Written by a Doctor from the Laboratory Department - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) account for a high proportion of infectious diseases. About thirty different STIs have been identified, caused by various pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites, transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact.
1. Overview of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Each year, WHO estimates there are millions of new cases of sexually transmitted diseases, of which about 357 million cases are related to at least 1 of 4 disease-causing agents: Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Treponema pallidum and Trichomonas vaginalis.
Each disease has different manifestations and health impact levels. If not properly diagnosed and treated, these diseases can lead to serious complications such as infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, urethral obstruction, tumors... Among them, HIV/AIDS, referred to as the "disease of the century," is an extremely dangerous sexually transmitted disease that has taken the lives of hundreds of millions of people.
Sexual behaviors include vaginal intercourse and unhealthy sexual relationships such as anal or oral intercourse... In Vietnam, the reluctance to seek medical examination and treatment as well as lack of knowledge about diseases among some people with venereal diseases makes their condition worse.

2. Some Common Sexually Transmitted Diseases Today
2.1 Genital Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
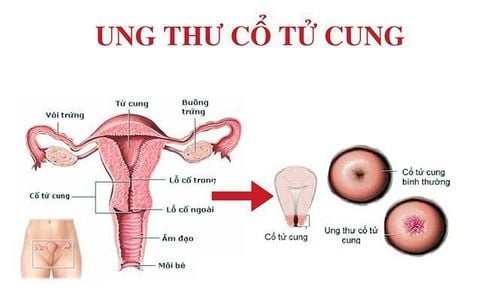
HPV is a type of virus that causes papillomas in humans and is one of the leading sexually transmitted diseases. Chronic high-risk genital Human Papilloma virus infection causes cervical cancer.
How many types of HPV are there?
There are more than 40 HPV strains that can cause disease in the genital area and anus. Among them, 15 HPV strains such as types 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 58, and especially types 16 and 18, are high-risk types commonly found in the cervix that can cause cancer ranging from cervical cancer to anal cancer and other genital organs. The Human Papilloma virus infection rate is about 10%, but this result varies depending on the region and country in the world.
In Vietnam, Human Papilloma virus infection rates range from 2% to 19.57%, with rates in Hanoi from 2% to 9.73%, in Hue from 0.9% to 19.57%, in Ho Chi Minh City from 10.82% to 12%, and in Can Tho from 3.3% to 10.9%. A statistic performed at Vinmec Da Nang Hospital shows that the Human Papilloma virus infection rate is 11.2%. Notably, the infection rate of the two types 16 and 18 accounts for up to 5.1%.
Does HPV cause cancer?
Cervical cancer is the most common type of cancer caused by HPV. In addition, patients may also suffer from other types of cancer such as vulvar, vaginal, penile, and anal cancer. Some rare cases such as oropharyngeal cancer may also occur.
How long does HPV persist in the human body?
The virus invades the cervical epithelium, creating cell changes, and this progression lasts from 10 to 20 years with manifestations ranging from simple inflammatory lesions to epithelial neoplasia, in situ cancer, and invasion. Therefore, cancers are often detected after many years to decades of living with HPV. There is no way to know if a person infected with HPV has the potential to develop cancer. Therefore, early testing for Human Papilloma virus is necessary, helping to increase prevention, early treatment of cervical lesions to reduce the mortality rate of the disease, and implement Human Papillomavirus vaccine in young women. Other cancers: are also better treated if detected early.
Less dangerous strains can cause warts on the feet (especially the soles), genital warts. In some cases, warts may appear several weeks to several months after sexual contact with an infected person.
Regular health check-ups and tests are essential for the diagnostic process of doctors for patients.
2.2. Gonorrhea
According to statistics from health authorities, the group of sexually transmitted infections currently has a tendency to increase, with gonorrhea considered one of the leading diseases (the newest number of cases is 56,259 compared to 14,000 in 2017). The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the causative agent. The disease is found in people with unhealthy sexual behaviors through vaginal, anal, or oral routes. Some cases are transmitted from mother to child during normal vaginal delivery.
Manifestations and symptoms of gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is common in both men and women. The manifestation of the disease in both genders also differs.
