Neometin is a medication used to treat vaginitis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, and Candida albicans, as well as co-infections of Trichomonas and yeast. Additionally, Neometin suppositories are effective in treating vaginitis caused by multiple combined pathogens. The medication is also used for prophylaxis five days before and after gynecological procedures.
1. Is Neometin Suppository Effective?
Each Neometin vaginal tablet contains the following active ingredients:
Nystatin: 22.73 mg
Metronidazole: 500 mg
Neomycin sulfate: 108.3 mg
Excipients: Sufficient quantity for one tablet
Dosage form: Uncoated tablet, vaginal suppository
Nystatin is a polyene antifungal antibiotic effective against molds and yeasts, including Candida spp. It is used to treat fungal infections of soft tissues and mucous membranes, such as oral thrush, pharyngitis, and vaginitis.
Nystatin has poor gastrointestinal absorption and is not absorbed through mucous membranes or the skin. It is primarily excreted unchanged in the feces via the gastrointestinal tract.

2. Indications of Neometin
Indications of the active ingredients in Neometin vaginal suppository:
• Nystatin: This is an antifungal antibiotic with both fungistatic and fungicidal activity. Its mechanism of action involves binding to sterols in the fungal cell membrane, altering membrane permeability and causing leakage of intracellular components, ultimately leading to fungal cell death.
• Metronidazole: A derivative of 5-nitroimidazole, metronidazole exerts its antibacterial effect by converting into a cytotoxic intermediate within parasites. It binds to the helical structure of DNA, breaking the strands and leading to bacterial death. Metronidazole is effective against both intestinal and extraintestinal amoebiasis, including acute and chronic forms. However, its efficacy in chronic amoebiasis is lower due to limited penetration into the colon. It is also active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia, anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria such as Bacteroides, Clostridium, and Helicobacter, but it is ineffective against aerobic bacteria. The nitro group in metronidazole is reduced by electron transport proteins or ferredoxin, and this reduced form disrupts DNA structure, leading to bacterial and protozoal death.
• Neomycin sulfate: This component exhibits bactericidal activity by inhibiting protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria. Its spectrum mainly targets Gram-negative bacteria. Neomycin is poorly absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract and, due to its high toxicity to the kidneys and auditory nervous system, it is mainly used topically (often in combination with bacitracin and polymyxin) or orally to eliminate aerobic bacteria in the gut before digestive surgery.
Neometin is prescribed for the treatment of conditions caused by the following pathogens:
• Vaginitis caused by common pyogenic bacteria.
• Vaginitis due to co-infection with Trichomonas vaginalis and Gardnerella vaginalis.
• Vaginitis caused by Candida albicans.
• Vaginitis due to co-infection with Trichomonas and yeast.
• Vaginitis caused by multiple combined pathogens.
• Prophylaxis for five days before and after gynecological procedures.
3. Adverse effects of Neometin
Some unwanted effects may occur during the use of Neometin vaginal suppositories. Common side effects include:
• Vaginal itching
• Skin rash
• Mild swelling
• Dizziness
• Shortness of breath
• Stomach pain
• Nausea and vomiting
• Burning sensation inside the vagina
Individual responses to Neometin may vary, and you may experience side effects not mentioned in this list. If any unusual symptoms occur, consult your doctor for appropriate management. Additionally, if these side effects persist or worsen, discontinue use and visit a gynecology specialist for further clinical and laboratory examinations to determine the cause.

