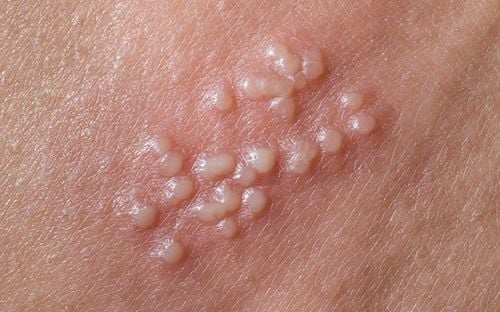
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection. While in some people, the condition may not cause any effects, in others, this agent can lead to cancer.
1. What Are Genital Warts?
Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Nearly all sexually active individuals will contract at least one type of human papillomavirus (HPV), the virus responsible for causing genital warts. This condition can occur at any time and at any stage in an adult’s life.
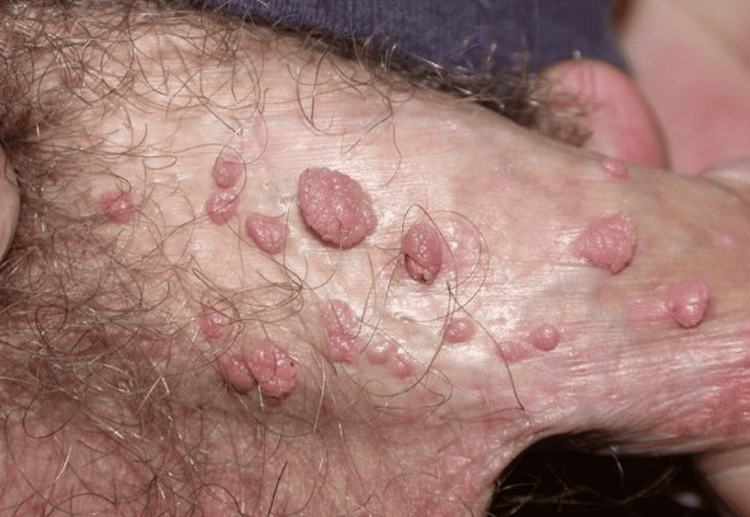
Genital warts typically affect the moist tissues of the genital area. They may appear as small, flesh-colored bumps or have a cauliflower-like texture. In many cases, the warts are too small to be easily seen and can be overlooked.
Some strains of genital HPV cause only warts, while others can lead to cancer. Vaccination can help protect against certain genital HPV strains, provided that individuals receive the vaccine early, ideally in adolescence before exposure to risk factors.
Although most sexually active individuals may contract genital HPV at some point in their lives and clear the infection on their own, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing genital warts, including:
- Engaging in unprotected sex
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Contracting a sexually transmitted infection
- Having sexual relations with a partner who has a history of sexually transmitted diseases, whether known or unknown
- Being sexually active at a young age
- Having a weakened immune system, such as co-infection with HIV or the use of immunosuppressive medications

