This article was written under the expert supervision of physicians from the Gastroenterology and Hepatology Department at Vinmec International General Hospital.
Elevated hepatic enzymes are indicative of hepatocellular injury, encompassing inflammation and necrosis. Upon hepatocyte destruction, specific enzymes (hepatic transaminases) are released into the circulation. Left untreated, persistently high liver enzymes can lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and even liver cancer.
1. What is elevated hepatic enzymes?
The liver is the largest organ in the body, performing various functions such as synthesis, metabolism, detoxification, etc. Liver enzymes are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions in the liver, helping the liver perform its metabolic functions. Liver enzymes include:
- Alanine transaminase (ALT or SGPT)
- Aspartate transaminase (AST or SGOT)
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), which is localized in the bile canaliculi and hepatic sinusoids of the hepatic lobule.
Normally, a small amount of liver enzymes is released into the bloodstream at a concentration below 35 IU/L when liver cells die naturally due to the aging process.
Elevated serum liver enzyme activity is a consequence of accelerated hepatocyte damage due to an underlying etiology. This condition can be graded into three categories: mild (1-2-fold elevation above the upper limit of normal), moderate (2-5-fold elevation), and severe (greater than 5-fold elevation).
2. What causes elevated hepatic enzymes?
- Viral causes: Viruses A, B, C, D, and E are the five types of viruses that cause hepatitis, destroying liver cells upon entering the body. In particular, hepatitis B and C viruses can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, thereby increasing the risk of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
- Alcohol abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption leading to liver damage and impaired liver function is one of the causes of elevated liver enzymes. In addition, other organs such as the stomach, cardiovascular system, and nervous system can also be affected by excessive alcohol consumption.
- Inappropriate medication use: The liver is the site of metabolism for most pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-tuberculosis drugs, etc. Overuse of medication will put a burden on the liver, causing liver damage, which can lead to elevated liver enzymes. In particular, the rate of hepatitis has been increasing recently due to the use of many functional foods.
- Diet: A certain amount of toxins and aflatoxin are often present in contaminated, moldy, and preserved foods, which can cause hepatitis, elevated liver enzymes, and even liver cancer.
- Biliary tract diseases: Bile duct infections, gallstones, and bile duct tumors…
- Because liver enzymes are not only produced in the liver, some diseases of other organs can also cause elevated liver enzymes, including: respiratory diseases, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases (cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction…) and iron metabolism disorders…
3. Signs of elevated hepatic enzymes
While the initial presentation of elevated hepatic enzymes is frequently asymptomatic, as enzyme levels rise, clinical manifestations become more apparent, encompassing:
- Some symptoms such as abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting appear in patients.
- Fatigue, mild fever.
- Right upper quadrant pain: A dull ache will appear in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen when liver enzymes are high.
- Skin rash/itching: Toxins accumulate in the body, causing itching on the skin due to impaired liver function.
- Pale stools, dark urine: Bile duct obstruction causes elevated liver enzymes, thereby bilirubin cannot enter the digestive tract and be excreted through urine, leading to pale stools and dark urine.
- Jaundice: Elevated liver enzymes are often most clearly manifested through the symptom of jaundice. However, when skin discoloration is noticed, the disease is already at an alarming stage.
A blood test is the simplest way to detect elevated liver enzymes, especially when the degree of enzyme elevation is minimal and associated symptoms are often nonspecific or absent.
4. Consequences of elevated hepatic enzymes
Long-term consequences of persistent elevation in liver enzymes can be substantial and include:
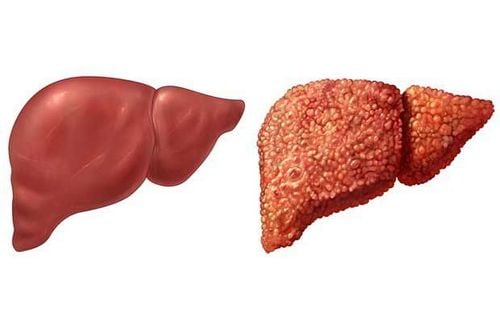
- Complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, etc., are very likely to occur if the condition of elevated liver enzymes persists without treatment.
- Elevated hepatic enzyme activity serves as an indicator of underlying hepatic pathology, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and other hepatic disorders. More dangerously, if the cause of elevated liver enzymes is due to poisoning, patients may face the risk of acute liver failure, hepatic coma, and even death.
5. How to prevent elevated hepatic enzymes?
- Proper diet: Foods rich in vitamins A, B1, B2, B6 such as fresh milk, egg yolks, liver, cereals, lean meat, green vegetables, and fruit juices… help lower liver enzymes and protect liver function. People should regularly add them to their diet. At the same time, people need to avoid using alcohol, beer, cigarettes, pipe tobacco, and stimulants.
- Proper rest: Sleeping early, getting enough sleep, and avoiding staying up late working under stress.
- Drink plenty of water: The blood circulation process is accelerated and the activity of liver cells will be enhanced when people drink water. Thanks to that, toxins will be eliminated from the body quickly. Therefore, people should drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day.
- People infected with hepatitis viruses or suffering from liver diseases should have regular check-ups every 6 months.
- Patients need to be cautious when using any supplements or medications.
Improve overall health by exercising regularly. - Maintain a healthy weight.
Generally, significant hepatic pathology can be indicated by elevated liver enzyme levels. However, in cases of mild enzyme elevation, clinical manifestations may be subtle or absent. The most direct method for accurate diagnosis is through laboratory analysis of liver enzymes.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, the Hepatobiliary Screening Package is currently offered to help customers assess liver function through liver enzyme tests, early screening for liver cancer and hepatobiliary diseases… thereby helping to timely detect liver diseases and provide effective treatment plans to bring the best results for patients' health.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.