1. Understanding Success Rates
One of the primary concerns for couples seeking infertility treatment is the success rate of IVF. The "success rate" is essentially a number, but it is not fixed and is influenced by multiple factors. Understanding the success rate correctly helps patients set realistic expectations and avoid psychological distress.
2. Terminology Related to Success Rates
The most common measures of success in IVF are the clinical pregnancy rate (confirmed by the presence of a gestational sac on ultrasound) and the live birth rate. These rates are calculated based on the number of clinical pregnancies or live births per total number of embryo transfers within a specific period. This article will clarify key terms, indices, and essential laboratory tests that patients should be aware of during treatment.
Beta-hCG possitive: Pregnancy confirmation is determined by measuring beta-hCG levels 10–14 days after embryo transfer. Beta-hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is a hormone produced by the placenta and is present when the embryo successfully implants into the uterine lining.

Determining Pregnancy Based on Beta-hCG Levels:
During the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, beta-hCG levels typically double every 48–72 hours, peaking between 8–11 weeks. International and our standards define pregnancy as follows:
- Beta-hCG < 5 mIU/mL: Negative result – not pregnant.
- Beta-hCG ≥ 25 mIU/mL: Positive result – pregnant.
- Beta-hCG between 6–24 mIU/mL: Requires follow-up testing after 48 hours.
Based on beta-hCG levels, doctors determine appropriate monitoring and management of pregnancy.
Clinical Pregnancy: Clinical pregnancy is confirmed when a gestational sac is observed via ultrasound, typically 4–6 weeks after embryo transfer, including cases of ectopic pregnancy. If beta-hCG ≥ 25 mIU/mL but no gestational sac is visible, the pregnancy is classified as a biochemical pregnancy.
Live Birth Rate: The live birth rate refers to the number of successfully delivered healthy babies, regardless of singleton or multiple pregnancies. This is the most clinically meaningful indicator used globally, including in Vietnam, to evaluate IVF treatment success.
3. Factors Affecting Success Rates
IVF success rates vary depending on factors such as maternal age, cause of infertility, embryo quality, maternal body weight, and more. Treatment outcomes may differ among patients and even across multiple treatment cycles for the same patient. Each cycle has unique characteristics, and not all cycles proceed to egg retrieval, embryo transfer, or embryo freezing. Doctors provide individualized treatment plans to optimize success.
3.1. Maternal Age
Age of woman is the most critical factor affecting IVF success and overall fertility. Women aged 24–34 have the highest IVF success rates (45–50%). As women age, egg quality and quantity decline. By age 40, the success rate drops to approximately 13.6%. Individualized treatment protocols are designed for each age group to optimize outcomes.

3.2. Cause of Infertility
IVF can address most causes of infertility, such as endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes (in females), and poor sperm quantity, motility, or morphology (in males). However, certain conditions like uterine fibroids, uterine abnormalities, and ovarian dysfunction may require surgical intervention, impacting success rates. Identifying these factors is crucial for accurate IVF success predictions.
3.3. Embryo Quality
To ensure high embryo quality, IVF Vinmec Department utilizes continuous embryo monitoring with time-lapse incubators. This advanced system provides real-time embryo development tracking, enabling embryologists to detect abnormalities that conventional incubation may miss. Selecting the best embryos for transfer increases implantation success rates.
3.4. Fresh vs. Frozen Embryo Transfer
Ovarian stimulation for egg retrieval leads to a temporary hormonal surge that may affect embryo implantation. Therefore, freezing embryos and transferring them at a later, hormonally stable stage may improves pregnancy success rates.
3.5. Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A)
PGT-A helps select embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, enhancing pregnancy success rates, reducing the risk of miscarriage and genetic disorders, and potentially leading to a healthy pregnancy.
