Pelvic head disproportion
The article was written by Doctor Dang Pham Quang Thai - Obstetrician and Gynecologist, Obstetrics Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Pelvic head disproportion is a situation where the fetus and the mother's pelvis are not compatible with the placenta due to the large fetus or abnormal maternal pelvis (narrow pelvis, distorted pelvis). Making the fetus not able to pass through the mother's pelvis, so it is not possible to give birth vaginally.
1. What is iliac disproportion?
Difficulty delivery due to abnormal pelvic causes with the rate of nearly 5%. In the past, difficult labor due to pelvic causes was paid special attention by doctors, meticulously examined to induce preterm labor, avoiding the risk of pelvic and fetal disproportionation if waiting for the fetus to reach full term.
Today thanks to the advances of science in general and medicine in particular, including the contribution of nutrition, pediatrics, endocrinology... the type of difficult birth due to pelvic causes is decreasing day by day. Thanks to the good work in assisted reproduction, which includes planned delivery, good pregnancy management examination, continuous progress in anesthesia and resuscitation, especially the technique of cesarean section through the lower uterine segment in At the beginning of the 20th century, indications for cesarean section were widely applied, the cephalic test was completed, so labor was difficult due to early diagnosis and timely treatment of pelvic causes and no longer a complicated cause. complex.
The pelvis is divided into two parts: the large pelvis (also known as the large pelvis) and the small pelvis (or the small pelvis).
Bất tương xứng đầu chậu gây khó sinh
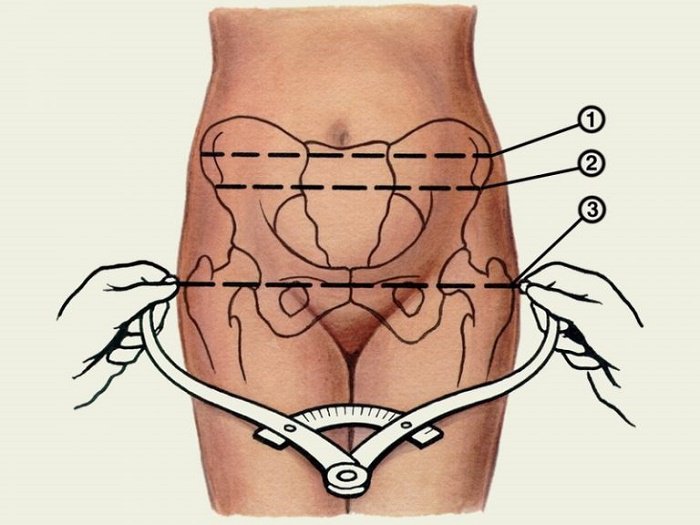
To measure the diameters of the great frame, obstetric compasses (also called Baudelocque compasses) are used. The great frame consists of 3 notable transverse diameters:
Diameter of the anterior superior iliac spines: 22.5cm. Diameter of the pelvic crest: 25.5cm. Diameter of the femur transition: 27.5cm and has an anteroposterior diameter, also known as a Baudelocque diameter of 17.5cm. But the large pelvis plays an important role in obstetrics, however, if the pelvis is too small, it will also lead to narrow pelvis causing difficulties for delivery.
The pelvis is visualized as a tube consisting of three waists: upper, middle, and lower.
There are many ways to divide the narrow pelvis. In which:
Symmetrical narrow pelvis : Fully symmetrical and symmetrical narrow pelvis, flat pelvis, transverse narrow pelvis, flat and narrow pelvis. Asymmetrically narrow pelvis: includes various types of pelvis with unequal narrow diameters, deformed pelvis is common in people with deformities or injuries such as hip dislocation, hip tuberculosis or scoliosis live... Abnormal pelvis after orthopedic bone.
