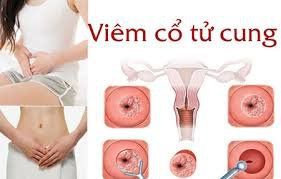
Endometritis is a prevalent gynecological disease among women of reproductive age, particularly those who have recently given birth. If not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can adversely affect a woman's reproductive health in the future.
1. Endometritis After Childbirth
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. If an egg does not meet sperm, this endometrium sheds and prepares for the next menstrual cycle. However, when conception occurs, the endometrium becomes the site for implantation of the fetus.
Endometritis is the inflammation of the endometrium, usually caused by bacteria, fungi, or parasites. Women of reproductive age are at risk for this disease. The risk increases for those who have recently given birth, suffered a miscarriage, or undergone an abortion.
While endometritis is typically not life-threatening, early treatment is crucial. Untreated infections may lead to serious complications, including infertility, pelvic peritonitis, abscess formation in the pelvis or uterus, as well as sepsis and septic shock, which can be life-threatening.
2. Causes of Endometritis
2.1 Causes in Postpartum Women
- Postpartum women may experience several gynecological issues, such as vaginitis, urethritis, cervicitis, and gonorrhea, chlamydia…. If these diseases are not treated promptly, bacteria can spread to the uterus, leading to postpartum endometritis.
- Sometimes, lochia (postpartum vaginal discharge) can accumulate in the uterus, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth, leading to endometritis.
- Failing to maintain proper hygiene in the genital area, especially with a significant amount of lochia, can allow harmful organisms to enter the vagina and cervix, resulting in endometritis.
- Damage to the genital area during delivery can heighten the risk of infection and subsequent endometritis.
- Other Factors: Retained placenta or membranes, amniotic infections, non-sterile uterine procedures, and non-sterile removal of the placenta.
2.2 Causes in Other Women
- Unsafe sexual practices that lead to sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia and gonorrhea.

- Tuberculosis.
- Disruption of the natural balance of vaginal bacteria.
- Complications following a miscarriage.
- Medical procedures such as hysteroscopy, the insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD), or dilation and curettage.
- Poor genital hygiene.
- Concurrent pelvic issues, such as cervicitis.
3. Symptoms of Endometritis
Endometritis is categorized into two stages: Acute Endometritis and Chronic Endometritis.
3.1. Acute Endometritis Symptoms
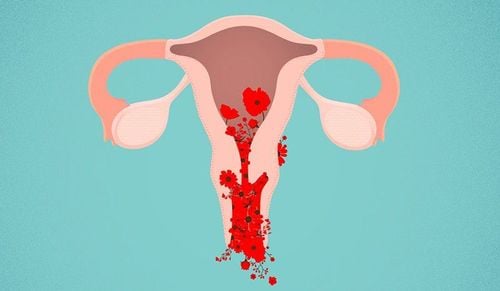
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Abnormal Vaginal Discharge: Discharge that may appear green, yellow, brown, or contains pus, has a foul odor, or is mixed with blood (This is often seen in cases involving retained placenta).
- Fever: Body temperature typically does not exceed 38°C. Patients may also experience discomfort, headaches, and dizziness. If the infection spreads to the uterine muscle layer, body temperature may rise further, and systemic symptoms may become more severe.
- Discomfort when defecating.
- Initial dull pain in the pelvis or lower abdomen can gradually intensify.
3.2. Chronic Endometritis Symptoms
- Abdominal distension.
- Vaginal discharge may be mixed with blood and changes in quality and odor.
- Constipation, feeling of discomfort, lower abdominal pain.
4. Diagnosis and Treatment of Endometritis
If you notice symptoms of endometritis, it’s crucial to visit a specialized medical facility for a prompt examination and treatment.
To diagnose endometritis, a doctor will perform a clinical examination, focusing on the abdomen, uterus, and cervix. Subsequent diagnostic tests may include: Sample collection or culture of uterine tissue to identify the bacteria causing the infection, endometrial biopsy, endoscopy, microscopic examination, blood tests (measure white blood cell count and the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation).
The treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause, the severity of the disease, and the patient's overall health. Patients will typically be prescribed antibiotics per the doctor’s instructions. Severe or complicated cases may require intravenous treatment and hospitalization. Women experiencing postpartum endometritis often follow this outline.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend uterine curettage; however, this procedure carries risks and potential complications related to infertility.
5. Prevention Measures for Endometritis
To reduce the risk of endometritis after childbirth or gynecological procedures, ensure that doctors use sterile equipment during delivery or surgery by choosing reputable hospitals staffed by experienced medical professionals.
Doctors may prescribe antibiotics for mothers undergoing cesarean sections or pre-surgical procedures to prevent infection.
Practice safe sex (using condoms), and schedule regular check-ups to facilitate the early diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases. Follow treatment regimens as recommended by your doctor.

- Maintain proper hygiene in the genital area.
- Follow a balanced diet and lifestyle, avoiding excessive consumption of spicy and greasy foods.
Endometritis is a common condition following childbirth. While it is generally not life-threatening, untreated endometritis can lead to complications such as miscarriage, difficulty conceiving, or even infertility. Therefore, it is essential for women to seek examination and appropriate treatment at specialized facilities when symptoms arise.
Vinmec International General Hospital is highly esteemed in obstetrics and gynecology, featuring a team of leading specialists renowned for their expertise and experience, along with modern, advanced equipment and facilities. The hospital offers a basic gynecological examination and screening package, enabling clients to detect inflammatory diseases promptly, facilitating easier and more affordable treatment. Screening for early detection of gynecological cancers, such as cervical cancer.
Importantly, Vinmec prioritizes the confidentiality of patients’ personal information. The hospital environment is respectful and supportive, allowing women to discuss sensitive issues in obstetrics and gynecology without hesitation.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.