Betadine Ointment is a versatile antiseptic used to treat and prevent skin infections. Its iodine content effectively eliminates bacteria and inhibits their growth, helping to protect scratches, cuts, or other skin wounds from becoming infected.
1. Uses of Betadine Ointment
Betadine Ointment is an antiseptic designed for application on skin that is infected or at risk of infection. It works by slowly releasing iodine, which helps eliminate or inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms.
This topical ointment is commonly used to treat and prevent infections in minor cuts, scrapes, small burns, and wounds from minor surgical procedures. It is also effective in managing fungal and bacterial skin infections, as well as treating infections in abscesses or wounds with pus accumulation.
Betadine Ointment is for external use only. For treating infections, it should be applied 1-2 times daily for a maximum of 14 days.
2. Contraindications of Betadine Ointment
It is important to be aware of the contraindications when using Betadine Ointment:
- Allergic reactions or hypersensitivity to iodine, povidone, or any other ingredient in the ointment.
- A history of thyroid disorders, such as hyperthyroidism or goiter, as well as other thyroid conditions like colloid nodules, endemic goiter, or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. and during or after radioactive iodine therapy.
- Patients with goiter, thyroid adenomas, or other thyroid abnormalities (especially older adults) who may be at risk of developing hyperthyroidism due to high iodine exposure.
- Children under 2 years of age.
- Patients undergoing lithium therapy.
3. How to Use Betadine Ointment
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully when using this medication. Before application, ensure the affected area is thoroughly cleaned and dried. To achieve the best results, apply the ointment regularly as directed. Avoid exceeding the recommended dosage, as using more will not speed up recovery and may increase the likelihood of side effects.If your condition lasts longer than four weeks or worsens at any point, contact your doctor promptly. For optimal effectiveness, keep the affected area clean and dry at all times. Remember to wash your hands both before and after applying the ointment to prevent the spread of infection.
4. Precautions When Using Betadine Ointment
The use of this product may interfere with thyroid function tests. Iodine is absorbed more slowly through burned or damaged skin than through intact skin, and in certain cases, can lead to dangerously high iodine levels in the blood, particularly in patients with kidney dysfunction. If you notice symptoms suggesting thyroid problems, seek medical attention immediately. For patients with kidney impairment, iodine levels should be closely monitored.
Side effects such as skin irritation, redness, or itching may occur at the application site. If these persist, consult your healthcare provider. Avoid contact with the eyes. In case of accidental eye contact, rinse thoroughly with clean water and seek medical care immediately. Discontinue use if you notice any signs of an allergic reaction, including rash, swelling of the lips, throat, or face, difficulty breathing or swallowing, dizziness, fainting, or nausea.
Betadine ointment may permanently discolor white gold jewelry, so it’s advisable to remove jewelry before applying the ointment.
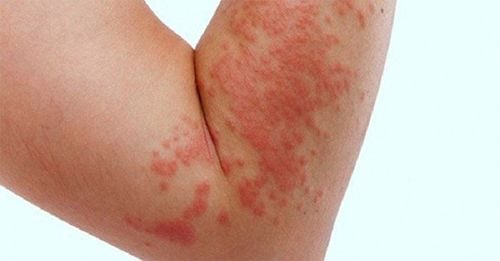
5. Adverse Effects of Betadine Ointment
Rare side effects: skin hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., delayed allergic contact reactions, presenting as itching, redness, small blisters, or similar symptoms). In some isolated acute cases, systemic allergic reactions including hypotension and/or shortness of breath (anaphylactic reactions) have been reported.
Prolonged use of the ointment for treating wounds and burns over large skin areas may lead to significant iodine absorption. In patients with a history of thyroid disorders, it may cause hyperthyroidism (iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis), occasionally manifesting as symptoms such as tachycardia or restlessness.
6. Use of Betadine Ointment During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Betadine Ointment is not recommended for use during pregnancy, as animal studies have demonstrated potential harmful effects on fetal development.
However, the ointment is deemed safe for use while breastfeeding. Research on humans suggests that the medication does not transfer into breast milk in significant amounts and poses no risk to the nursing infant.

7. How to Handle Betadine Overdose
Accidental or intentional ingestion of a large amount of povidone-iodine can raise iodine levels in the blood and cause gastrointestinal irritation, resulting in symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, systemic toxicity may occur, leading to complications like shock, low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, fever, metabolic acidosis, and kidney failure.Management involves symptomatic and supportive treatment, with careful monitoring of electrolyte balance, kidney function, and liver function. Hemodialysis is an effective method for removing iodine and is strongly recommended in cases of severe iodine poisoning, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney impairment. Continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) is less effective compared to hemodialysis for these situations.
This information highlights the importance of understanding Betadine usage. However, patients should always consult their doctor or pharmacist before use to ensure proper and safe application. Using medications correctly not only enhances treatment efficacy but also helps reduce unnecessary healthcare expenses.
Reference source: drugs.com
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.