What is normal blood sugar 2 hours after eating?
This is an automatically translated article.
Blood glucose charts determine a person's ideal blood sugar level throughout the day, including before and after meals. It can help a person control their sugar levels if they need to keep their blood glucose levels within normal limits, such as those with diabetes. A glycemic index people also need to pay attention to is the blood sugar level 2 hours after eating.
1. What is the blood sugar 2 hours after eating?
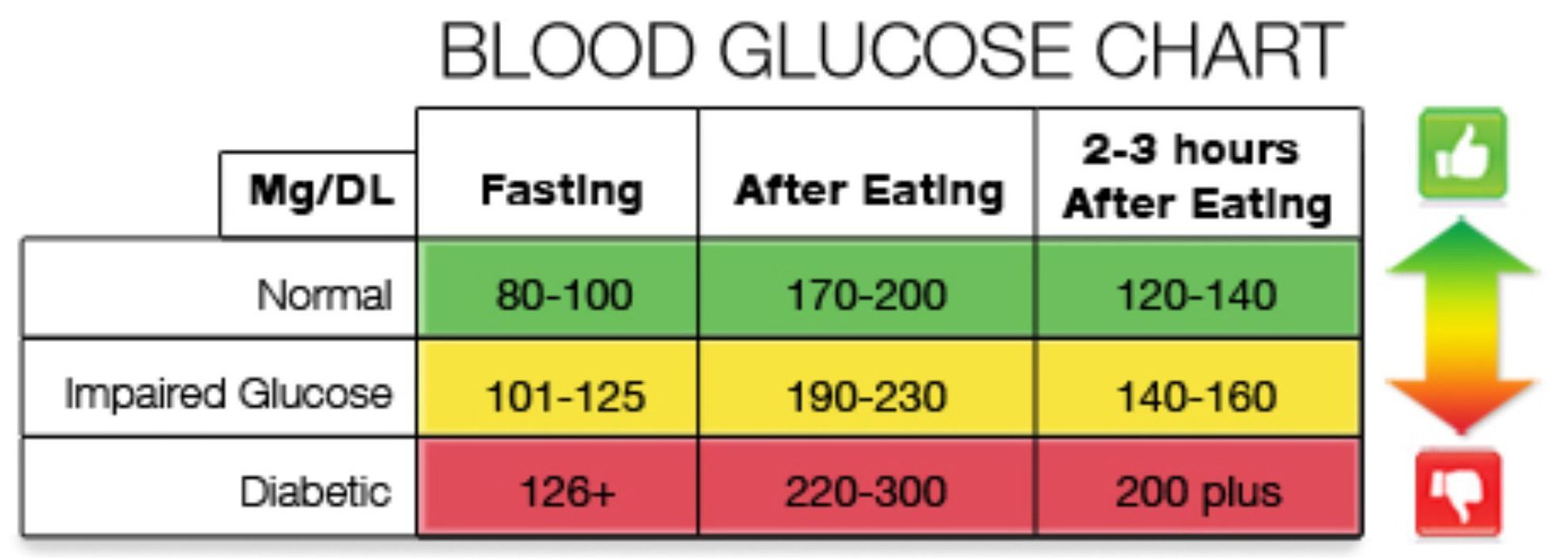
Normal blood glucose level is less than 100 mg/dL after not eating (fasting) for at least 8 hours. This number is less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating.
Blood sugar levels during the day tend to be at their lowest just before a meal. Pre-meal blood sugar levels in people without diabetes range between 70 and 80 mg/dL. For some people, 60 mg/dL is normal; for others, 90mg/dL is the norm.
However, in addition to the 2 hour postprandial glycemic index, there are other time point blood glucose readings that are used to assess whether a person has diabetes and to monitor glycemic control at people who already have diabetes.
2. Blood sugar assessment
2.1. Normal blood sugar range and diabetes
For most healthy people, normal blood glucose levels are as follows:
When fasting: Between 4.0 and 5.4 mmol/L (72 to 99 mg/dL). 2 hours after eating: Up to 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL). Blood sugar levels in people with diabetes are as follows:
Before meals: 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. After meals: Less than 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and less than 8.5 mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes.
Với phần lớn những người khỏe mạnh, mức đường huyết sau ăn 2 giờ thường lên đến 140mg/dL.
2.2. Blood sugar in the diagnosis of diabetes
| Xét nghiệm glucose huyết tương | Bình thường | Tiền tiểu đường | Bệnh tiểu đường |
| Ngẫu nhiên |
Dưới 11,1 mmol / l. Dưới 200 mg / dl. |
11,1 mmol / l trở lên. 200 mg / dl trở lên. |
|
| Nhịn ăn |
Dưới 5,5 mmol / l. Dưới 100 mg / dl. |
5,5 đến 6,9 mmol / l. 100 đến 125 mg / dl. |
7,0 mmol / l trở lên. 126 mg / dl trở lên. |
| 2 giờ sau khi thực hành nghiệm pháp dung nạp |
Dưới 7,8 mmol / l. Dưới 140 mg / dl. |
7,8 đến 11,0 mmol / l. 140 đến 199 mg / dl. |
11,1 mmol / l trở lên. 200 mg / dl trở lên. |
Random blood sugar test: Blood sample can be taken for blood glucose test randomly at any time. This requires no planning and is therefore used in the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes where time is of the essence. Fasting blood glucose test: A fasting plasma glucose test is performed after fasting for at least 8 hours and, therefore, is usually taken in the morning. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): An oral glucose tolerance test is done after a fasting blood sugar test and then, drinking a cup of water containing 75g of very sweet glucose. After drinking this glass of water, you need to rest until more blood samples are drawn in 2 hours. HbA1c test to diagnose diabetes: The HbA1c test does not directly measure blood glucose levels. Normal: Less than 42 mmol/mol (6.0%). Prediabetes when the HbA1c level is between 42 and 47 mmol/mol (6.0 to 6.4%). Diabetes when the HbA1c level is 48 mmol/mol (6.5%) or higher.
