Use fat properly
This is an automatically translated article.
Fat goes bad even though it's a nutrient we need in our diet, just not too much. Learn all about dietary fat and how too much or too little affects our health.
1. What is fat?
Dietary fats are an essential part of the diet, providing us with small amounts of non-essential fatty acids (which the body cannot make on its own) and helping us absorb vitamins fat-soluble A, D, E, and K. Reduce saturated fat, as it can raise our blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Combining saturated fat with unsaturated fat has been found to lower blood cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
All fats are high in energy (calories) and should therefore be limited in the diet, to avoid consuming more calories than we need.
Dietary fat is essential for fueling the body and supporting cell growth. They also help protect your organs and help keep your body warm. Fats help your body absorb certain nutrients and produce important hormones. Your body definitely needs fat.

Chất béo là một trong những chất quan trọng trong chế độ ăn
2. Saturated fat
2.1. What is saturated fat?
From a chemical point of view, saturated fats are simply fat molecules that do not have double bonds between carbon molecules because they are saturated with hydrogen molecules. Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature.
2.2. How does saturated fat affect my health?
Replacing foods high in saturated fat with healthier options can lower blood cholesterol levels and improve lipid profiles
2.3. Which foods contain saturated fat?
Saturated fats occur naturally in many foods. Much of it comes mainly from animal sources, including meat and dairy products.
Examples of foods with saturated fat are: fatty beef, lamb, pork, poultry with skin, beef fat (tallow), lard and cream, butter, cheese and other dairy products made from whole milk or reduced fat milk (2%).
Also, many baked goods and fried foods can be high in saturated fat. Some plant-based oils, such as palm oil, palm kernel oil, and coconut oil, are also mostly saturated fat, but not cholesterol.

Sữa và sản phẩm từ sữa có hàm lượng chất béo bão hòa cao
2.4. Proper use of fats
The American Heart Association recommends a reasonable use of saturated fat, limiting the amount found in butter, cheese, red meat and other foods of animal origin. Decades of science has proven it can raise your "bad" cholesterol and put you at a higher risk of heart disease.
Recommended to aim for a diet that gets 5% to 6% calories from saturated fat. For example, if you need about 2,000 calories a day, no more than 120 of those calories should come from saturated fat. That's about 13 grams of saturated fat per day.
The more important thing to remember is the overall picture of the diet. Saturated fat is only one part of the puzzle. All in all, you can't go wrong with eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fewer calories.
When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
3. Trans fats
3.1. What is trans fat?
There are two major types of trans fats found in foods: natural trans fats and artificial trans fats. Trans fats are naturally created in the intestines of some animals, and foods prepared from these animals (e.g. milk and meat products) may contain small amounts of this fat. Artificial trans fats (or trans fatty acids) are created in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid.
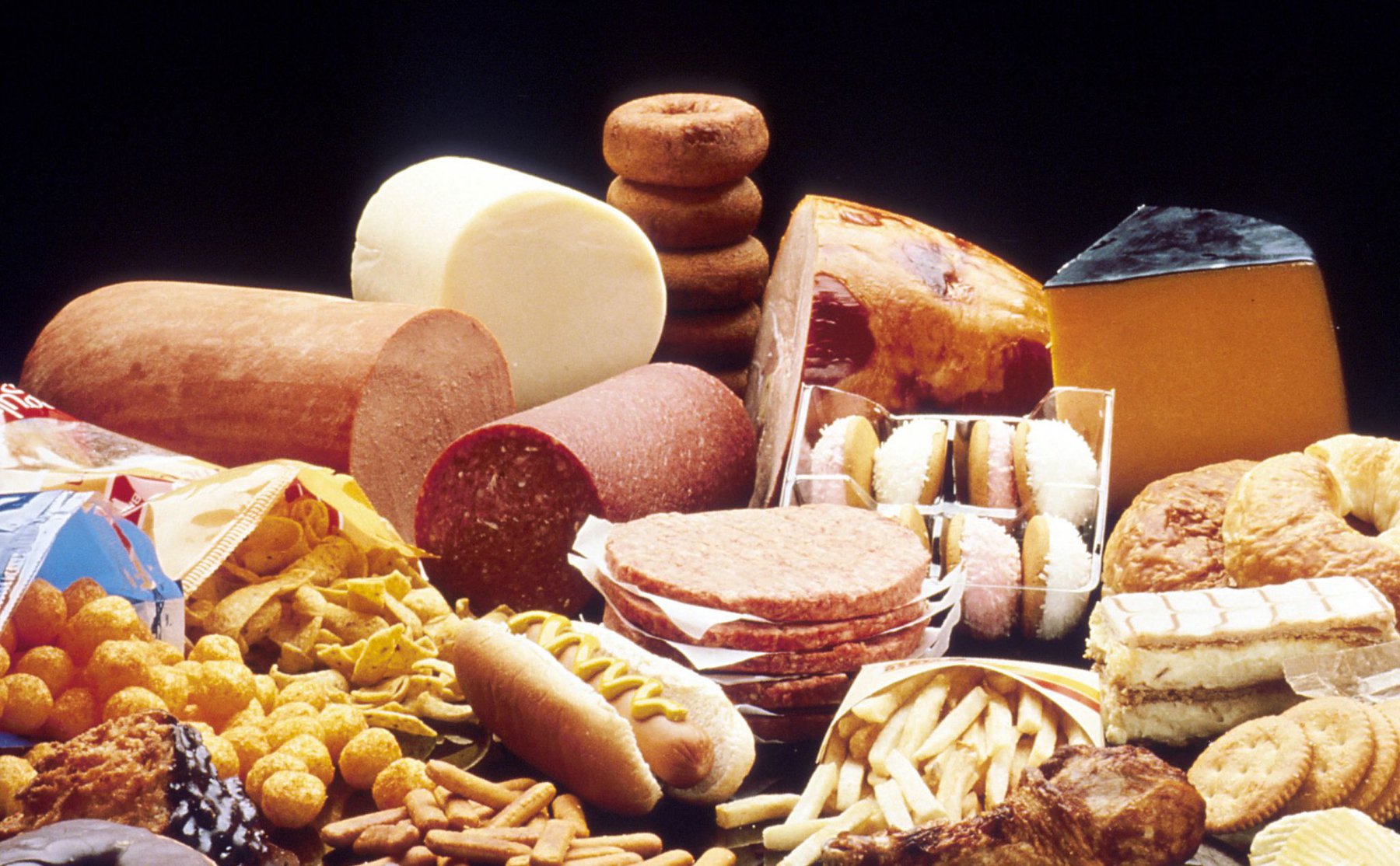