At IVF Vinmec Department, we have recorded a clinical pregnancy rate of 62.1% and a live birth rate of 49.4% in frozen embryo transfers. For cases involving PGT-A embryos, the clinical pregnancy and live birth rates reach 68.8% and 60.7%, respectively. These success rates are comparable to leading IVF centers in the region and globally. Our detailed success rate statistics from January 1, 2022, to December 31, 2022, are illustrated in the graphs below.
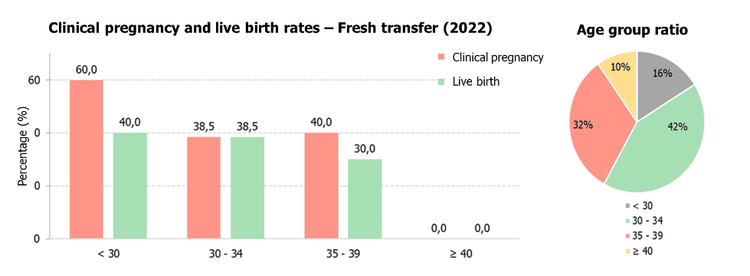
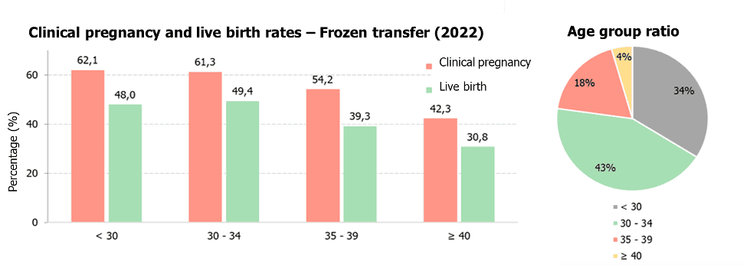
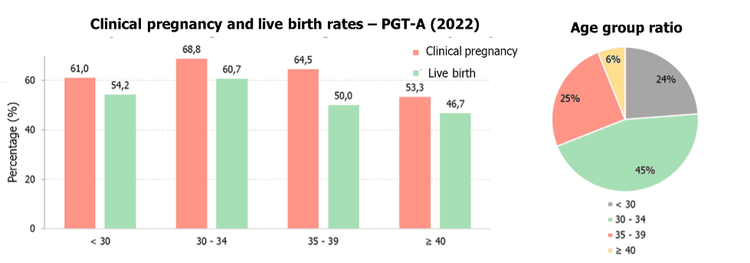
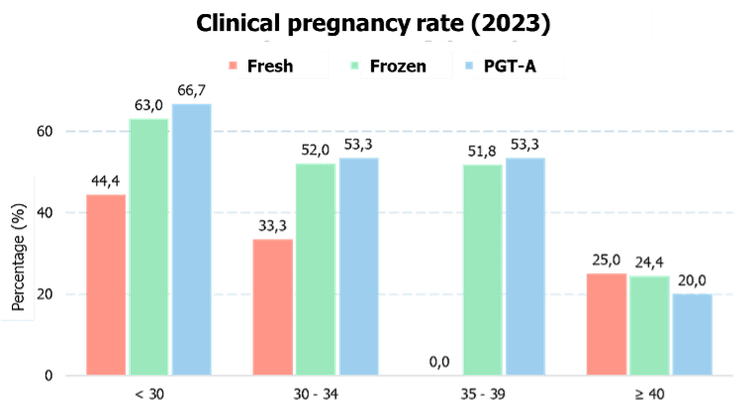
4. Important Considerations
A common misconception among IVF patients is that transferring multiple embryos increases success rates. In reality, the human uterus is naturally designed to carry a single fetus. Multiple pregnancies pose higher risks for both mother and baby, and current medical guidelines recommend single embryo transfer over multiple embryo transfers.
Many variables must be considered when evaluating IVF success rates. Couples seeking fertility treatment should ensure they understand all relevant information. Do not hesitate to ask your doctors for further clarification about success rates and treatment expectations.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.


