic biopsy, cut 3-5 pieces of tissue in the biliary lumen.
4.3. Reset percutaneous biliary drainage
Withdraw endoscopic biopsy forceps from the biliary tract and intravascular catheter; Insert the guide wire into the biliary lumen and remove the lumen catheter; Place a percutaneous bile duct catheter.
5. Complications and treatment
If the tissue biopsy piece is tough, opaque, and the size and quantity are large enough according to the pathological requirements, the technique is considered successful. A few rare cases of intraluminal biopsies have a risk of complications such as:
Biliary tract bleeding Requires medical treatment, combined with clinical monitoring, stool, mucosa, and red blood cell volume of the patient. . If biliary tract bleeding persists, consultation with an interventional radiologist is required. Management may be replacement of the drainage catheter or consideration of embolization.
Biliary perforation This condition usually resolves on its own. Very rare complications of biliary peritonitis, if signs are present, consult a surgical specialist.
Biopsy in the lumen of the biliary tract under the guidance of digital scanning of the background brings many advantages, providing information for diagnosis and treatment support. Because of the view into the biliary lumen, the technique allows the diagnosis of biliary tract lesions. Biliary tract diseases, if not treated in time, will cause many dangerous complications, so people need to go to a reputable hospital for timely treatment when there are signs, avoiding complications that affect their health. .
DSA background digitization and percutaneous intraluminal biopsies have been widely used. At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a team of experienced specialists, with modern equipment, using digital angiography to erase the DSA background in biliary tract biopsies, helping doctors in Diagnosis and treatment are quick and accurate.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International Hospital from December 2017, Doctor Dang Manh Cuong has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging in Transport Hospitals. Hai Phong, MRI Department of Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital and Diagnostic Imaging Department of Becamex International Hospital.
For examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please come directly to Vinmec Health System or register online HERE.
Biliary tract bleeding Requires medical treatment, combined with clinical monitoring, stool, mucosa, and red blood cell volume of the patient. . If biliary tract bleeding persists, consultation with an interventional radiologist is required. Management may be replacement of the drainage catheter or consideration of embolization.
Biliary perforation This condition usually resolves on its own. Very rare complications of biliary peritonitis, if signs are present, consult a surgical specialist.
Biopsy in the lumen of the biliary tract under the guidance of digital scanning of the background brings many advantages, providing information for diagnosis and treatment support. Because of the view into the biliary lumen, the technique allows the diagnosis of biliary tract lesions. Biliary tract diseases, if not treated in time, will cause many dangerous complications, so people need to go to a reputable hospital for timely treatment when there are signs, avoiding complications that affect their health. .
DSA background digitization and percutaneous intraluminal biopsies have been widely used. At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a team of experienced specialists, with modern equipment, using digital angiography to erase the DSA background in biliary tract biopsies, helping doctors in Diagnosis and treatment are quick and accurate.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International Hospital from December 2017, Doctor Dang Manh Cuong has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging in Transport Hospitals. Hai Phong, MRI Department of Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital and Diagnostic Imaging Department of Becamex International Hospital.
For examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please come directly to Vinmec Health System or register online HERE.