The science of hair: The hair growth cycle and how hair works
Hair is one of the important factors that create beauty in humans, but hair does not simply have this task but also contains many complex things inside. We all know that it not only plays an important role in the physical expressions of both men and women, but also helps to transmit sensory information as well as create gender identity in humans.
1. Origin of hair
22 weeks of pregnancy, all the hair follicles have been formed. At this stage, the fetus has about 5 million body hair follicles. In the head region, there are about 1 million hair follicles and of which about 100,000 are located on the scalp, which is the source of hair blood later on. At this time, the number of hair follicles is the largest, because we will not create new hair follicles but only gradually lose them for the rest of our lives.
Most of us will notice that scalp hair density decreases as we mature as the area of oily skin increases, but the number of hair follicles does not change. Besides, the hair follicles will be gradually lost due to aging as well as some diseases that cause hair loss.
2. Structure of hair

Cấu tạo của tóc
Simply put, hair has a fibrous structure and is made up of 70% keratin and 30% compounds including water, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and other minerals. Hair has two distinct structures namely the follicle located in the skin, and the second hair shaft that grows above the scalp that we see.
2.1. Hair follicles The hair follicle is a short section of the epidermis that extends down to the dermis. The hair follicle structure contains several layers with distinct functions. At the base of the follicle is the papilla, which contains capillaries, or small blood vessels that provide nutrients to nourish the hair follicle. The part of the hair that is likely to grow (the living part) is the bottom part that surrounds the papilla, called the hair bulb. The cells of the papillae divide after 23 to 72 hours, the fastest growth rate of any other cell in the body.
Hair has two sheaths, an inner sheath and an outer layer, which surrounds the hair follicle. These structures protect and form the hairs that grow upwards. The inner sheath runs along the hair shaft and ends below the opening of the sebaceous (oil) and sometimes apocrine (scent) glands. The outer sheath continues to run all the way down to the line below. A muscle called the pili erector muscle attaches below the gland with a fibrous layer around the outer sheath. When this muscle contracts, it makes the hair stand up and also causes the sebaceous glands to secrete oil.
The sebaceous gland is very important because it produces sebum for the hair and skin. After puberty our bodies produce more sebum but as we age we start to produce less sebum. Women produce much less sebum than men.

Melanin
2.2. Hair shaft The hair shaft is made of a tough protein called keratin and is made up of three layers. This protein is the dead layer of protein, so the hair you see is not a living structure. The inner layer is marrow. The second layer is the cortex and the outer layer is the epidermis. The bark makes up most of the hair shaft. The epidermis is a tight structure made up of overlapping layers of scales. The cortex and marrow contain the hair's pigment that gives it its color.
The medulla is the innermost layer of the hair, containing many keratin cells. If your hair is very thin, your hair probably won't have this layer. But don't worry, because the shine of the hair is not affected if your hair does not have a pulp layer.
The core layer is the thickest and most important layer of the hair, consisting of bundles of small fibers and the compound melanin. Melanin is a natural pigment that determines the color of hair. There are two types of Melanin: Eumelanin (black brown pigment) and Pheomelanin (red pigment). Blonde, tawny, brown, red, and black hair are due to the mixing ratio between these two types of pigments. White hair is hair that does not contain the pigment melanin.
Depending on environmental influences, genetics, and age, the percentage of melanin pigment changes in the core layer of the hair. Make your hair change from black to silver or blonde to brown. So this middle layer of hair determines the strength and color of your hair.
The cuticle is the outermost layer of the hair, consisting of layers of keratin scales stacked on top of each other. Between these layers is the KIT adhesive. The cuticle layer is also covered by an oil layer with the task of waterproofing and moisturizing the hair
When the hair is affected by the environment such as dust, UV rays or chemicals in dyes and perms. Hair straightener, shampoo, conditioner, hairspray or chlorine in the pool, KIT adhesive will be damaged, breaking the texture of the keratin flakes, causing the hair to lose its smooth shine. It should be noted that when using a hair dryer, straightening tools or combing the hair too hard and too much will damage the cuticle, make the hair dry, frizzy and dull.
3. Hair Growth Cycle
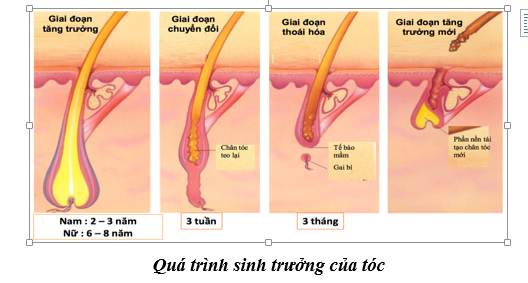
The hair on the scalp grows about 3 to 4mm per day or about 18cm per year. Unlike other mammals, human hair growth and shedding is random and not seasonal or cyclical. At any given time, a random number of hairs will be in one of three stages from growth to shedding, including anagen, catagen, and telogen.
3.1. Anagen Anagen is the active phase of hair. The cells in the hair root are dividing rapidly. A new hair is formed and pushes the hair in the hair follicle upwards. This is the part of the hair that has stopped growing or is no longer in the anagen phase and eventually comes out.
During this phase, hair grows about 1cm every 28 days. Scalp hair remains in this active growth phase for two to six years.
Some people have trouble growing hair that doesn't exceed a certain length because of a rather short hair growth phase. On the other hand, people with very long hair due to having a long active growth phase. The hair on the arms, legs, eyelashes and eyebrows has a very short active growth period of about 30 to 45 days, which explains why they are so much shorter than scalp hair.
3.2.Catagen The catagen phase is the transitional phase and is about 3% of all hairs. This phase lasts for about two to three weeks. Growth stops and the outer sheath shrinks and clings to the hairline. This is the formation of what is known as the hair follicle.
3.3.Telogen Telogen is the resting phase and usually makes up 6% to 8% of the total hair. This phase lasts for about 100 days for hair on the scalp and longer for hair on the eyebrows, eyelashes, arms and legs.
During this phase, the hair follicle is completely at rest and the hair bulb is fully formed. Pulling out a single hair during this stage will reveal a solid, hard, dry, white structure at the base. Approximately 25 to 100 telogen hairs are shed each day physiologically.
4. Function of hair
Hair is a very important feature for each person, expressing beauty, vitality and helping to make a personal mark. A smooth, fragrant hair can be painful. The hair is combed and neatly styled to help the guys look more dashing. Through hairstyle, hair color, people express their own personality, not overlapping with anyone else. It's a vehicle that helps express everyone's fashion statement.
In addition to the aesthetic effect, hair also plays an important role in the human body. Thick hair helps protect the scalp, avoiding foreign objects falling directly. In addition, according to scientists, hair also protects the scalp from direct damage from the sun. Specifically, when the sun shines down, heat and radiation will meet an obstacle - the hair, before affecting the human head.
Another lesser known use of hair and body hair is sexual attraction. Each person is attracted to a different mate pattern, in terms of length, color, position of hair, body hair. A certain amount of hair and body hair amplifies each person's unique scent, thereby increasing the chances of mate pairing. In addition, hair also has a thermoregulating effect, and the sebaceous and sweat glands in the hair follicles also help excrete and detoxify the body.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






