The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of bladder tumors
This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Khong Tien Dat, Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 14 years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Bladder tumor is one of the most common cancers in the urinary tract. There are many methods of diagnosing bladder tumors, in which, ultrasound is an effective method to help detect, monitor and differentiate bladder tumors from other urinary tract diseases.
1. Overview of bladder tumors
Bladder tumor is one of the most common cancers in the urinary tract. The disease occurs more often in men than women, between the ages of 50 and 70 years old.
According to the classification of the World Health Organization (WHO), bladder tumors are divided into the following types:
Epithelial tumors: Most bladder tumors develop from epithelial cells, of which the majority are excretory epithelium - transitional tumor. In addition, there are squamous cell cancers - papillary tumors and adenocarcinomas - adenomas. Non-epithelial tumors: Very few cases of bladder tumors develop from the dermis, classified into two types as smooth muscle tumors and rhabdomyomas. Most cases of non-epithelial neoplasms are malignant tumors with a poor prognosis. Other types of tumors include some very rare tumors and secondary tumors that invade or metastasize to the bladder (colon cancer, rectal cancer, uterine cancer, prostate cancer, etc.). ..)

Hút thuốc lá thường xuyên làm tăng nguy cơ ung thư bàng quang
Most cases of bladder tumors when detected are at the stage of cancer in situ, a few cases are detected at the metastatic stage.
There are many causes of bladder cancer, some of which are thought to increase the risk of the disease:
Chemicals cause urinary tract cancer. People who have a habit of smoking. Use of drugs that affect the bladder. Bladder schistosomiasis.
2. Diagnosis of bladder tumor
Diagnosis of bladder tumor is based on clinical symptoms and using a number of laboratory diagnostic methods.
2.1 Clinical symptoms of bladder tumor The common clinical symptoms of bladder tumor are:
Blood in urine: This is a common and typical symptom of the disease. Most patients have a lot of blood in the urine, but they can also urinate at the end of the field. Hematuria is usually spontaneous, which may then clear up but recur. The patient may have transient hematuria but also microscopic hematuria. Urinary urgency and pain: Bladder irritation leads to urinary disorders. When you see frequent urination, painful urination, you should immediately think of a bladder tumor. In addition, some other symptoms may appear late such as back pain, pain in the lower abdomen, below the navel, swelling in the groin and scrotum.
Most cases of bladder tumors show symptoms for clinical examination and are already at a late stage. At this time, the doctor using his hand to feel on the abdomen combined with rectal or vaginal examination can detect an infiltrating tumor in the upper region of the pubic bone. When the tumor metastasizes to the orifice of the ureter, it can cause the kidneys to enlarge due to fluid retention.
2.2 Diagnostic methods for bladder tumors
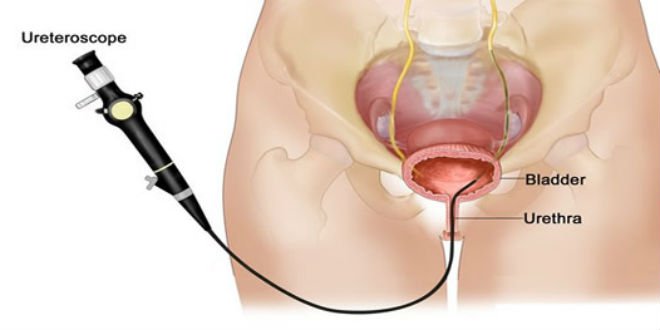
Nội soi bàng quang là một phương pháp giúp chẩn đoán u bàng quang
There are many methods applied to diagnose bladder tumors such as:
Cystoscopy: This is an important method to be performed first for patients with signs of blood in the urine. For men, this technique needs to be performed under local anesthesia. This method allows to detect tumors with characteristics such as location, number, size and morphology. Intravenous urogram (UIV): This is the basic imaging method that allows the evaluation of the urinary system. In some cases, this method allows detection of bladder tumors in the upper part of the urinary tract. Urinary ultrasound: Ultrasound is considered an effective method for detecting bladder tumors with high accuracy. Ultrasonography showed the tumor with characteristics in number, size as well as infiltrate status. In addition, urinary ultrasound also shows other organs such as prostate, renal pelvis, ...

Hình ảnh siêu âm tiết niệu bàng quang
Urine test : This is a simple method done to look for cancer cells in the urine. Based on the results can predict the disease. Biopsy: Combination of cystoscopy and tissue biopsy to identify bladder tumors. However, to perform this technique, regional or general anesthesia may be required, and the tumor tissue needs to be deep below the muscle layer. Computed tomography: This method is used to evaluate tumor invasion or metastasis. Radionuclide bone scan: Combined with an ultrasound of the liver, this technique is done to check for tumor metastasis. This method is often used to evaluate before performing a total cystectomy.
3. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of bladder tumors
In a recent study, ultrasound was evaluated as an effective method of diagnosing bladder tumors, with a high accuracy rate. Ultrasound plays a role in tumor detection and monitoring, providing information about the location, number, shape, and other associated lesions. Specifically:
Tumor classification: epithelial tumors include transitional, papillary or glandular tumors; non-epithelial tumor. Tumor characteristics and stage: location, number, size, shape, contour, area of tumor attachment to the bladder wall. Classification of the degree of malignancy of bladder tumors: From high to low. Other features and abnormalities: calcifications in the tumor, infiltrates, enlarged prostate, hydronephrosis, intra-abdominal fluid, .... Assess the status, extent of invasion or metastasis of the tissue position u.

Hình ảnh u bàng quang trên siêu âm
In addition, ultrasound also plays a role in differential diagnosis of bladder tumors with other pathologies in the urinary tract:
Based on the non-mobility, no shadow of the tumor, to differentiate bladder tumors bladder with thrombosis and bladder stones. In some cases, it is difficult to distinguish bladder tumors from tumors of the pelvic organs (especially prostate cancer) that invade the bladder. Ultrasound is also used to monitor bladder tumor treatment by laparoscopic tumor resection or total or partial cystectomy.
Ultrasound plays an important role in screening and diagnosing bladder tumors, and helps to monitor and evaluate during and after treatment. Therefore, patients should choose reputable medical facilities with modern facilities for implementation.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied ultrasound technology in examining and diagnosing many diseases, including bladder tumors. Ultrasound and imaging techniques at Vinmec are carried out methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals and modern machinery, thus giving accurate results, contributing to It is not small in determining the disease and the stage of the disease to coordinate with other specialties to come up with the most effective treatment regimen.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
This article is written for readers from Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.





