Distinguish between benign and malignant tumors
This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted - Head of Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Not all tumors are cancerous. There are tumors that are not cancerous and there are also cancers that are not. Noncancerous tumors are usually benign. Distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors requires a specialist doctor who combines many methods such as medical examination, imaging, blood tests and especially histopathology.
1. What is melanoma?
Tumors in cancer, also known as malignant tumors, not only grow in size but also form roots that plug into the surrounding area, destroying these areas. This is called the invasive nature of cancer. The image of a crab with claws and legs spread around depicting this property has become a symbol of cancer.
In cancer, cells proliferate into a mass that we can see (directly or through means) or feel. Most cancers have tumors, but not all cancers form tumors. Leukemias do not usually form tumors because malignant blood cells multiply and circulate in the bloodstream.
Cancer cells, also known as malignant cells, have the ability to break away from the original tumor, drift to other places in the body, and continue to multiply there like bees breaking out of a colony and arriving. another creates a new hive. This property is called metastasis.
In cancer, cells proliferate into a mass that we can see (directly or through means) or feel. Most cancers have tumors, but not all cancers form tumors. Leukemias do not usually form tumors because malignant blood cells multiply and circulate in the bloodstream.
Cancer cells, also known as malignant cells, have the ability to break away from the original tumor, drift to other places in the body, and continue to multiply there like bees breaking out of a colony and arriving. another creates a new hive. This property is called metastasis.
2. What is a benign tumor?
If the cells of the tumor are not cancerous, the tumor is benign. Benign tumors do not invade nearby tissues or spread to other areas of the body (metastasize). A benign tumor is of little concern unless it presses on nearby tissues, nerves, or blood vessels and causes damage. For example, fibroids in uterine fibroids or lipomas are good examples of benign tumors.
Benign tumors may need to be removed surgically as they can grow very large and heavy. In some cases, benign tumors can be dangerous, as when the tumor is present in the brain and concentrated in the enclosed space of the skull. In addition, benign tumors can press on vital organs or block their functioning. Some types of benign tumors such as bowel polyps are considered precancerous and are removed to prevent them from becoming malignant. Benign tumors usually do not recur after removal, but if they do, they often recur in the same place.
Benign tumors may need to be removed surgically as they can grow very large and heavy. In some cases, benign tumors can be dangerous, as when the tumor is present in the brain and concentrated in the enclosed space of the skull. In addition, benign tumors can press on vital organs or block their functioning. Some types of benign tumors such as bowel polyps are considered precancerous and are removed to prevent them from becoming malignant. Benign tumors usually do not recur after removal, but if they do, they often recur in the same place.

U xơ tử cung hoặc lipomas là ví dụ điển hình của khối u lành tính
3. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumors
Although there are exceptions, for example, although most malignant tumors grow rapidly and benign tumors do not, there are examples of both slow-growing cancerous tumors. and not rapidly growing cancers, the main difference between the 2 types of tumors is clear and consistent. Here are some key differences between the 2 types of tumors:
3.1 Characteristics of benign tumors Cells tend not to spread; Most growth is slow; No invasion of nearby tissue; Has not metastasized to other parts of the body; Have clear boundaries; Under the microscope, the shape, chromosomes and DNA of the cells appear normal; Does not secrete hormones or other substances (one exception: pheochromocytomas of the adrenal glands); May not need treatment if not threatening health; It is unlikely to recur if removed or requires further treatment such as radiation or chemotherapy. 3.2 Characteristics of malignancies Cells can spread; Usually grows quite quickly; Often invades nearby healthy tissue; Can be spread through the blood or lymphatic system; May recur after deletion, sometimes in other organs; Cells with abnormal chromosomes and DNA are characterized by large, dark nuclei; may have an irregular shape; May secrete substances that cause fatigue and weight loss (paraneoplastic syndrome); Aggressive treatment may be needed, including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy drugs.
