1. What is Bruising Under the Skin?
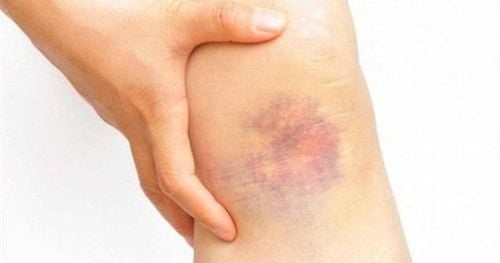
Bruising under the skin is a condition where the blood vessels are damaged, causing blood to seep into the surrounding tissues, and creating patches of blue or purple bruises.
The phenomenon of bruising can cause irritation and inflammation, depending on the location and size of the bruise. Some signs to recognize bruising under the skin include:
- Swelling or redness (blue or purple bruises);
- Aching or painful sensations;
- Warmth or slight heat.
Additionally, you may experience other signs not mentioned here. However, it is important to note that there are many cases where unexplained bruises appear on the skin (especially on thinner skin areas like the thighs or upper arms). These individuals may not have experienced any bumps or strenuous activities, may not be taking any medications, and may even notice the appearance of bruises upon waking up. Experts warn that these "mysterious" bruises could indicate serious underlying health issues, so individuals should be cautious.
2. Causes of Bruising Under the Skin
Any physical impact, from minor bumps to car accidents, sports injuries, etc., can lead to bruising under the skin. Additionally, other factors may contribute to this condition, including:
2.1. Nutritional Deficiencies
When lacking certain vitamins, the body can develop bruises. Some vitamins that can be deficient include:
- Vitamin B12: contributes to red blood cell production;
- Vitamin K: plays a role in synthesizing blood-clotting factors;
- Vitamin C: promotes cell production;
- Vitamin P: participates in collagen production, increasing blood vessel thickness to withstand blood flow pressure.
If there is a deficiency in these vitamins, blood vessels can become weak and fragile, making it easier to form bruises.
2.2. Use of Blood-Acting Medications
The use of certain medications that affect blood can also lead to bruising. Some related drugs include: antidepressants, pain relievers, iron-containing medications, and asthma medications. Notably, one common medication that causes this is Aspirin.
Therefore, if you are taking a medication and notice bruising, it is advisable to consult a doctor for timely adjustment and to prevent internal bleeding.
2.3. Blood Disorders
Many studies indicate that blood disorders (such as inherited clotting disorders, decreased platelet count, etc.) can lead to bruising. These cases may come with additional symptoms like leg swelling, leg pain, gum bleeding, nosebleeds, or prominent blood vessels visible under the skin. If you notice these signs, it is essential to seek medical attention for timely intervention.
2.4. Blood Cancer
One type of blood cancer that affects blood flow and bone marrow is leukemia. Experts state that this type of cancer can make the body more susceptible to gum bleeding and bruising under the skin.
2.5. Hormonal Imbalance
Another common cause of bruising is hormonal imbalance. Women entering menopause often face a deficiency in estrogen, which can weaken blood vessels, leading to damage and bleeding. Additionally, with aging, blood vessel elasticity diminishes, resulting in more frequent bruising, especially on the legs.
2.6. Diabetes
Bruising can also be a warning sign of diabetes, as this condition negatively affects blood circulation. Besides bruising, patients may experience other symptoms such as fatigue, thirst, and blurred vision. If you notice bruising along with these symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor for timely treatment.
2.7. Other Causes
Besides, the appearance of unusual bruises can also arise due to other causes such as:
- Side effects of anticoagulants (Warfarin, Clopidogrel, Aspirin, Dipyridamole, etc.).
- Certain infections or autoimmune diseases such as dactylitis (sausage fingers), nail fungus, ankylosing spondylitis, compartment syndrome, etc.
- Bruising under the placenta in pregnant women (occurring in 25% of cases). Most of these hematomas are small and recede without danger. However, blood clots or bleeding in the last trimester can signal issues like placental abruption or placenta previa and are considered medical emergencies.
3. How to Diagnose Bruising Under the Skin?
To check the condition of bruising under the skin, physical examinations and a comprehensive medical history review are applied. Currently, there is no specific blood test to assess bruises. However, depending on the situation, several necessary tests can include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC);
- Metabolic panel evaluation;
- Coagulation profile assessment;
- Functional tests.
Additionally, some imaging tests may sometimes be indicated, such as CT scans or MRI scans.
There are many causes of bruising under the skin, so if you notice unexplained bruises on your body that do not improve or are accompanied by other dangerous symptoms, you should visit a healthcare facility for a specialized examination and treatment if necessary.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.