2. What Are the Symptoms of Genital Warts?
In women, genital warts can develop on the vulva, vaginal walls, anus, anal canal, and even deep inside the cervix. In men, lesions may appear on the head or shaft of the penis, scrotum, or anus.
Genital warts can also develop on the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue, cheeks, uvula, or throat in individuals who have engaged in oral sex with an infected partner.
Upon examination, affected individuals may exhibit the following characteristics:
- Small, flesh-colored, brown, or pink bumps in the genital area
- A cauliflower-like appearance when multiple warts cluster together
- Itching or discomfort in the genital region
- Bleeding during intercourse or from friction
- In some cases, genital warts may be small and flat, making them nearly invisible on the skin. However, it is rare for genital warts to grow into large clusters, even in individuals with a weakened immune system.
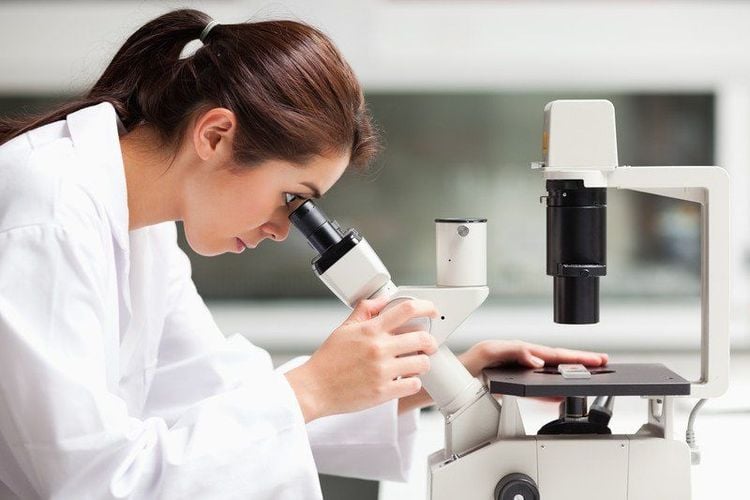
3. What Is the Role of Genital Wart Biopsy?
With skin lesions as described and the impact on sexual health, early diagnosis and treatment of genital warts are crucial.
Among diagnostic methods, the significance of genital wart biopsy is particularly notable. When individuals notice skin lesions accompanied by itching or easy bleeding, they should seek medical evaluation promptly. If these lesions appear consistent with genital warts, a doctor will confirm the diagnosis by performing a biopsy. This involves extracting a tissue sample from the lesion for microscopic examination. In men, the biopsy procedure is relatively straightforward. However, in women, especially when lesions are located on the vaginal walls or cervix, the biopsy must be performed alongside a gynecological examination using a speculum on a specialized examination table.
After the biopsy sample is collected, it is preserved before being processed in the laboratory. There, the tissue is stained and examined under a microscope to determine whether the lesion is caused by HPV. A normal result indicates that no HPV-related cellular abnormalities were found. In such cases, the lesion may be caused by other pathogens, requiring further specialized testing if the presentation is atypical.
If the biopsy sample shows characteristic HPV-related lesions, the result is considered positive. However, an important aspect of pathology assessment is determining the stage of HPV-related changes. In the early stages, the virus may only cause chronic inflammation. Some high-risk HPV strains can induce cellular transformation into precancerous or malignant stages. This evaluation is critical in the significance of genital wart biopsy, as it informs appropriate treatment and monitoring plans for the patient.
Regardless of the results, they typically become available a few days after the procedure. Since these lesions can cause pain and bleeding, it is advised to abstain from sexual activity until the biopsy site has fully healed.

4. What Are the Complications of Genital Warts?
If a patient does not seek early medical evaluation or undergo a genital wart biopsy for confirmation, HPV-related infections can lead to the following complications:
Cancer: Cervical cancer is strongly associated with genital HPV infection. Certain HPV strains are also linked to cancers of the vulva, anus, penis, mouth, and throat. Although not all HPV infections lead to cancer, it is crucial for women to undergo regular Pap smears, even in the absence of visible lesions, especially those infected with high-risk HPV strains.
Pregnancy-related complications: Although rare, genital warts may enlarge during pregnancy, making urination difficult. Warts on the vaginal wall can interfere with the stretching of vaginal tissues during delivery, complicating labor. Additionally, large warts on the vulva or inside the vagina may cause prolonged bleeding during and after childbirth.
Neonatal warts: Some babies born to mothers with genital warts may develop warts in their throat. If the lesion grows large, surgical intervention may be necessary to prevent airway obstruction.

In summary, genital wart biopsy plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of the condition. Early detection, when the disease is still in its initial stages, allows for timely and appropriate treatment, potentially leading to complete recovery. Conversely, any delay increases the risk of a biopsy revealing cancerous changes, making prognosis more challenging.
Vinmec International Hospital offers a Screening Package for Sexually Transmitted Diseases, allowing patients to detect conditions early and receive effective treatment to prevent dangerous complications. This screening package is available for individuals of all ages, both men and women.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.