Causes and symptoms of chronic interstitial nephritis
The article was professionally consulted by a General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Chronic interstitial nephritis is often detected at a late stage when kidney function declines and disease symptoms are obvious. Therefore, in order to minimize complications, patients need to visit a doctor to know the causes and symptoms of chronic interstitial nephritis, so that they can have timely treatment.
1. What is chronic interstitial nephritis?
The kidney is the organ responsible for removing toxins, balancing the amount of fluid in the body, the unit of the kidney is called the nephron; The nephrons are responsible for carrying urine through the ureter to the bladder.
In terms of terminology, chronic interstitial nephritis is distinguished into two types: chronic bacterial interstitial nephritis called chronic pyelonephritis and chronic nonbacterial interstitial nephritis called chronic interstitial nephritis.
Chronic interstitial nephritis occurring in the renal interstitial and tubular tissues is not caused by bacteria. Clinical manifestations are renal tubular dysfunction, leading to chronic renal failure. The disease may be stable, non-progressive, or insidious, or have episodes of worsening activity, causing renal interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, and renal papillary necrosis, progressive loss of renal function, and renal failure. romantic.
In terms of terminology, chronic interstitial nephritis is distinguished into two types: chronic bacterial interstitial nephritis called chronic pyelonephritis and chronic nonbacterial interstitial nephritis called chronic interstitial nephritis.
Chronic interstitial nephritis occurring in the renal interstitial and tubular tissues is not caused by bacteria. Clinical manifestations are renal tubular dysfunction, leading to chronic renal failure. The disease may be stable, non-progressive, or insidious, or have episodes of worsening activity, causing renal interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, and renal papillary necrosis, progressive loss of renal function, and renal failure. romantic.

Tình trạng viêm thận
2. Causes of chronic interstitial nephritis
Medications: Pain relievers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, lithium salts, laxatives. Kidney toxicity: Poisoning with heavy metals (beryl, bismuth, cadmium, lead). Metabolic disorders: Hypercalcemia, hyperuricemia, prolonged hypokalemia, high oxalateuria. Age: Elderly people have a higher risk of developing chronic interstitial nephritis. The presumed cause of renal interstitial fibrosis may be due to a history of acute pyelonephritis, urinary tract obstruction, or toxicity or prostatic hyperplasia, due to renal ischemia. Upstream bacterial infection: Occurs in chronic pyelonephritis, pyelonephritis, fungal nephritis. Malignancy: Acute myeloid leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, lymphocytic leukemia.
Obstructive nephropathy: Acquired or congenital malformations of the urinary tract favoring retrograde infection, nephrolithiasis, vesicoureteral reflux, prostatic hyperplasia, ureteral-bladder malformations ureter and ureter are enlarged. Immune reactions: Multiple myeloma, renal transplant rejection, lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, sarcoidose, AIDS. Physical agents: Seen in post-irradiation nephritis.
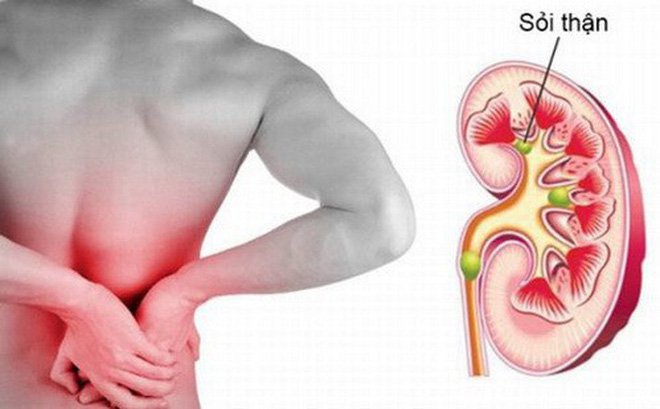
Sỏi thận là nguyên nhân gây viêm kẽ thận mạn
3. Symptoms of chronic interstitial nephritis
In the early stages, chronic interstitial nephritis has almost no symptoms. At a later stage, when the disease has worsened and kidney function declines, the new symptoms will manifest. In particular, the common symptoms of chronic interstitial nephritis include rash and fever. In addition, accompanying systemic symptoms such as nausea, weakness, mouth feeling like metal inside, high blood pressure, difficulty urinating, painful urination, bloody urine.
4. Diagnostic test for chronic interstitial nephritis
Urinalysis: Proteinuria (less than 2.5g/day) and presence of leukocytes Blood chemistry: There are blood biochemical indicators similar to those with chronic renal failure. In some people, there may be less sodium than more sodium loss in the urine; metabolic acidosis (the kidneys cannot excrete H+ ions or reabsorb bicarbonate) accompanied by hypokalemia, hypercalciuria, osteomalacia.

Xét nghiệm nước tiểu giúp chẩn đoán viêm kẽ thận mạn
5. Treatment of chronic interstitial nephritis
Depending on the cause of chronic interstitial nephritis, the appropriate treatment method is selected. If the patient has an infection, it is treated with antibiotics. If there are gout, urolithiasis, myeloma, then these diseases should be completely treated. If long-term use of certain drugs causes side effects, then the drug should be discontinued.
Patients with chronic interstitial nephritis need to follow the doctor's treatment. Take medicine on time, visit the doctor on time to monitor the disease, absolutely do not quit taking medicine or buy medicine to use without a doctor's prescription. If you have any unusual signs or suspect that the disease is more serious, you should seek medical attention immediately.
For advice and registration to book an appointment, customers can contact Vinmec hospitals and clinics nationwide HERE.
Patients with chronic interstitial nephritis need to follow the doctor's treatment. Take medicine on time, visit the doctor on time to monitor the disease, absolutely do not quit taking medicine or buy medicine to use without a doctor's prescription. If you have any unusual signs or suspect that the disease is more serious, you should seek medical attention immediately.
For advice and registration to book an appointment, customers can contact Vinmec hospitals and clinics nationwide HERE.






