The article was written by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist, Cardiology Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Electrolytes are substances that can dissolve in body fluids, creating ions with negative and positive charges. These minerals play a very important role in the body because they help perform nerve and muscle functions, help maintain fluid balance in the body, blood pressure and blood pH.
1. The role of electrolytes in the human body
Normally, when the body is healthy, without any pathological disorders, there is always a balance of electrical charges inside and outside the cell membrane. But if there are only small disorders of diseases, especially cardiovascular - metabolic diseases, stress or after surgery... then this balance will be broken, causing the concentration of free ions in the blood such as Ca++, K+, Na+, Cl-, Mg++... to increase or decrease suddenly.
Sodium is the main cation of extracellular fluid, playing a fundamental role in maintaining water distribution and osmotic pressure in the body's tissues. Sodium is abundant in table salt. Balancing sodium in the diet is extremely important to help the body become healthier. Normal blood sodium concentration is 135-145 mmol/l.
Potassium is the main cation of intracellular fluid, which has the function of maintaining the response to stimulation of neuromuscular cells. Potassium in the body plays a very important role, especially in the cardiovascular system, the concentration of potassium is closely related to the excitability of the heart muscle, conduction, and heart rate.
Potassium is abundant in foods such as bananas, sweet potatoes, radishes, ....
The normal concentration of potassium in the blood is 3.5 - 5 mmol / l.
Calcium plays an important role in many biological functions of the body, especially blood clotting function.
Electrolyte disorders are common in people with an unbalanced diet (eating too bland, eating too salty, abusing soft drinks, energy drinks, ...) and in people who are sick or have systemic diseases. Among them, we can mention the disorder of the two most important minerals in the group of electrolytes, Sodium and Potassium.
2. Electrolytes and Cardiac Function
The electrolytes potassium, sodium, magnesium, and calcium play a vital role in the function of the heart muscle and cardiac tissue. The movement of these ions across the cardiac muscle cell membrane causes the transmembrane voltage to exceed a threshold and generate an action potential, resulting in muscle contraction. Electrolytes carry electrical charges and are maintained at tight physiological concentrations through various mechanisms to maintain proper cardiac function.
Electrolyte imbalances: Imbalances in these electrolytes can have adverse effects on the heart, causing or contributing to arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.
Potassium imbalances are the most common electrolyte-related cause of arrhythmias. Potassium plays an important role in nerve conduction. Low potassium levels can cause relatively stable arrhythmias, while high potassium levels can rapidly lead to fatal arrhythmias. Imbalances in sodium, magnesium, and calcium also put the heart at risk for arrhythmias.
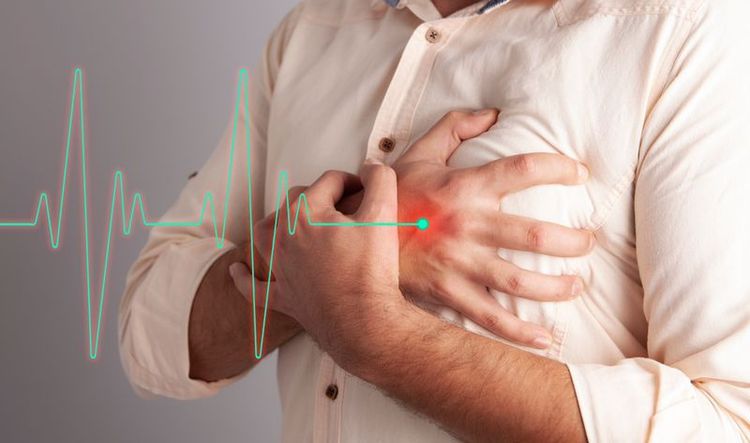
3. Symptoms of arrhythmia
Arrhythmia can make the heart's blood pumping function less effective and cause symptoms:
Pancreatic palpitations: This is the most common manifestation of arrhythmia. You may have a feeling of "missing", or the feeling that your heart stops for a few seconds, often followed by a strong "drumming" beat in your chest. Along with the symptoms of palpitations, the patient may faint or feel dizzy. These are often signs that lead the patient to see a doctor.
Feeling that the heart is beating faster or slower than normal.
Feeling tired, short of breath: Prolonged arrhythmia will reduce the heart's pumping and pumping efficiency, causing you to have symptoms of shortness of breath and fatigue.
Chest pain: Is one of the dangerous signs of arrhythmia, especially when it appears on the background of existing cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction...

4. Diagnosing Electrolyte Disorders
A blood test can accurately measure the levels of electrolytes in your blood. Your doctor may also perform a physical exam and order other tests to confirm the diagnosis.
5. When to see a doctor?
When the above symptoms appear, you should see a doctor soon to prevent dangerous health events. In some cases, arrhythmia can be harmless, but most of the time it is a manifestation of a serious medical condition that threatens your life regardless of the cause, including electrolyte disturbances. Therefore, if you feel any abnormalities in your heart, it is best to go to a medical facility to be examined and detect cardiovascular problems early. Especially in the following cases:
- Fast or slow heartbeat accompanied by a feeling of palpitations, dizziness or fainting.
- Arrhythmia accompanied by shortness of breath, pain in the chest, neck, shoulders, arms or back.
- Arrhythmia occurs when you first use a certain medication.
- Arrhythmia occurs simultaneously with other symptoms such as weight loss, prolonged fatigue and palpitations accompanied by headaches and sweating...

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.