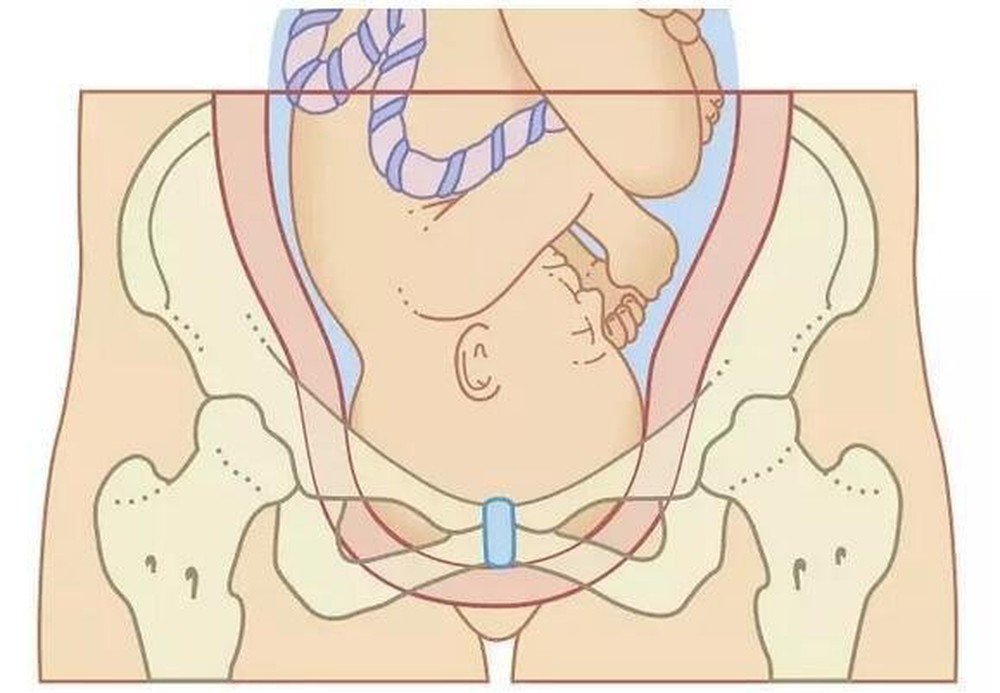
Khung chậu hẹp đối xứng
2. How to deal with pelvic head disproportion
If fetal and pelvic disproportion are suspected and if the head is cephalic a "ceremony test" will be conducted as appropriate. To avoid possible complications for mother and fetus. Suspected pelvises should be monitored for delivery at the surgical site and carefully examined during pregnancy management.
Induction of preterm labor in narrow pelvises is no longer used today, because cesarean section is complete with clear indications and avoids the burden on the pediatric specialist, having to take care of these babies. weak infants whose future development is the future of each nation.
It is a test to see if the fetus can get through or not, when the fetal position is clearly defined and the doctor suspects that there is a mismatch between the fetus and the mother's pelvis.
2.1. Indications for performing the cephalothorax test Limited pelvis where the fetus is normal: the test is performed in pelvises with protrusion-back diameter from 8.5 to 10.5 cm. The fetal position is the head position, the fetus is of normal weight and has been in actual labor.
Suspected fetal and pelvic disproportion: this indication already includes the limited pelvic indication above. The pelvis here can be normal but the fetus is large or even spacious but the fetus is too large, the doctor suspects that there is a mismatch of the fetus and pelvis. But it must always be remembered that the maneuver is only performed when there is actual labor and the fetus is in the cephalic position.
2.2. The condition for testing the crown of the crown The Thai throne must be the crown, which is a prerequisite for the test. Must be done in a place where caesarean section is possible. The crown test can be successful, but it can also fail, especially when it's done, there can be complications and risks such as: prolapse of the placenta, threatened uterine rupture or fetal distress... It takes time to transfer the pregnant woman, there will be complications for the mother and the fetus. And if it is more prudent, it should be done when the facility is qualified and has good neonatal resuscitation facilities.
Must have been in actual labor : The cephalotomy should only be performed when the cervix is dilated > 4 cm in varices and > 5 cm in preterm infants. Must have close and careful monitoring: It is best to do the test and monitor it regularly by a certain person on continuous monitoring. Especially when using prostaglandin or oxytocin . Any changes on the part of mother and fetus must be recorded and analyzed meticulously.
