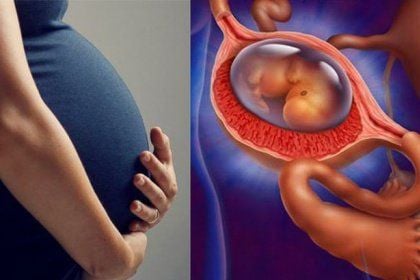
An ectopic pregnancy, also known as a pregnancy outside the uterus, occurs when the fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterine cavity. This is a highly dangerous obstetric condition that can threaten both the fertility and life of the pregnant woman.
1. Understanding ectopic pregnancy
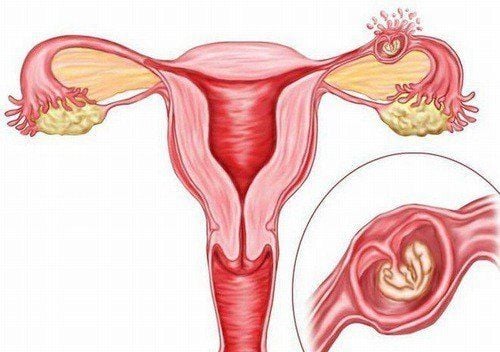
Ectopic pregnancies do not develop in a fixed location but can implant in various areas, such as:
- Pregnancy in the fallopian tube: This is the most common type of ectopic pregnancy, accounting for 95% of cases.
- Pregnancy in the ovary, cervix, abdominal cavity, or fallopian tube
If diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, timely and proper treatment is crucial. This condition is an acute medical emergency; if left untreated, a ruptured gestational sac can cause massive bleeding, posing a life-threatening risk to the mother.
According to statistics, for every 1,000 pregnancies, about 4 to 5 cases are ectopic.
Typically, ectopic pregnancies are detected between the 5th and 10th week of pregnancy, which corresponds to at least the 15th day of the menstrual cycle. If you experience symptoms such as vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, or a sudden drop in blood pressure, you should immediately go to the hospital for specialized tests to confirm whether you have an ectopic pregnancy.
2. Signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Many women wonder whether a pregnancy test would show positive if they have an ectopic pregnancy. In reality, pregnancy tests detect the hormone HCG in urine, regardless of where the gestational sac implants. Therefore, even in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, you may still have typical pregnancy symptoms, and the test will likely show two lines.
However, the beta-HCG level rises slowly, meaning subsequent tests may show darker lines. HCG levels only drop when the ectopic pregnancy begins to regress.
From a medical perspective, apart from cases where the pregnancy is too early to implant in the uterus, doctors will recommend a transvaginal ultrasound to locate the gestational sac if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected. Timely diagnosis and intervention are essential. You should not worry too much but follow your doctor's instructions to help protect your health.
The signs of ectopic pregnancy are often subtle and difficult to detect. You may only discover it during routine prenatal checkups, or in severe cases, be hospitalized with intense abdominal pain and hemorrhagic shock when the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured.
If you have an ectopic pregnancy, you may still experience typical pregnancy symptoms such as: Mild abdominal cramps, breast tenderness, nausea, missed periods,... However, unusual symptoms may follow, including:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: In cases of ectopic pregnancy, the bleeding tends to be prolonged and dark red. Only a small number of cases show no abnormal bleeding.
- Abdominal pain: You may feel pain at the implantation site of the ectopic pregnancy or in the lower abdomen. The pain is often persistent and uncomfortable, sometimes becoming severe and accompanied by vaginal bleeding. As the ectopic pregnancy develops, the intensity of pain typically increases. If the gestational sac ruptures, you may experience severe and continuous abdominal pain, along with symptoms such as sweating, shoulder pain, dizziness, blurred vision, limb weakness, shortness of breath, and possibly fainting.
To ensure your health and prevent life-threatening complications, if you notice any signs of ectopic pregnancy, you must go to the hospital immediately for examination and treatment by healthcare professionals.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.