This article has been professionally consulted by Tran Thi Linh Chi, Specialist Level II, MD - Deputy Head of the Pediatrics - Neonatology Department at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Pneumonia is a condition in which the lungs are damaged due to the attack of bacteria, viruses, parasites, etc. These pathogens proliferate and create infection sites in the lungs. When newborns have pneumonia that is not detected early and treated promptly, it can lead to dangerous complications, even resulting in death. The following article will provide detailed guidance on how to care for newborns with pneumonia, helping them recover quickly and avoiding complications that may affect their development in the future.
1. Pneumonia in Newborns
Pneumonia is a common illness among newborns and young children, most frequently occurring in children under 3 years old (over 80%), with 65% being under 12 months.
Pneumonia in newborns often appears early, within 12 hours to a few days after birth, and progresses rapidly and severely.
Unlike pneumonia in older children, the typical symptoms include high fever, frequent coughing, and wheezing sounds when listening to the back. In newborns, due to the underdevelopment of the respiratory system, clinical symptoms are often unclear and easily overlooked.
Initial symptoms of pneumonia in newborns may include:
- Poor feeding or refusal to eat
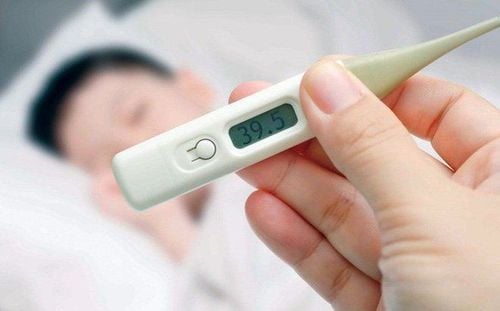
- Fever above 37.5°C or hypothermia
- Rapid breathing over 60 times per minute or difficulty breathing
When clear symptoms are present, the condition has already become severe: the child may have fever or hypothermia, lethargy, poor feeding or refusal to eat, frequent vomiting, abdominal distension, difficulty breathing, retraction of the chest wall, and cyanosis. Therefore, parents or caregivers need to pay attention to the child's condition to quickly detect early signs and take the child to a medical facility for timely examination and treatment to avoid serious pneumonia complications.
If pneumonia in newborns is not treated promptly, it can lead to many dangerous complications affecting the child's development later on, such as meningitis, sepsis, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, cardiac collapse, antibiotic resistance, and rickets.
2. How to Care for a Newborn with Pneumonia
The choice of treatment medication for a child with pneumonia depends on the underlying cause of the illness and is prescribed by a doctor. Parents must not buy antibiotics or cough medications on their own to treat their child at home. Antibiotics will not be effective if the pneumonia is caused by a virus. Coughing is a beneficial reflex that helps expel mucus from the airways and clear them, so cough medications should not be given to the child without a doctor's prescription.

Here are some effective care methods that parents can use to help their newborn recover from pneumonia:
Reducing Fever
- Use warm compresses (the water temperature can be tested by dipping an adult's elbow into the basin; if it feels warm, it's suitable).
- If the child has a fever above 38.5°C, administer fever-reducing medication as prescribed by a doctor.
Chest Percussion and Assisting Mucus Excretion
Perform back percussion when the stomach is empty, preferably before meals or at least 1 hour after eating to avoid causing vomiting. Parents can perform chest percussion multiple times throughout the day. Be sure to suction mucus from the child's nose and throat before and after percussion. Remove any tight clothing from the child and place them in an appropriate position. Parents should remove rings, watches, and bracelets before proceeding with the following steps:
- Cover the child with a thin cloth (if they are bare-chested) to avoid direct contact with the skin.
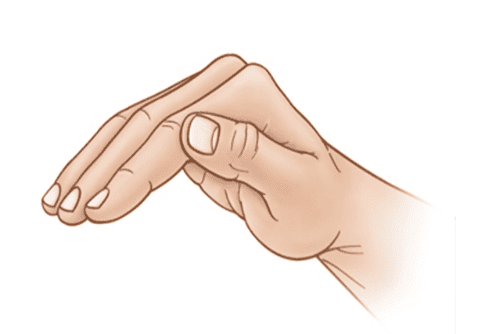
- Bend your hand at the wrist and cup your hand. Keep your thumb pressed against your index finger. When you tap the chest, you should hear a hollow sound created by the air trapped between your cupped hand and the chest. If the sound is flat, like when clapping, check your hand position as it may not be cupped enough. Tapping correctly should not cause pain.
Proper Hand Position for Chest Percussion
- While tapping the chest, only move your wrist, not your arm and shoulder. Alternate tapping between the right and left sides. Avoid tapping on the stomach, sternum, or spine.
- Continue tapping firmly and evenly, but not too hard, for about 3-5 minutes on each area.
Hygiene and Diet for the Child
- Soft tissues should be used to gently wipe away mucus and saliva, and they should be discarded immediately after use. If using a cloth, special attention must be paid to keeping it clean. Reusing a contaminated cloth that hasn’t been properly washed can allow bacteria and viruses to transfer back to the child’s body.
- It is advisable to clean the home, toys, and utensils used by the child. Caregivers should wash their hands thooughly when caring for and preparing food for the child.
- Feed the child nutritious, liquid, soft foods that are easy to digest and swallow.
- Provide meals according to the child's needs, dividing them into several smaller meals throughout the day, and do not force the child to finish the food you have prepared.
- Honey-steamed kumquats, rose petals steamed with sugar, ginger, and lemon can be given to the child to help reduce coughing.
Disease Prevention
- Maintain cleanliness to prevent the spread of illness, avoid smoking, and cooking in rooms with young children. Keep children away from sick individuals to prevent outbreaks.
- The living environment should be well-lit and well-ventilated.
- Ensure that the child receives all vaccinations on schedule, including vaccines for pneumococcus, influenza, diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus, and others.
- Early detection of respiratory infection symptoms in children, such as coughing, fever, runny nose, difficulty breathing, and other issues like diarrhea, poor feeding, refusal to breastfeed, and slow weight gain, is crucial for timely care and treatment.
- Breastfeed the child immediately after birth and continue until the age of two to promote overall development and strengthen their immune system.
Pneumonia is a common illness and one of the leading causes of death in children. The younger the child, the higher the mortality rate from pneumonia. Therefore, as soon as any suspicious symptoms are observed, it is essential to take the child to a medical facility for examination and timely treatment. We hope this article is helpful for parents to care for their newborns correctly, aiding in quick recovery and preventing dangerous complications.
The Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital is a facility that diagnoses and treats common conditions in newborns and young children, such as viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, and pneumonia. With modern equipment and a sterile environment, we minimize the impact and risk of disease transmission. Additionally, our dedicated and experienced doctors ensure that medical examinations are no longer a source of concern for parents.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.