The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phung Quang Thuy - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Tubal ligation is a permanent method of contraception for women. This minor surgery is simple, highly safe, and provides lifelong effectiveness. However, many women are still very concerned when hearing about this method, fearing it may affect their subsequent menstrual cycles. Refer to the information in the article below to understand this method better.
1. What is tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation (sterilization) is a method of preventing sperm and egg from meeting. There are many ways to block the fallopian tubes, such as tying, burning, clamping with clips, or placing a ring.
At that time, the ovarian hormone role remains as normal because the ovaries function normally, secreting female hormones and nurturing, maturing, and ovulating eggs, so physiology and menstruation are still normal. Since the fallopian tubes are blocked, the egg cannot meet the sperm, preventing conception.
2. When to choose tubal ligation?
Any woman can undergo this sterilization method after a thorough consultation and careful selection.
Sterilization is usually considered for women over 30 years old, having at least two healthy children who are developing normally, with the youngest being over 3 years old.
Additionally, sterilization is appropriate for women with severe medical conditions, those who are not capable of carrying a pregnancy, or those with mental disorders.
Contraindications include being pregnant or suspected of being pregnant, having acute infections in the reproductive organs or the body, or having an infected surgical wound.
3. Pre-surgery consultation

Afterward, both must agree and sign the consent for sterilization because:
- This is a permanent method of contraception.
- There is a certain failure rate (1/10,000 cases still get pregnant after tubal ligation), with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Complications from the surgery itself (bleeding, infection...), although at a very low rate.
4. Timing and implementation
The ideal time for tubal ligation is during the regenerative phase of the menstrual cycle, from day 5 to day 10, avoiding the luteal phase from day 14 to day 28, for women with a regular 28-day menstrual cycle.
Tubal ligation can also be combined with a cesarean section. However, it is not recommended to perform a cesarean section solely for sterilization due to the inherent risks for both mother and baby. In the postpartum period, from 24 to 36 hours after a vaginal birth, tubal ligation can be performed since the uterine fundus is still high at the navel level, making it easy to locate the fallopian tubes, requiring only a small incision under the navel. The postoperative and postpartum recovery period coincides, facilitating monitoring for doctors and the mother.
The day before surgery, the woman will undergo a general gynecological examination, tests, cervical smear, and exclusion of cases of menstrual disorders, tumors, genital prolapse, and urinary disorders.
On the surgery day, the woman will undergo bowel preparation, catheter insertion, change of clothing, and surgical site cleaning. Gynecologists can easily access the fallopian tubes through laparoscopy or a small incision in the lower abdomen or through the vagina. The fallopian tubes are blocked by electrocoagulation, placing a ring, cutting, and tying…
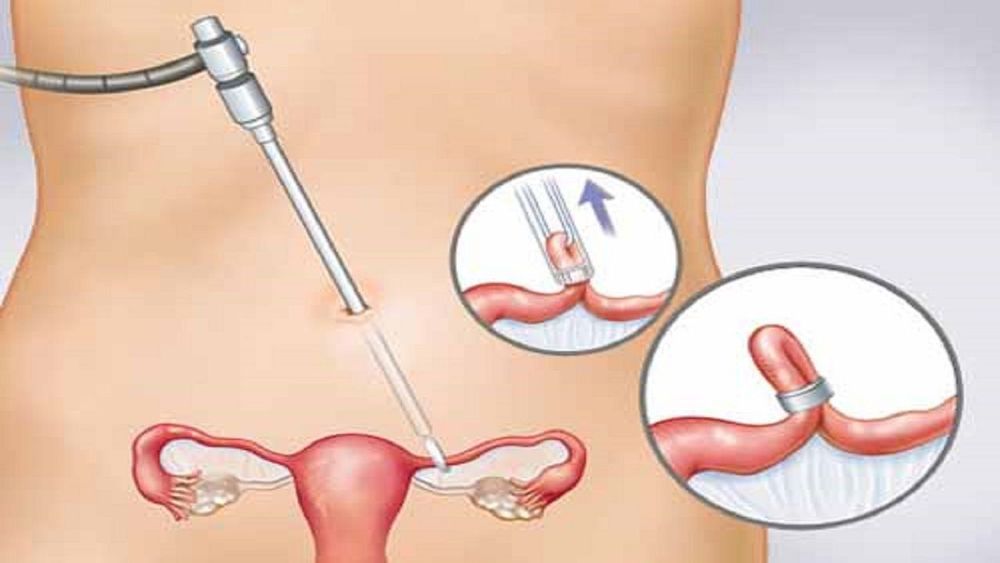
After surgery, the woman should stay in the medical facility for at least one to two days for monitoring and pain relief. Additionally, doctors will monitor for possible surgical complications such as bladder, bowel, blood vessel, nerve injury, infection, surgical wound bleeding... as well as late anesthetic complications. If favorable, the patient will be discharged with instructions for follow-up visits after 1 month and 3 months
5. Related notes
Tubal ligation does not affect the menstrual cycle at all. Tubal ligation merely interrupts the continuity of the fallopian tubes without impacting the ovaries. The ovaries alone have the endocrine function, regulating the menstrual cycle. Sterilization also does not affect a woman's femininity, personality, skin, hair, or marital relations.
Although this is a permanent method of contraception, it is not 100% effective. Some cases of ectopic pregnancy or intrauterine pregnancy can occur due to the natural reconnection of the fallopian tubes.
In summary, tubal ligation is an effective and safe contraceptive method that does not affect endocrine function. Both husband and wife need to understand clearly before making this decision. Tubal ligation does not affect the menstrual cycle or the long-term health of women.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.