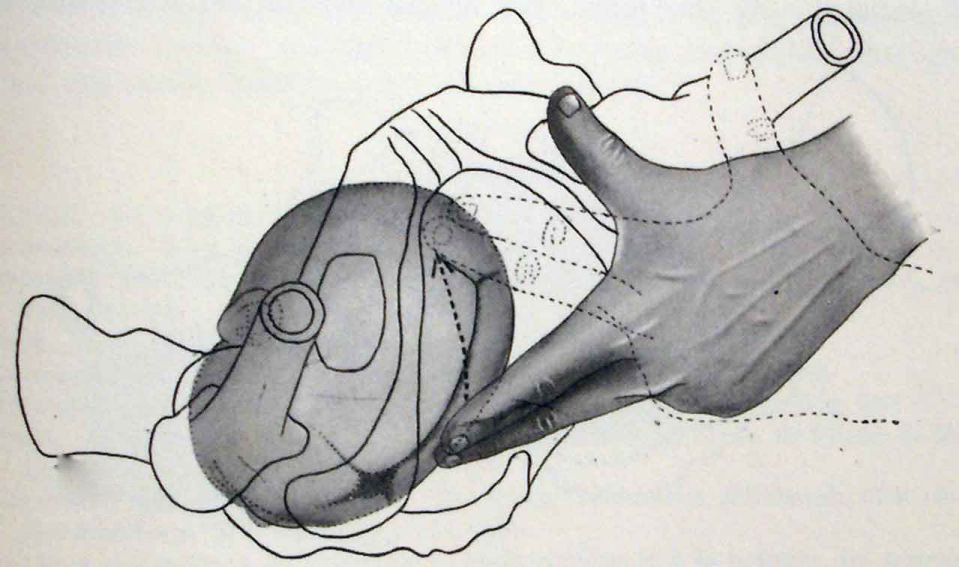
Xác định khớp dọc giữa và các thóp qua thăm khám âm đạo
2.3. How to conduct the cephalic maneuver Amniocentesis is the first effect of the cephalic maneuver. Immediately after that, it is necessary to evaluate the amount of amniotic fluid, the color of the amniotic fluid, the progress of the fetal position, the fetal status through the fetal heart and uterine contractions and possible complications. After amniocentesis: prolapse of the placenta, prolapse... After the rupture of membranes, check carefully the position, position, position to decide whether to continue with the test or to have a cesarean section if the position is not favorable. (front fontanelle, forehead...).
Monitoring uterine contractions Uterine contractions are the main driver of labor, so monitoring of uterine contractions is necessary and important. It is best to continuously monitor on monitoring one will evaluate all three: intensity, amplitude and frequency. Uterine activity should be consistent with the stage of labor and in harmony with cervical dilation.
Monitoring the mother's condition The mother's health directly affects the fetus through placenta - fetal circulation, so the mother must always be closely monitored mentally and physically: pulse, temperature, blood pressure.. Whether the crown test is successful or not depends in no small part on the cooperation of the pregnant women with the physician.
Monitoring fetal status Best monitored on continuous Monitoring. The fetal status is shown by how the fetal heart rate fluctuates: physiologically normal or there are pathological occasions when uterine contractions occur. The crown test should be stopped immediately when there is obvious fetal distress.
One can also monitor the fetal status by classical methods if there is no monitoring such as auscultation of the fetal heart with a wooden tube, monitoring of stools in amniotic fluid, sensation of fetal movements of the mother... But in general these methods are either less accurate or less objective.

Theo dõi tình trạng thai nhi qua monitoring
Monitor and evaluate the progress of the fetal position The purpose of the test is to test whether the position of the fetus can descend, pass and pass, that is, can deliver via the lower line, should monitor the position of the fetus. Pregnancy is very necessary and must be carried out regularly, with limited external or vaginal examination to avoid cervical edema causing difficulty in opening the cervix and retrograde infection because at this time we have amniocentesis. already.
Follow up cervical dilation If the test is successful, the cervix will dilate harmoniously over time, the fetal position will fall and the delivery is performed via the lower route. Many times the test fails simply because the cervix is not dilated (which clinicians are familiar with as cervical non-progression); Today, in advanced countries, thanks to modern monitoring equipment and adequate medication, it is very rare to fail a test due to non-collapse of the cervix.
Time to perform the test Usually, doctors agree to take the time as 06 hours. Because after 6 hours of amniocentesis, the test continued to be prolonged, the doctors worried that there would be potential infection or fetal distress. But here, time is also understood and applied flexibly depending on the general situation: if it has been 6 hours of testing and has to wait another 30 minutes or 1 hour, the birth will end in bot lane without any risk. for the mother and the fetus, it is still possible to continue testing. But there are also cases where only 1 to 2 hours later, the doctor can assess whether to continue or stop the test successfully.
Even, if you have just finished amniocentesis, you have fetal distress or prolapse of the placenta, you must immediately stop the test of the crown to appoint a cesarean section.

Mẹ bầu nên đi khám thai theo đúng lịch hẹn của bác sĩ
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.






