Indications for dialysis in acute pancreatitis
This is an automatically translated article.
Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammatory process of the pancreas with a diverse clinical presentation. In recent years, patients with acute pancreatitis are increasing, the disease is complicated, the mortality rate is high (from 20 to 50%) with multiple organ failure and infections. Patients with acute pancreatitis may be prescribed dialysis for treatment.
1. What is acute pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis is described as an acute inflammatory process in the pancreas, caused by mild to severe inflammatory damage to the pancreatic parenchyma. In mild acute pancreatitis, patients only need a short hospital stay, with few complications. If the disease is severe, it will have a complicated course, many complications and a high mortality rate.
2. Causes of acute pancreatitis
The pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis is due to elevated levels of cytokines in the blood, increased reactivity of white blood cells and blood vessel endothelium. Specific causes varied:
Alcohol abuse. Mechanical causes: Gallstones, pancreatic stones. Due to metabolic disorders, hypercalcemia (in hyperparathyroidism, thyroid tumors, ...) or hypertriglyceridemia. Complications after surgery, especially abdominal surgery near the pancreas. Complications after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Complications after liver and kidney transplantation. Due to trauma and bruising to the abdomen. Due to infection: mumps, roundworms, hepatitis Virus. Acute fatty liver in pregnant women. Due to side effects of drugs: 6MP, Sulfonamide, Ethanol, Furóemide, Oestrogen,... Due to connective tissue diseases such as necrotizing vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Schonlein Henoch,... In addition, there are up to 10% of cases of acute pancreatitis have no known cause.
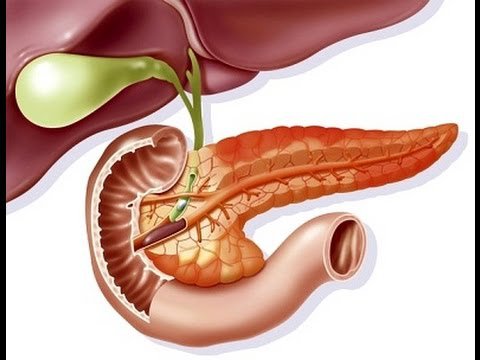
Viêm tụy cấp do nhiều nguyên nhân khác nhau gây ra
3. Clinical symptoms of acute pancreatitis
The clinical symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur very suddenly, the course is complicated, there may be mixed surgical signs, especially in acute necrotizing pancreatitis.
3.1 Functional symptoms include:
Abdominal pain: patients with acute pancreatitis have sudden pain in the epigastrium, which can spread to the chest, ribs or back. The pain is constant, intense for many hours. Vomiting: Most patients with acute pancreatitis have vomiting or nausea, initially vomiting food, then vomiting fluid. Secretion of defecation: Due to functional bowel paralysis, the patient does not defecate, the abdomen is distended and full. Shortness of breath: due to pain, peritoneal effusion, pleural effusion. 3.2 Systemic symptoms Fever: The patient usually has a mild fever, but if it is due to cholangitis caused by worms, stones or extensive pancreatic necrosis, the fever will be high. Pulse and blood pressure. In mild acute pancreatitis, the patient usually does not have serious systemic symptoms, the body is tired, but the veins, pulse and blood pressure are stable.
Patients with severe acute pancreatitis may experience shock, sweating, paleness, cold limbs, rapid pulse, mental sluggishness, and low blood pressure. The patient may feel agitated or lethargic. Bruises appear on hands and feet.

Tụt huyết áp do viêm tụy cấp nặng
3.3 Physical symptoms The symptoms of acute pancreatitis are clearly seen in the abdomen:
The abdomen is evenly distended, sometimes more distended above the navel. The hard plaque above the umbilicus can be palpated in the epigastrium, is not mobile, is painful, and sometimes spreads to the two areas below the ribs. Pain in 1 or 2 flanks on both sides. Symptoms of jaundice, with hepatomegaly if the cause of acute pancreatitis is related to the gallbladder or liver. In case of severe necrotizing pancreatitis, bruises are seen under the skin around the navel or on both sides of the ribs.
4. Treatment of acute pancreatitis
Principles of treatment of acute pancreatitis is early, aggressive treatment and close monitoring of: circulatory, respiratory, liver and kidney function and multi-organ failure. Patients with severe acute pancreatitis require intensive care in the intensive care unit.
4.1 Emergency management and transport Patients with acute pancreatitis need urgent medical care, perform:
Insert 1 - 2 peripheral lines of fluid replacement 3 - 4 liters of isotonic saline, insert a nasogastric tube if vomit. Give 1g of paracetamol intravenously over 15 minutes for pain relief. Ensure breathing.

Đảm bảo hô hấp khi chuyển bệnh nhân viêm tụy cấp đi cấp cứu
4.2 Hospital treatment First, general resuscitation measures should be taken such as: circulatory resuscitation, respiratory resuscitation, renal resuscitation, pain resuscitation, antibiotic use, intravenous nutrition. In particular, patients with acute pancreatitis need continuous dialysis throughout the course of treatment. Dialysis is indicated in patients with severe acute pancreatitis coming early in the first 72 hours, or in patients with multiple organ failure in late disease. Perform continuous veno-venous dialysis with a replacement volume greater than 45 ml/kg body weight/hour. In addition, treatment of percutaneous abdominal drainage when patients with acute pancreatitis have outbreaks located in the omentum omentum, prerenal space, spreading along the colonic groove to the pelvic fossa or behind the peritoneum. Patients with acute pancreatitis without stones are indicated for abdominal fat reduction surgery to reduce pressure, which can be combined with surgery for acute intra-abdominal bleeding, pancreatic abscess, pancreatic pseudocyst,... Depending on the cause of acute pancreatitis that prescribe appropriate treatment of the cause. Thus, the indication for dialysis in acute pancreatitis is very important, in addition, it is necessary to combine symptomatic treatment and treatment of the cause to achieve the best effect.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
This article is written for readers from Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.