MSG allergy is a condition that many scientific studies have indicated lacks sufficient evidence to confirm a connection between MSG and severe allergic reactions. Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is a food additive used to enhance the flavor of dishes. Despite its widespread use, many people have long believed that MSG can cause symptoms and side effects resembling allergic reactions.
1. What is MSG Allergy?
Monosodium glutamate (MSG), commonly known as a flavor enhancer, is a popular food additive used to enhance the taste of various dishes, canned foods, soups, and processed meats.
Although MSG is classified as safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), similar to salt and pepper, reports of "MSG-related symptoms" or "Chinese Restaurant Syndrome" have increased over time. From the perspective of most doctors, this condition is not considered a true allergy because the symptoms that occur after consuming MSG differ from typical allergic mechanisms and are not linked to abnormalities in the immune system.
2. Signs of MSG allergy
Some individuals who are allergy to MSG may experience symptoms such as:
- Headache
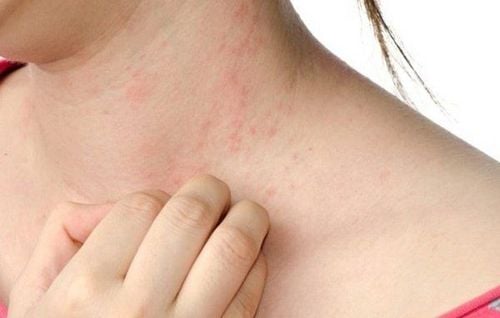
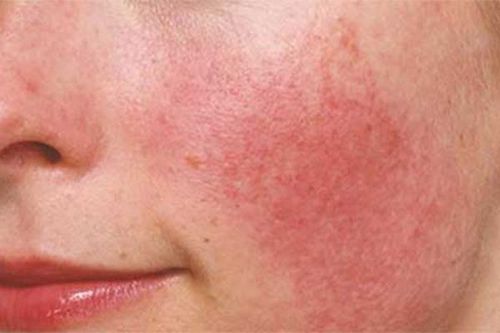
- Skin rash
- Mild chest pain
- Nausea
- A numbness or burning sensation on the face, neck, and other areas, particularly around the mouth
- Facial muscle tightness or swelling
- Sweating
- Digestive disorder
- Mood changes: Altered serotonin levels, a key neurotransmitter governing mood and emotions, may lead to depression
- Fatigue
- MSG has the potential to harm T lymphocytes and affect DNA integrity.
- Excessive MSG consumption over a prolonged period can cause kidney damage and increase the risk of "MSG intoxication syndrome."
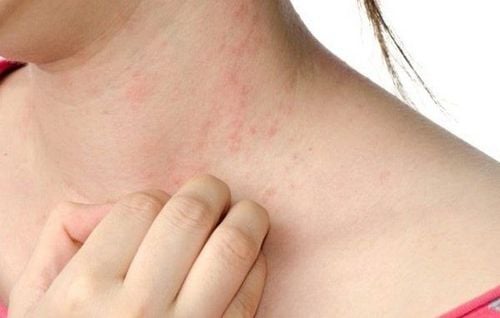
Although some studies have not definitively confirmed the link between MSG and these symptoms, some sensitive individuals may experience short-term reactions to MSG. These allergy symptoms are usually mild and do not require medical treatment.
3. Diagnosis and treatment
When a doctor suspects that a patient is allergic to monosodium glutamate (MSG), they will ask detailed questions about the foods the patient has consumed in the past two hours, especially dishes commonly containing MSG.
If signs of MSG allergy appear, the following steps should be taken immediately:
Mix a glass of warm water with lemon and salt (without sugar), and drink it right away. Then, find a cool, well-ventilated place to lie down and rest for about 15-20 minutes. Vomiting, if possible, can help improve the situation.
Drink plenty of warm water, which has diuretic effects, aids in detoxification, and helps the body quickly and effectively eliminate toxins.
Never take medication without a doctor's prescription. If a person with MSG allergy requires emergency hospitalization, remember to bring the medication packaging to provide the doctor with necessary information for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
If initial measures for mild MSG poisoning symptoms do not improve the condition, take the patient to the hospital for a timely medical examination and treatment.
It is best to temporarily stop using MSG for a period once this allergy is identified.
As mentioned above, most cases of MSG allergy are mild and resolve on their own. Treatment mainly focuses on limiting the use of MSG and alleviating individual symptoms during episodes, such as using pain relievers for headaches.
Although anaphylactoid shock due to MSG is rare, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction and require immediate emergency care if symptoms such as chest tightness, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat occur.

4. Precautions for people with MSG allergy
The best way to treat a food allergy is to avoid consuming the allergenic food. However, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) states that MSG, a common allergen, naturally occurs in many foods, especially protein-rich foods such as:
- Meat
- Poultry
- Cheese
- Fish
In addition, MSG can also be found in many other foods, such as:
- Dried meat: beef jerky, chicken jerky, etc.
- Meat extract: a common ingredient in many products.
- Broth: made from bones, poultry, etc.
- Hydrolyzed protein: used as a binder, emulsifier, or flavor enhancer in food.
- Maltodextrin: partially hydrolyzed plant starch, commonly used as a food additive.
- Modified starch: a derivative of starch.
For individuals with MSG allergies, it is best to minimize the consumption of packaged and processed foods. Instead, prioritize fresh foods that contain naturally occurring sweeteners, such as fruits, fresh vegetables, and organic meats.
For those with a complex medical history or a predisposition to allergies, it is advisable to limit the use of MSG. To assess MSG sensitivity, individuals can follow an elimination diet by removing MSG and other allergens temporarily
Then, gradually reintroduce each food back into the diet and carefully observe the body's reactions. This testing method helps us accurately identify foods that do not suit our bodies.
In conclusion, monosodium glutamate (MSG) is a food additive that has been widely used for decades. Although there are reports of negative reactions to foods containing MSG, current scientific studies do not yet provide sufficient evidence to confirm a direct link between MSG and these symptoms.
While rare, a small number of people may experience MSG allergies and short-term reactions. Generally, most MSG allergy symptoms are mild and do not require medical treatment. The most effective way to prevent allergic reactions is to avoid foods suspected of containing MSG.
If any unusual symptoms occur, it is advisable to visit a doctor and seek their advice for specific guidance.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
Reference source: Healthline.com; Mayoclinic.org
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.