In men, the symptoms of gonorrhea are very easy to recognize. After being infected with gonorrhea from 2-7 days, there will be clinical manifestations such as painful urination, frequent urination, urinating multiple times. In addition, there are other symptoms such as: discharge of pus when urinating, fatigue and symptoms of mild fever, appearance of inguinal lymph nodes. Pain around the pelvic area, lower back, pain in the head of the penis (pain during sexual intercourse). Appearance of blood in urine. Especially, when the disease becomes severe, there will be a lot of pus discharge in the early morning or after defecation (swollen inguinal lymph nodes make it increasingly difficult for men to urinate).
In women, gonorrhea is often very difficult to recognize, with symptoms often unclear and easily confused with other diseases. Gonorrhea often occurs quite discreetly, with symptoms seemingly similar to the manifestations of vaginal inflammation, cervicitis, or urethral infection. In addition, there are other symptoms such as: Pain around the pelvic area after intercourse. Gonorrhea in women is often detected when the disease has progressed to a severe stage with severe inflammation, typically the phenomenon of increased discharge accompanied by lemon-yellow pus, thick pus with a foul odor. Women may also experience additional signs of difficult urination, burning urination, and vaginal pain.
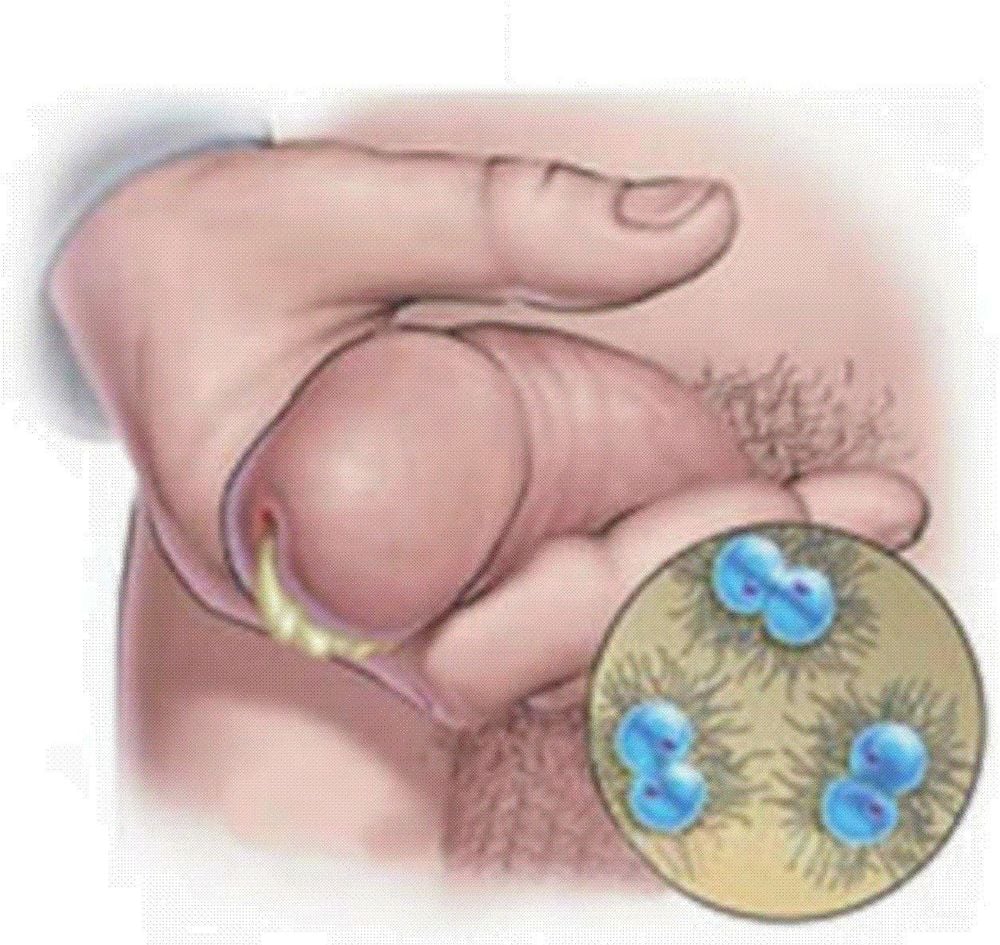
How dangerous is gonorrhea?
When men experience symptoms of gonorrhea without early remedies, it can cause inflammation of the urethra and testicles, leading to bloody ejaculation. In addition, the penis may become swollen, reducing the ability to have intercourse. The disease can spread to other parts causing dangerous complications such as prostatitis, sperm deformity, testicular atrophy, increased risk of infertility, or more severely, permanent infertility if not treated promptly.
