1. Overview of Cervical Cancer
1.1. What is Cervical Cancer?
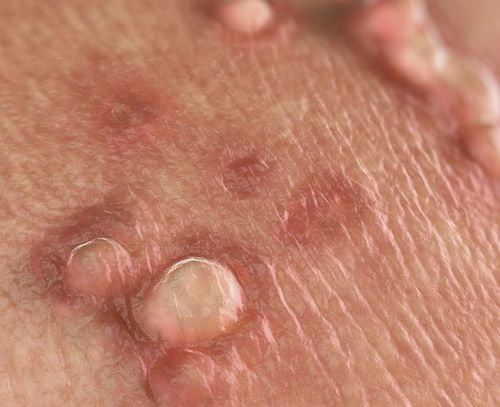
Cervical cancer is a malignant disease affecting the cervical glandular epithelium or squamous cells. It occurs when cells in the cervix develop abnormally, leading to tumor formation that can invade surrounding tissues and other organs in the body.
Approximately 99% of cervical cancer cases are linked to strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). Research indicates there are more than 140 HPV strains identified in humans, with about 40 strains responsible for infections in the genital area. Among these, HPV strains 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous due to their deep penetration into the cervix and their association with other serious diseases, including vaginal, penile, and anal cancers…
At the onset of sexual activity, everyone is at risk of contracting HPV at least once in their lifetime. About 50% of individuals are infected with high-risk HPV strains, including 16 and 18. While the body's immune system typically responds to fight HPV infections, in some cases, particularly with high-risk strains, the immune response may fail, increasing the risk of cervical cancer in the future.
1.2. Who is at High Risk for Cervical Cancer?
Understanding the factors that elevate the risk of cervical cancer can help individuals take better precautions. Research indicates the following risk factors can contribute to the transformation of normal cells into malignant cells:
- History of HPV or chlamydia infections.
- Early sexual activity or multiple sexual partners: Studies suggest that women with more than two sexual partners in a year, or over seven partners in their lifetime, face a higher risk. Engaging in sexual activity at a young age also raises vulnerability due to immature cervical cells.
- Smoking: The nicotine in cigarettes can weaken the immune system, increase oxygen and stress, thereby leading to an imbalance of cancer-related genes.
- Long-term use of birth control pills.
- Early pregnancies or multiple pregnancies: Becoming pregnant before the reproductive organs are fully developed, or having four or more pregnancies, poses a higher risk of cervical or uterine cancer.
- Personal or family history of cervical cancer.
- HIV infection or weakened immune system.
1.3. What Are the Symptoms of Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer can manifest through the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: This is the most typical symptom of cervical cancer.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding can include bleeding after sex, bleeding between menstrual cycles, postmenopausal bleeding, or heavier than usual menstrual bleeding…
- Unusual vaginal discharge, like foul-smelling, opaque gray, or greater in volume than normal.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Pelvic or lower back pain: This may suggest that cancer cells have invaded surrounding areas.
- Swelling and pain in the legs: As tumors grow, they may press on nerves and blood vessels in the pelvic area, leading to persistent leg pain and swelling.
In the early stages or precancerous conditions, women often experience very few noticeable symptoms. The progression of cervical cancer is typically challenging to manage, and symptoms are easily mistaken for common gynecological issues. Symptoms typically emerge as cancer cells grow and invade deeper into the cervix and surrounding organs. Therefore, most patients discover the disease at an advanced stage, complicating treatment efforts and outcomes.
1.4. How to Prevent Cervical Cancer
According to the Ministry of Health, there are three effective methods to prevent cervical cancer: HPV vaccination, practicing safe sex, and regular gynecological exams every six months. Cervical cancer can be completely cured if detected early. To safeguard their health, women should prioritize HPV vaccination and regular screenings to reduce the risk of genital organ diseases and cervical cancer.
2. What age is the cervical cancer vaccine recommended?
The HPV vaccination is the most effective method to prevent cervical cancer. A common question is, "At what age should I get the HPV vaccine?" or "Can I receive the HPV vaccine if I am over 30?"
Experts recommend that the optimal age for HPV vaccination is between 9 and 26 years old. Some people believe that receiving the HPV vaccine at 9 years old is too early; however, this misconception can increase the risk of disease. The later the vaccination is administered—especially after a woman has become sexually active—the less effective it will be. Early vaccination provides stronger protection, as the immune response from the three doses of the HPV vaccine can last up to 30 years. Women over 30 who have previously been sexually active can still receive the HPV vaccine, but its preventive effect will not be as significant as for those in the recommended age range.
3. Important Considerations for HPV Vaccination
3.1. Cervical Cancer Vaccines
There are two types of cervical cancer vaccines: Gardasil and Cervarix.
Gardasil: This vaccine protects against four common HPV strains (Types 6, 11, 16, and 18) that can cause gynecological diseases. The vaccination schedule consists of three doses administered as follows:
- First injection: On the first day
- Second injection: Two months after the first injection
- Third injection: Six months after the first injection
Cervarix: This vaccine protects against the two most common HPV strains (Types 16 and 18). The vaccination schedule consists of three doses administered as follows:
- First injection: On the first day
- Second injection: One month after the first injection
- Third injection: Six months after the first injection
3.2. Recommendations for Vaccination Candidates
According to the World Health Organization, women aged 9 to 26 are encouraged to receive the HPV vaccine for optimal preventive efficacy. Vaccination is not limited by age or sexual history; therefore, women over 30 can still receive the vaccine, though its effectiveness may not be as high.
Recipients of the cervical cancer vaccine should meet these conditions:
- Be in good health.
- Not have received any vaccines or taken immunosuppressive drugs (such as corticosteroids or anti-rejection medications) for four weeks prior to the first vaccination.
- A Pap test is not required before vaccination.
Certain individuals should not receive the vaccine, including:
- Those with acute illnesses.
- Individuals with hypersensitivity to yeast or any other ingredient in the vaccine.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those planning to become pregnant within the next six months. If a person discovers that they are pregnant while on the vaccination schedule, they must pause further injections until after childbirth, with subsequent doses to be completed within the allowed time frame of two years.
3.3. Additional Considerations When Getting the Vaccine
Although most patients experience effective outcomes post-vaccination, it is essential to follow certain guidelines before and after receiving the HPV vaccine:
- Women who have had sexual intercourse should undergo a gynecological examination and cervical cancer screening tests before registering for the vaccine.
- Ensure that all three doses are administered according to the specified schedule.
- If a subsequent dose is delayed, it should be administered as soon as possible without starting the series over from the first shot.
After vaccination, some common side effects may occur, such as pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, rash, itchiness, fever, chills, or shortness of breath... Any concerning symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider for prompt care.
In addition to receiving the cervical cancer vaccine, women should adopt healthy lifestyle habits to enhance their immunity, practice safe sex to further prevent cervical cancer, and maintain regular health check-ups combined with cervical cancer screening. Early detection and treatment of any potential issues will lead to more effective outcomes in managing gynecological diseases and cervical cancer.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.