3. Why is it important to ensure blood sugar levels?
You must control your blood sugar levels because too much sugar for a long time increases the risk of developing diabetes complications.
Complications of diabetes include:
Kidney disease. Nerve damage. Retinal disease. Heart disease . Stroke . The risk of these problems can be minimized through good control of blood sugar levels. Small changes can make a big difference if you stay dedicated and stick to those changes most of the day.

Lượng đường quá cao trong thời gian dài sẽ làm tăng nguy cơ phát triển các biến chứng tiểu đường.
4. What is the target blood sugar level everyone should achieve?
Doctors use blood sugar charts to set goals and track diabetes treatment plans. Blood glucose charts also help people with diabetes evaluate and self-monitor their blood glucose test results. The ideal blood sugar level for an individual depends on when they take their blood sugar test during the day, as well as when they ate their last meal before the test.
Most diabetes treatment plans involve keeping blood sugar levels as close to normal or target levels as possible. This requires frequent home and physician-ordered testing, along with the ability to compare results with target norms.
To help interpret and evaluate blood sugar results, the following charts outline normal and abnormal blood glucose levels for people with and without diabetes.
| Thời gian kiểm tra | Lượng đường trong máu mục tiêu cho những người không bị tiểu đường | Lượng đường trong máu mục tiêu cho những người mắc bệnh tiểu đường |
| Trước bữa ăn | Dưới 100 mg / dl. | 80–130 mg / dl. |
| 1 – 2 giờ sau khi bắt đầu bữa ăn | Dưới 140 mg / dl. | Dưới 180 mg / dl. |
| Trong khoảng thời gian 3 tháng, lượng HbA1C trong máu. | Ít hơn 5,7%. | Ít hơn 7%. |
Blood sugar levels change from time to time and from person to person. Blood sugar levels are usually lowest before breakfast and before other meals. Blood sugar is usually highest right after a meal. People with diabetes will often have blood sugar goals that are higher or within an acceptable range than people without the disease.
Blood glucose goals to be achieved in each person will vary depending on many factors, some of which include:
Age. Duration of diabetes. Has been diagnosed with cardiovascular disease. Problems with the smallest arteries in the body. Any known damage to the eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, brain, or heart. Living habits and lifestyle factors of each individual. Unrecognized low blood sugar. Stress. Other health conditions. Most blood sugar charts show recommended levels as a range, allowing for variation within that range between individuals. Some transient forms of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes, also have separate blood glucose recommendations.
| Thời gian kiểm tra | Mức đường trong máu |
| Nhịn ăn 8 tiếng hoặc trước khi ăn sáng | 60 – 90 mg / dl |
| Trước bữa ăn | 60 – 90 mg / dl |
| 1 giờ sau bữa ăn | 100 – 120 mg / dl |
Recommendations for fasting blood glucose levels:
| Mức đường huyết lúc đói | Mức độ rủi ro và hành động được đề xuất |
| 50 mg / dl trở xuống | Mức độ nguy hiểm: Tìm kiếm sự chăm sóc y tế. |
| 70 – 90 mg / dl | Có thể quá thấp: Bổ sung đường khi có các triệu chứng của lượng đường trong máu thấp hoặc tìm kiếm sự chăm sóc y tế. |
| 90 – 120 mg / dl | Mức bình thường. |
| 120 – 160 mg / dl | Tìm kiếm sự chăm sóc y tế. |
| 160 – 240 mg / dl | Quá cao: Tìm cách làm giảm lượng đường trong máu. |
| 240 – 300 mg / dl | Quá cao: Đây có thể là dấu hiệu của việc quản lý lượng đường huyết không hiệu quả, vì vậy, hãy đi khám bác sĩ. |
| 300 mg / dl trở lên | Rất cao: Cần tìm kiếm sự chăm sóc y tế ngay lập tức. |

Người có mức đường huyết lúc đói từ 120 mg/ dl trở lên nên tìm kiếm sự chăm sóc y tế.
As long as the blood sugar levels aren't too dangerous, there are ways to get them back in the normal range when the readings become too high.
Some measures to help reduce blood sugar include:
Limit carbohydrate intake but do not fast. Increase water intake to maintain hydration and dilute excess blood sugar. Increase physical activity like walking after meals to burn excess blood sugar. Eat lots of fiber. These methods cannot replace medical treatment, but they are a useful addition to any diabetes treatment plan. Managing blood sugar is an important step in preventing diabetes complications. Ensuring blood sugar levels are in the normal range can also be an indication that treatment is working.
Each person will have their own requirements and characteristics that shape their own blood glucose goals. Your doctor will set these goals using a blood glucose chart at the start of treatment. Your doctor can adjust these goals as treatment progresses. If you notice any symptoms of extremely low or extremely high blood sugar, you should seek medical attention.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is implementing a screening package for diabetes and dyslipidemia under the implementation of a team of highly qualified, experienced doctors and the support of equipment. Modern technology, will help give the most accurate diabetes test results, thereby, recommending an appropriate treatment regimen.
References: webmd.com, diabetes.co.uk, medicalnewstoday.com
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
This article is written for readers from Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.





