What is Stickler syndrome?
This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr. Duong Van Sy – Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Stickler syndrome is a group of genetic conditions characterized by a distinctive facial appearance, eye abnormalities, hearing loss, and joint problems. A characteristic feature of Stickler syndrome is a slightly flat face. This appearance is due to underdeveloped bones in the middle of the face, including the cheekbones and bridge of the nose. A specific group of physical characteristics known as Pierre Robin syndrome are also common in people with Stickler syndrome. Problems with the bones of the spine can also occur, including abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis) and flattened vertebrae (spondylolisthesis). Researchers have described several types of Stickler syndrome, distinguished by their genetic causes, and their signs and symptoms. In this article we will provide useful information to better understand Stickler syndrome.
1. What is Stickler syndrome?
Stickler syndrome is a genetic disorder that can cause serious vision, hearing, and joint problems. Also known as hereditary progressive arthropathy, Stickler syndrome is usually diagnosed during infancy or childhood.
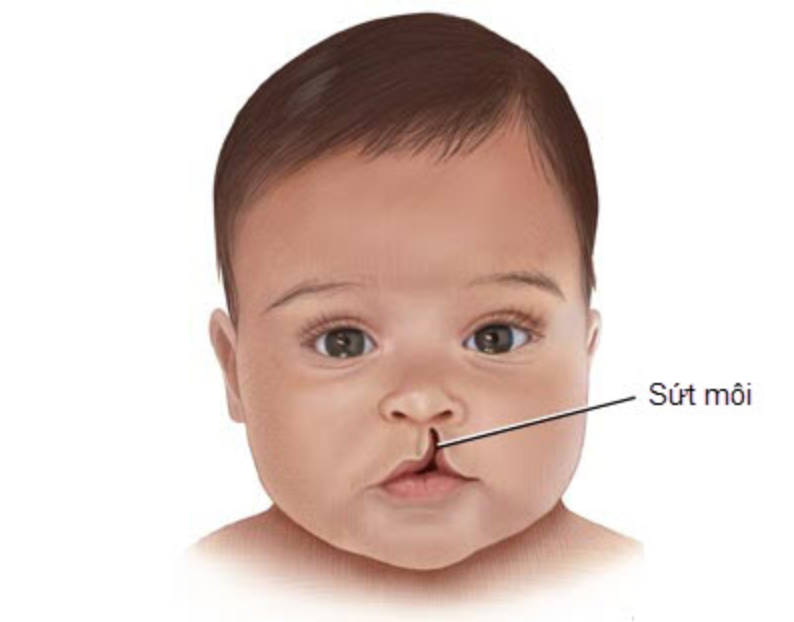
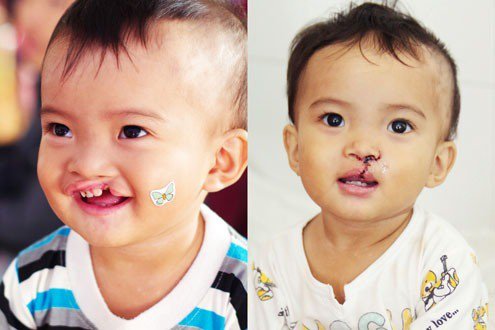
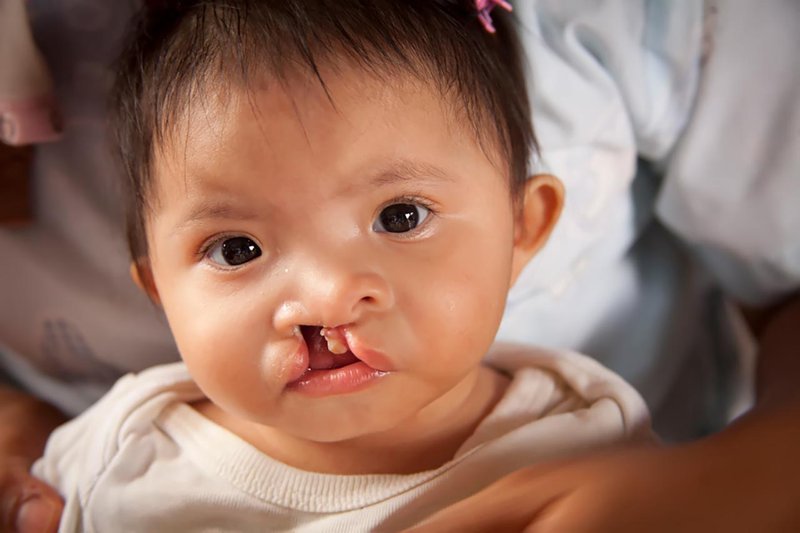
Children with Stickler syndrome often have distinctive facial features such as bulging eyes, small noses, upturned faces, and indented chin. Babies are often born with a cleft palate (cleft palate).