3.1 Characteristics of benign tumors Cells tend not to spread; Most growth is slow; No invasion of nearby tissue; Has not metastasized to other parts of the body; Have clear boundaries; Under the microscope, the shape, chromosomes and DNA of the cells appear normal; Does not secrete hormones or other substances (one exception: pheochromocytomas of the adrenal glands); May not need treatment if not threatening health; It is unlikely to recur if removed or requires further treatment such as radiation or chemotherapy. 3.2 Characteristics of malignancies Cells can spread; Usually grows quite quickly; Often invades nearby healthy tissue; Can be spread through the blood or lymphatic system; May recur after deletion, sometimes in other organs; Cells with abnormal chromosomes and DNA are characterized by large, dark nuclei; may have an irregular shape; May secrete substances that cause fatigue and weight loss (paraneoplastic syndrome); Aggressive treatment may be needed, including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy drugs.

Sự khác nhau giữa bướu lành tính và bướu ác tính
4. Benign tumors can turn malignant?
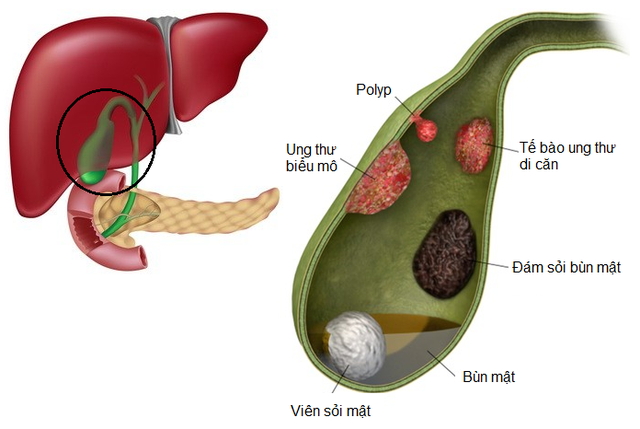
Some types of benign tumors very rarely turn into malignancies, for example adenomatous polyps (adenomas) in the colon have a high risk of turning cancerous. That's why benign polyps are removed during colonoscopy. Removing them is one way to prevent colon cancer.
It is not always clear whether a tumor is benign or malignant, and your doctor may use a number of different factors to make a diagnosis. In addition, it is possible that the biopsy finds precancerous cells or misses the area where the cancer cells are, in which case what is thought to be benign can turn malignant.
Therefore, patients need to go to reputable facilities with modern equipment to detect the disease in time and not miss any organs that can develop into cancer. Typically, the Department of General Internal Medicine and the Department of Endocrinology of Vinmec International General Hospital, this is the trusted address of many loyal customers who have trusted Vinmec Hospital in the examination and detection of tumor classification. as early as endocrine examination to detect tumors in the thyroid gland, pituitary gland .., from which to provide timely and accurate treatment and care regimens. With a team of well-known doctors with many years of experience in successfully detecting and treating many cases of tumors from simple to complex, it has brought happiness and health to the vast majority of patients.
Associate Professor. Dr. Hoang Dang Mich has over 42 years of medical practice, has strengths in the specialized fields of Liver - Kidney - Immune pathology... Currently, he is a Specialist Consultant in General Internal Medicine Department of Examination. Medicine & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Reference article source: Verywellhealth.com
MORE:
How many types of goiter are there? Are the results of the diagnosis of benign tumors worrisome? Goiter: When to operate?
It is not always clear whether a tumor is benign or malignant, and your doctor may use a number of different factors to make a diagnosis. In addition, it is possible that the biopsy finds precancerous cells or misses the area where the cancer cells are, in which case what is thought to be benign can turn malignant.
Therefore, patients need to go to reputable facilities with modern equipment to detect the disease in time and not miss any organs that can develop into cancer. Typically, the Department of General Internal Medicine and the Department of Endocrinology of Vinmec International General Hospital, this is the trusted address of many loyal customers who have trusted Vinmec Hospital in the examination and detection of tumor classification. as early as endocrine examination to detect tumors in the thyroid gland, pituitary gland .., from which to provide timely and accurate treatment and care regimens. With a team of well-known doctors with many years of experience in successfully detecting and treating many cases of tumors from simple to complex, it has brought happiness and health to the vast majority of patients.
Associate Professor. Dr. Hoang Dang Mich has over 42 years of medical practice, has strengths in the specialized fields of Liver - Kidney - Immune pathology... Currently, he is a Specialist Consultant in General Internal Medicine Department of Examination. Medicine & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Reference article source: Verywellhealth.com
MORE:
How many types of goiter are there? Are the results of the diagnosis of benign tumors worrisome? Goiter: When to operate?
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
This article is written for readers from Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.