What is the longest cell in the human body?
All organs in the human body are made of cells. The number of cells in the human body is very large, up to about 75 trillion. There are many different types of cells in terms of shape, size, function... So which is the longest cell in the human body?
1. Shape and structure of cells in the human body
Cells in the human body differ in shape:
Spherical (egg cell); Disc-shaped (erythrocytes); Cubes (epidermal cells); Cones, rods (retinal cells); rhombus (muscle cell); Astrocytes (neurons — neurons); Fibrous (hair, feathers); Shaped like other organisms (white blood cells, sperm)... Cells in the human body are different in size: long, short, large, small... and the functions of the cells are also different. Depending on the location of their existence in which organ, or even in the same organ, the function of the cell is also different. Although different in many aspects, but in general, cells in the human body are made up of 3 basic parts: plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus.

Một số tế bào trong cơ thể con người
1.1. The plasma membrane is the outer membrane of the cell, mainly composed of proteins and lipids. The plasma membrane helps the cell to exchange substances with the surrounding environment;
1.2. Cytoplasm Inside the plasma membrane is the cytoplasm, which contains many organelles and complex substances. These cellular activities mainly take place in the cytoplasm. The main organelles are the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, centrosomes:
The endoplasmic reticulum is a system of membrane-bound flat sacs and sinuses. The endoplasmic reticulum consists of a granular endoplasmic reticulum (which may carry ribosomes) or a smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The main function of the endoplasmic reticulum is as a medium for the binding of organelles, synthesis and transport of substances; Ribosomes: Located on the endoplasmic reticulum or floating in the cytoplasm. Composed of two subunits that contain rRNA and are the site of protein synthesis; Mitochondria: Consists of many folds forming crests containing the matrix, surrounded by 2 membranes. The function of mitochondria is to participate in cellular respiration to generate ATP; Golgi apparatus: A system of many flattened membranous sacs stacked on top of each other. The main task is to acquire, complete, distribute and stock products; Centrosome: The task of centrosome is to participate in cell division. 1.3. Core
Has an oval or spherical shape, surrounded by an outer nuclear membrane and has nuclei and many daughter nuclei inside:
Chromatin: Inside the nucleus fluid and is the substance that makes up chromosomes, contains DNA that plays a role genetic game; Nucleus: Contains rRNAs that form ribosomes, which play an important role in the cell.
Chromatin: Inside the nucleus fluid and is the substance that makes up chromosomes, contains DNA that plays a role genetic game; Nucleus: Contains rRNAs that form ribosomes, which play an important role in the cell.
2.The chemical composition of the cell
Cells are made up of many different organic and inorganic substances. In which, the most important are still organic substances:
Protein (protein): Is a complex made up of chemical elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N). , sulfur (S) and some other elements. Protein is considered a macromolecule, which is an important component present in all cells; Glucid (carbohydrate): Including elements C, H and O. In the body, glucide is in the form of glucose (in the blood) and glycogen (in the liver and muscles); Lipids (fats) : Exist in many organs, including 3 main elements C, H, O but in different proportions with glucid. Lipids are the body's reserve substances. Nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) are mainly found in the nucleus of cells, these are macromolecules that play an important role in the genetic process.
3. Which cell is the longest in the human body?
To find out which cell is the longest in the human body, let's list some of the sizes of the large cells in the body:
Platelets length: 2 - 3 micrometers; Red blood cell length: 6.2 - 8.2 micrometers;
Tế bào thần kinh có thể dai đến 1 mét
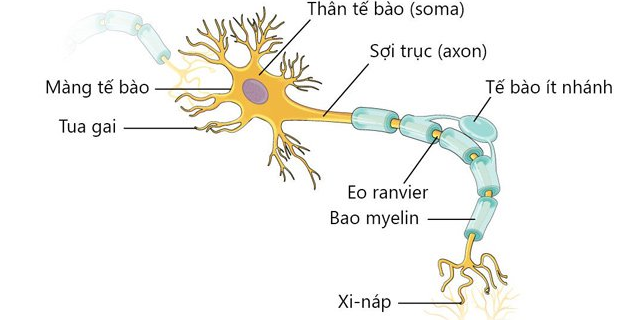
Skin cells length: 7 - 12 micrometers; Embryonic stem cells long: 12 - 13 micrometers; Long granulocytes: 12 - 17 micrometers; Lymphocyte length: 7 - 20 micrometers; monocyte length: 20 micrometers; Macrophages long: 20 - 30 micrometers; Chondrocytes length: >20 micrometers; Fat cell length: 100 micrometers; Stem cells length: 50 - 200 micrometers; Sperm length: 50 - 60 micrometers; Egg cell length: 100 - 200 micrometers; Cardiac muscle cell length: 50 - 100 micrometers; Smooth muscle cell length: 600 micrometers; Skeletal muscle cells: 10 - 40 millimeters; Nerve cells can be up to 1 meter long. As can be seen, nerve cells are the longest cells in the human body. The neuron is the basic unit that makes up the nervous system of most animals and is the most important part of the brain, capable of sensing, emitting nerve impulses, and conducting electrical impulses.
There are an estimated 100 billion neurons in the human brain. Neurons are the longest cells in the human body, highly differentiated, so they lose centrosomes and the ability to divide, but neurons have the ability to regenerate the end of the axon in cases of injury.
4.Cell life activity

Các tế bào trong cơ thể người đều được cung cấp dinh dưỡng từ hệ thống mạch máu
The living activity of cells in the body includes many processes such as anabolism and catabolism, reproduction and induction, growth and development.
Every cell in the human body is supplied with nutrients from the vascular system. At the same time, in every cell the process of synthesizing complex organic compounds from simple ones is always taking place.
Corresponding to synthesis is the breakdown of organic compounds into simpler substances and the release of energy for the body to function. The two processes of synthesis and degradation are called anabolism and catabolism. They are considered to be the two most important cellular activities.
In addition, in order to maintain cells, cells must also reproduce by dividing directly or indirectly to create new cells. The ability to perceive and respond to external stimuli is called induction.
On the other hand, cells reproduce quickly so that the body can grow and develop. This process is rapid and intense in young people and slows down in adults. At the same time, cells in the human body also die and are replaced by new cells.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