For women, gonorrhea easily causes vaginitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and most dangerously, inflammation of the ovaries, inflammation of the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of infertility.
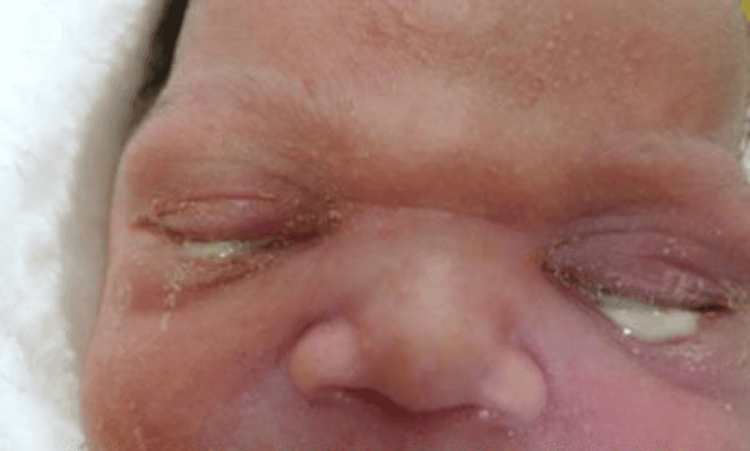
Pregnant women with gonorrhea will have risks such as miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth. The most dangerous effect of gonorrhea on newborns during normal delivery is that gonorrhea bacteria can enter the baby's body through the baby's eyes and cause conjunctivitis, causing the child to be born with congenital gonorrhea that can lead to permanent blindness... particularly dangerous is that gonorrhea bacteria can enter the brain and cause meningitis in children.
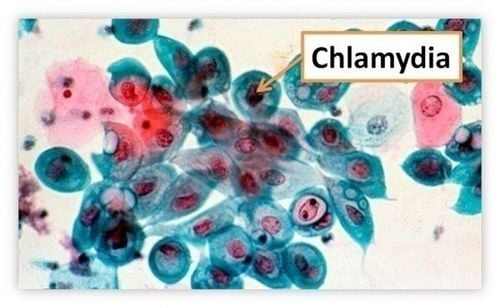
3. Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common STD that both men and women can contract. You can get chlamydia if you have unsafe sex with someone who has chlamydia through vaginal, anal, or oral routes. Notably, you can still get chlamydia even if your male partner does not ejaculate.
Manifestations of Chlamydia
Most people with chlamydia have no symptoms. Even when not causing symptoms, chlamydia can still damage your reproductive organs.
Symptoms in women may include abnormal pain, abnormal vaginal discharge such as discharge with a foul odor, burning sensation when urinating, or bleeding when not during menstruation, usually appearing after several weeks since having sex with an infected partner.
Symptoms in men may include:
- Penile discharge
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles (this symptom is less common).
Men and women can also be infected with chlamydia in the rectum. This phenomenon is due to anal sex or transmission from other infected areas (such as the vagina). Although these infections are often asymptomatic, they can still cause
- Rectal pain;
- Discharge
- Bleeding.
How dangerous is chlamydia?
The initial damage from chlamydia is often undetectable. However, chlamydia can cause serious health problems.
- If you are a woman, untreated chlamydia can spread to your uterus and fallopian tubes (the tubes that carry fertilized eggs from the ovary to the uterus). This can be the cause of pelvic inflammatory disease, leading to pain in the abdomen and pelvic area and can cause long-term pelvic pain. Even if there are no symptoms initially, the disease can still cause permanent damage to your reproductive organs and cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
- If you are pregnant and have chlamydia, the disease can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth. Your child may be born with eye infections or pneumonia due to Chlamydia. The disease can also cause premature birth
- Men in some rare cases can experience infertility
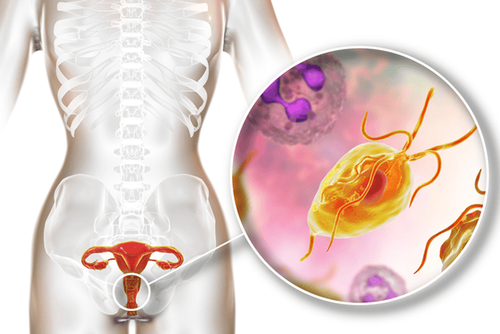
4. Trichomonas vaginalis
The disease, also called Trichomoniasis, is a sexually transmitted disease (STD), the most common. In the United States, an estimated 3.7 million people are infected. Although symptoms vary, most people infected with this parasite cannot know they are infected, and only about 30% show symptoms. This may be due to factors such as age and health. Infected people without symptoms can still transmit to others.