Although there is no cure for Stickler syndrome, treatments can help control symptoms and prevent complications. In some cases, surgery can correct some of the physical abnormalities associated with Stickler syndrome.
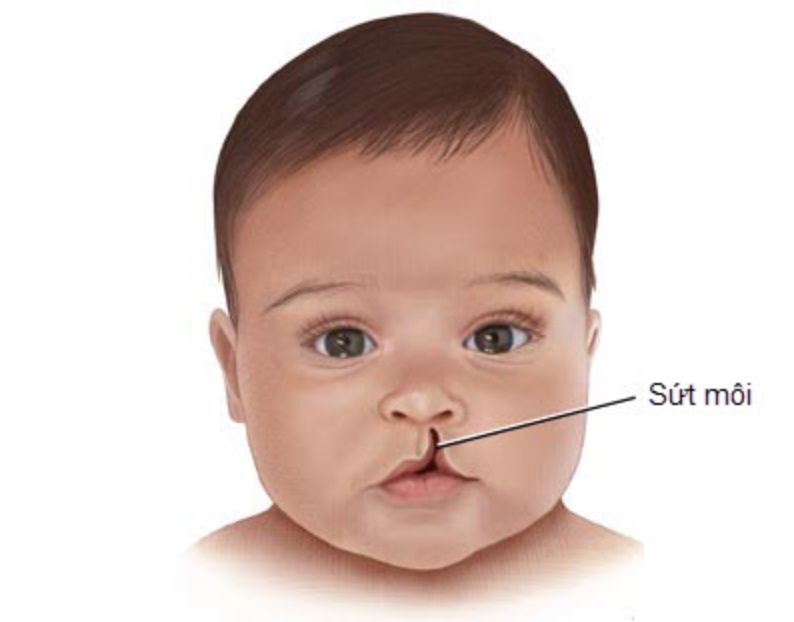
Những đứa trẻ mắc hội chứng Stickler sinh ra thường bị hở hàm ếch
2. Cause
The main cause of Stickler syndrome is a genetic mutation in one of 6 genes: COL2A1, COL11A1, COL11A2, COL9A1, COL9A2, or COL9A3. These genes are all responsible for providing instructions for the body to produce collagen. The type of collagen most commonly affected is used to produce joint cartilage and the jelly-like material (vitreous) found in the eye. Collagen is involved in determining the length and structure of connective tissues. Connective tissues are found in many parts of the body including the eyes, skin, and joints. When there are pathogenic variants in any of the genes involved in Stickler syndrome, it causes collagen in the body to not be synthesized properly. This causes the signs and symptoms associated with Stickler syndrome.
3. Symptoms
Symptoms of Stickler syndrome in members of the same affected family may not be the same. Common symptoms include:
Eye problems: In addition to being severely nearsighted, children with Stickler syndrome often develop cataracts, glaucoma, and retinal detachment. Hearing difficulties: The degree of hearing loss varies from person to person. Usually affects hearing at high frequencies. Musculoskeletal abnormalities: Children with this syndrome often have loose or too flexible joints and are prone to abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis) or flat vertebrae (with discs). Children with Stickler syndrome may also have osteoporosis that increases the risk of fractures. Osteoarthritis of the knee or hip... can begin in adolescence.
4. Which children can get Stickler syndrome?
Because it is hereditary, when you or your partner has Stickler syndrome, your baby is more likely to have the disorder as well.