Chất béo chuyển hóa có nhiều trong các loại thực phẩm chế biến sẵn
3.2. How does trans fat affect my health?
Trans fats increase your bad cholesterol (LDL) levels and lower your good cholesterol (HDL) levels. Eating trans fats increases your risk of developing heart disease and stroke. It is also associated with a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
3.3. Which foods contain trans fats?
Trans fats can be found in a wide variety of foods - including fried foods like donuts and pies including cakes, pie crusts, cookies, frozen pizza, cookies, crackers and stick margarine and other powders. You can determine the amount of trans fat in a particular packaged food by looking at the Nutrition Facts table. However, products may be listed as “0 grams trans fat” if they contain between 0 grams and less than 0.5 grams of trans fat per serving.

Trong pizza có chứa chất béo chuyển hóa
3.4. How is it reasonable to use fat?
The American Heart Association recommends that adults who benefit from lowering LDL cholesterol reduce their trans fat intake and limit saturated fat consumption to 5 to 6% of total calories.
Here are some ways to get there:
Eat a diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, poultry, fish and nuts. At the same time limit red meat and sugary foods and drinks. Regularly use natural, non-hydrogenated vegetable oils such as canola, safflower, sunflower or olive oils. Look for processed foods made with hydrogenated oils rather than hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated vegetable oils or saturated fats. Use a soft margarine instead of butter and choose a soft margarine (liquid or tub) over a firmer form. Donuts, cookies, crackers, muffins, pies, and cakes are examples of foods that may contain trans fats. Limit how often you eat them. Limit fried foods and commercial baked goods made with shortened or partially hydrogenated vegetable oils. Not only are these foods very high in fat, but that fat is also likely trans fat.
4. Polyunsaturated Fats
4.1. How do polyunsaturated fats affect my health?
Polyunsaturated fats can help lower bad cholesterol levels in the blood, which in turn can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. They also provide nutrients to help grow and maintain your body's cells. Oils rich in polyunsaturated fats also contribute dietary vitamin E, an antioxidant vitamin.
Oils rich in polyunsaturated fats also provide essential fats that your body needs but cannot produce on its own - such as omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. You must get the necessary fats through food. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are important for many functions in the body.
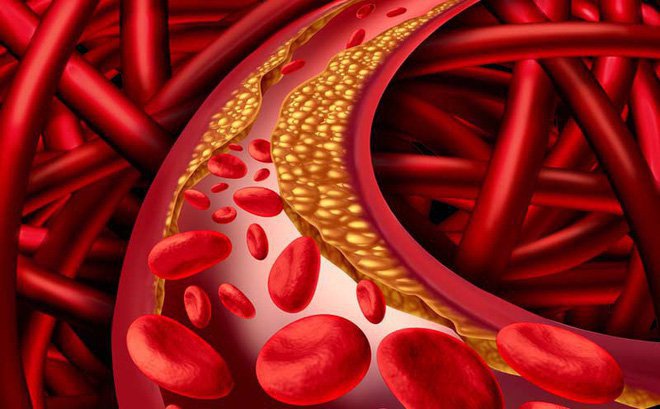
Chất béo không bão hòa giảm nguy cơ bị tăng cholesterol trong máu
4.2. Are polyunsaturated fats better for me than saturated or trans fats?
It's correct. While all fats provide 9 calories per gram, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can have a positive impact on your health, when eaten in moderation. Bad fats, saturated fats, and trans fats can negatively affect your health.
4.3. Which foods are high in polyunsaturated fats?
Most foods are high in fat. Foods rich in polyunsaturated fats include several types of vegetable oils, including: soybean oil, corn oil, sunflower oil
Other sources include certain nuts such as walnuts and sunflower seeds, tofu and soybeans. The American Heart Association also recommends eating tofu and other forms of soybeans, rapeseed, walnuts and flaxseeds, and their oils. These foods contain alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), another omega-3 fatty acid. Polyunsaturated fats like all fats contain 9 calories per gram

Đậu nành thuộc nhóm thực phẩm nhiều chất béo không bão hòa đa
5. Can fats be part of a healthy diet?
Eating foods with fat is definitely part of a healthy diet. Just remember to choose foods that provide good fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats) and balance the calories you eat from all foods with the calories you burn. Aim for a diet that emphasizes eating lots of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains; including low-fat dairy products, poultry, fish, legumes, non-tropical vegetable oils and nuts; and limit your intake of sodium, sweets, sugary drinks and red meat. Doing so means your diet will be low in saturated fat and trans fat.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.