This disease is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. During sexual intercourse, the parasite typically spreads from the penis to the vagina or vice versa. It can also spread from one vagina to another.
Manifestations of Trichomoniasis
This disease is more common in women than men. Older women have a higher risk of contracting trichomoniasis. Symptoms of trichomoniasis can range from mild irritation to severe inflammation. Symptoms, if any, will appear within 5 to 28 days from the day of infection. Symptoms appear and disappear on their own.
In women, the most frequently infected areas are the vulva, vagina, cervix, or urethra. Itching, burning, redness or pain in the genitals, discomfort when urinating. Changes in vaginal discharge, for example, increased discharge with clear, white, yellowish, greenish characteristics, accompanied by an unusual fishy smell.
In men, the most infected part of the body is the urethra. Itching or irritation inside the penis, burning after urination or ejaculation, discharge from the penis.
Trichomonas infection can make sexual intercourse uncomfortable.
Infection can last for several months or even years if untreated.
How dangerous is Trichomoniasis?
Complications of trichomoniasis can increase the risk of getting or spreading other sexually transmitted diseases. For example, trichomoniasis can cause genital tract inflammation, thereby increasing the risk of HIV infection or transmission of the HIV virus to partners.
Pregnant women infected with trichomoniasis have a high risk of premature birth, and children born to infected mothers will also have a high risk of being underweight.
Trichomoniasis cannot be diagnosed based on symptoms alone. Both men and women can be examined and tested to diagnose trichomoniasis.
5. Mycoplasma Disease
The disease is caused by Mycoplasma bacteria, which have an affinity for respiratory mucosa and genital tract mucosa, causing many diseases such as: respiratory system diseases (pneumonia), joint diseases (synovitis)..., sexually transmitted diseases - urinary tract and can cause diseases affecting reproduction and the fetus during pregnancy. Especially, Mycoplasma bacteria may be the "culprit" causing infertility.
Diseases caused by mycoplasma bacteria
Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes respiratory disease,
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the causative agent of primary atypical pneumonia in humans. The main symptoms are fever, chills, sweating, severe dry cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. The disease can occur at any age but is common in children. M. pneumoniae often causes small outbreaks in spring and autumn.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes diseases in the genital - urinary tract:
Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, and Mycoplasma urealyticum (Ureaplasma) are agents of genital tract disease.
Mycoplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma genitalium cause urethritis, Bartholin's gland abscess, fallopian tube inflammation.
Mycoplasma hominis causes pelvic inflammatory disease in pregnant women, can cause miscarriage. Newborns can get pneumonia, blood infection, meningitis... due to maternal genital infection by this bacterium.
Manifestations of Mycoplasma disease in the genital - urinary tract: Usually progresses in 2 stages: acute and chronic.
Acute stage
- Men have manifestations of frequent urination, painful urination, discharge of white or yellow pus, accompanied by pain along the urethra...
- For women, at this stage, the disease manifests discreetly, not as dramatically as in men. Common manifestations are: frequent urination, painful urination, pain in the pubic area, foul-smelling discharge, pain during sexual intercourse....
Chronic stage:
- For men, when entering the chronic stage, patients often have manifestations: burning urethra, difficult urination, in the early morning, often have mucus like banana sap flowing out of the urethral opening before urinating for the first time.
- For women, the main symptom of chronic disease is still discharge, foul odor (women find it difficult to distinguish between the two stages of acute and chronic).
- To identify Mycoplasma bacteria, tests must be conducted.

Currently, the Social Disease Screening Package at Vinmec International General Hospital is trusted by many people for the following reasons:
- Equipped with the most modern medical system providing quick and accurate diagnostic results.
- Thorough, professional examination and consultation services.
- Modern, spacious infrastructure, ensuring sterile conditions.
- Patient information confidentiality.
Lam Duc Tam, Nguyen Vu Quoc Huy, (2013), "Study on the prevalence of Human Papilloma virus and factors related to cervical precancerous lesions in women aged 18-60 years old" , Medicine of Ho Chi Minh City, volume 17(1) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (2013), Ministry of Health. Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines (2015), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Cdc.gov
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.