Hội chứng Stickler có khả năng cao di truyền từ cha mẹ sang con cái
5. Complications
Potential complications of Stickler syndrome include:
Difficulty breathing or sucking can occur in babies born with cleft palate (cleft palate), small lower jaw, and tendency to retract the tongue. throat. Permanent vision loss: can occur when a child has retinal detachment but is not treated in time. Ear infection. Children with structural facial abnormalities associated with Stickler syndrome are more likely to develop ear infections than children with normal facial structures. Complete hearing loss may get worse over time in children with Stickler syndrome. Heart problems: Some people with Stickler syndrome may have a higher risk of heart valve problems. Dental problem. Most children with Stickler syndrome have abnormally small jaws, so there is often not enough room for adult teeth. Braces or, in some cases, dental surgery may be the way to go.
6. Diagnosis
Stickler syndrome can be diagnosed based on your child's medical history or physical exam, but definitive confirmation is still needed for additional tests to determine the severity of symptoms and help make direct treatment decisions. Tests include:
X-rays can reveal abnormalities or damage in the joints and spine. Eye exams can help your doctor detect problems with the vitreous fluid that fills the eye or lines the back of the eye (retina), which is important for vision. Eye exams can also check for cataracts and glaucoma. Hearing test. These tests measure a sound's ability to detect different pitches and volumes. Children born into families with a hereditary Stickler syndrome will be counseled by their doctors to make available genetic tests to aid in the diagnosis. These tests can also be used to advise in family planning and to determine the genetic risk of the disease in children in some families with no clear history.

Bác sĩ cần tiến hành các xét nghiệm để bổ sung cho kết quả chẩn đoán hội chứng Stickler
7. Treatment methods:
There is no cure for Stickler syndrome. Doctors can only come up with workarounds to treat the symptom of disease
7.1. Speech Therapy: Your child may need speech therapy if hearing loss interferes with his or her ability to learn to pronounce certain sounds. Physical therapy: In some cases, physical therapy can help with mobility problems associated with joint pain and stiffness. Devices such as splints, canes, and arch supports may also be helpful. Hearing aids: If your child has hearing problems, it is advisable to use hearing aids to improve his or her life. Special education model: because hearing or vision problems can make school difficult, your child needs to go to places that have special education programs for children with learning difficulties. Communicate like your child. 7.2. Surgery may need to be performed Tracheostomy . Newborns with very small jaws and crooked tongues may need a tracheostomy to create a hole in their throat so they can breathe. The surgery is done again after the baby has grown big enough that the baby's airway is no longer blocked. Jaw surgery. Surgeons can lengthen the lower jaw by cutting the jawbone and implanting a device that gradually stretches the bone until it heals. Cleft palate surgery. Babies born with a hole in the roof of their mouth (cleft palate) often have surgery to lengthen tissue from the roof of their mouth to cover the cleft. Place the ear canal. Surgically placing a short plastic tube in the eardrum can help reduce the frequency and severity of ear infections, which are especially common in children with Stickler syndrome. Eye surgery. Surgery to remove the cataract or a procedure to reattach the back lining of the eye (retina) may be necessary to preserve vision. Joint replacement. Early-onset arthritis, especially in the hips and knees, may require joint replacement surgery at a much younger age than the general population. Spinal splinting or fusion surgeries. Children who develop abnormal curves in the spine, such as scoliosis and kyphosis, may need surgery to correct. Milder curves can often be treated with a splint.
Trẻ em cần được tiến hành một số phẫu thuật để điều trị các triệu chứng của bệnh
8. Lifestyle and home remedies:
Lifestyle changes and the following measures can help you cope with the symptoms and complications of Stickler syndrome.
Take pain relievers: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve) can help reduce joint swelling, stiffness, and pain. Avoid contact sports. Strenuous physical activity can put extra strain on the joints, and sports, such as soccer, can increase the risk of retinal detachment. Seek educational help. Your child may have difficulty at school due to hearing or vision problems. You should talk to your child's teacher about your child's special needs.
9. When to see a doctor
Routine check-ups, as well as annual check-ups with your doctor, are important to monitor any progression of symptoms. Early treatment can help prevent life-changing complications. Hearing and eye exams are recommended every six months in children under 5 years of age and for years thereafter.
Currently at Vinmec International General Hospital, there are general health checkup packages for babies.
In the health checkup package, your baby will be comprehensively examined, from eyes, teeth, blood pressure, weight to necessary tests, combined with imaging diagnosis and functional assessment. liver and kidney baseline, blood sugar, nutritional status and hepatitis B virus. The examination package helps you check your baby's overall health, screen for symptoms for early detection and treatment if needed.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the nationwide health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
This article is written for readers from Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.