The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually transmitted virus. HPV can lead to several serious health conditions in males, such as genital warts, anal cancer, and penile cancer.
1. What is HPV ?
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) is a virus that spreads through sexual contact or skin-to-skin contact.
There are currently over 100 strains of HPV. Most HPV strains are harmless, asymptomatic, and will resolve spontaneously. However, approximately 40 strains of HPV can cause diseases in the genital and anal regions.
Some low-risk strains, such as HPV-6 and HPV-11, can lead to genital warts; HPV-2 and HPV-1 cause warts on the hands and feet. There are 15 high-risk HPV strains, particularly strains 16 and 18, that can lead to precancerous lesions, cervical cancer, anal cancer, and cancers of other genital sites.
2. What diseases does HPV cause in males?
Most males infected with HPV do not exhibit any abnormal health signs. However, certain strains of the HPV virus in males can lead to several serious health conditions such as:
2.1 Genital warts
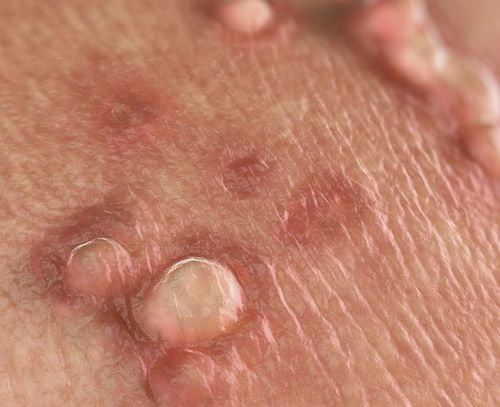
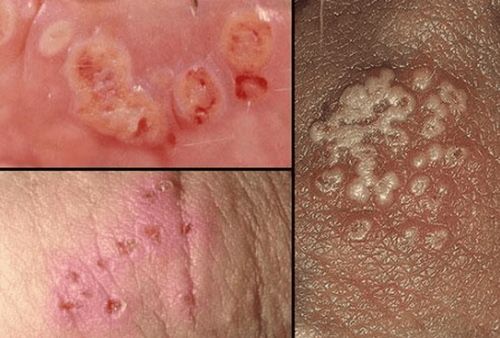
Genital warts (also known as condylomata acuminata) are visible lesions located in the genital area of males: the glans, shaft of the penis, urethral opening, scrotum, pubic region, and perianal area… caused by infection with human papillomavirus (HPV). Furthermore, warts may also manifest in the oral cavity or throat of individuals who engage in oral sex with an infected partner.
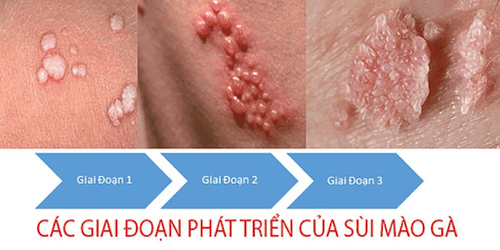
Some warts that are close to each other can form a shape resembling cauliflower, causing itching or discomfort in the genital area and leading to bleeding during sexual intercourse.
Condylomata acuminata appear due to HPV-6, HPV-11, and other strains such as HPV-16, HPV-18, HPV-31, HPV-33, HPV-35, …
For treatment, patients may use medications, cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen, or surgical excision of the warts. However, patients should consult with a medical specialist to assess the condition and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
2.2 Anal Cancer
It is one of the most severe complications associated with HPV virus infection in males, caused primarily by HPV strains 16 and 18. Men with a history of genital warts are at significantly increased risk for developing anal cancer.
Many men may not exhibit clear symptoms of anal cancer, aside from mild pain and swelling. Others may experience certain symptoms such as: rectal bleeding, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, anal swelling or pain, itching, or additional bleeding.
To diagnose the condition, patients may undergo anal cytology tests and biopsy to identify any abnormal cells.
2.3 Penile Cancer
Some patients with penile cancer may not exhibit clear symptoms until the disease has progressed to a severe stage. If there are ulcers, color changes, or nodules present on the penile tissue, the patient should seek evaluation at reputable medical facilities. To determine if penile cancer is present, a penile tissue biopsy is necessary.

3. Methods to Reduce the Risk of HPV Infection
- Vaccination against HPV
- Maintaining a monogamous relationship with a single partner and minimizing the number of sexual partners.
- The correct use of condoms is an effective protective measure against sexually transmitted infections.
Males should begin vaccination with the 9vHPV, 4vHPV, or 2vHPV vaccine before the age of 15 and receive two doses of the HPV vaccine according to the recommended immunization schedule (0, 6 - 12 months) or three doses of the HPV vaccine according to the recommended schedule (0, 1 - 2, 6 months), which is considered complete vaccination.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.