4. Usage and Dosage of Neometin
4.1. How to Use Neometin
Before using the medication, carefully read the instructions provided on the packaging. If you have any questions, consult your doctor for detailed guidance. The method of use depends on the dosage form.
How to use Neometin based on its formulation:
• Oral tablets: Take the medication directly with water. Swallow the tablet whole to ensure its therapeutic effect. In cases of oral fungal infections, your doctor may advise dissolving the tablet in your mouth.
• Oral solution: Use a medical measuring device to measure the prescribed dose. The solution can be taken directly or diluted with water.
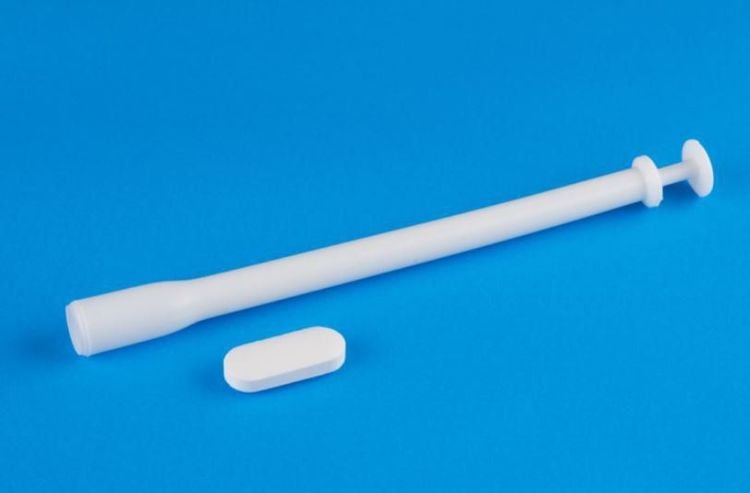
• Vaginal suppository: Wash your hands and clean the vaginal area before inserting the suppository. To remove the tablet from the aluminum packaging, cut along its length with scissors. Soak the suppository in water for 20–30 seconds before inserting it into the vagina. Limit movement for 10–15 minutes after insertion. Vaginal suppositories should be placed deep inside the vagina using an applicator. After each use, clean and dry the applicator. This form of medication can be used during menstruation.
• Topical ointment: Clean your hands and the affected skin area before applying the medication. Apply a small amount and gently massage it onto the infected area. Your doctor may provide specific instructions on how to use the ointment. Follow medical advice strictly to achieve the best treatment results.
Before handling Neometin suppositories, ensure your hands and intimate area are clean to prevent contamination. After applying the medication, wash your hands with soap.
It is recommended to use the vaginal suppository at night before bedtime when movement is minimal. This allows the medication to penetrate deeply into the vagina and be fully absorbed for optimal effectiveness. The dosage should be determined based on the severity of the infection, so consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis before starting treatment.
4.2. Dosage of Neometin
The following dosage recommendations are for common infections. If you experience any unusual symptoms, consult your doctor for appropriate dose adjustments.
Standard dosage:
• 1 suppository per day
• Treatment duration: approximately 10 consecutive days
• In severe cases, the dose may be increased to 2 suppositories per day
If menstruation occurs during treatment, consult your doctor for advice. Do not discontinue the medication without medical guidance, as it may lead to recurrent infections.
Currently, there is no established dosage for children. Parents should not administer Neometin to children without a doctor’s approval.
4.3. What to Do in Case of Missed or Overdosed Doses
If you miss a dose:
• Skip the missed dose if it is close to the time for your next scheduled dose. Take the next dose as planned.
• Do not double the dose to compensate for a missed one, as this may reduce the effectiveness of treatment.
In case of overdose:
• Symptoms: There are no reported cases of overdose symptoms.
• If you accidentally take an excessive dose and experience severe side effects, seek immediate medical attention for proper management.

5. Interactions of Neometin
Neometin vaginal suppositories may reduce the effectiveness of certain other vaginal suppositories and topical medications. To minimize this risk, your doctor may recommend adjusting the frequency or dosage of each medication.
Additionally, Neometin may interact with the following drugs:
• Anticoagulants: Lithium, Warfarin, Disulfiram, Phenytoin, etc.
• Antifungal medications: Metronidazole, Nystatin, etc.
Consult your doctor for a complete list of potential drug interactions before using Neometin.
6. Precautions When Using Neometin
• Pregnant women: Metronidazole has been reported to pose a risk of fetal abnormalities when used during the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, Neometin should not be used unless absolutely necessary.
• Breastfeeding mothers: The drug may be excreted in breast milk, so it should be discontinued during breastfeeding.
• Drivers and machine operators: Dizziness is a possible side effect, which may impair the ability to drive or operate machinery. Use caution in such cases.
• Avoid vaginal intercourse while using Neometin suppositories.
• If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue the medication immediately and take appropriate measures.
Neometin is an effective treatment for vaginitis caused by various pathogens. To ensure safe and effective use while avoiding unwanted side effects, carefully read the instructions or follow your doctor’s guidance.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.