This article has been consulted with Specialist I, MD, Néang Chanh Ly - Obstetrics and Gynecology - Obstetrics and Gynecology Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection. If not detected and treated promptly, genital herpes in men can lead to severe complications.
1. What is Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes, also known as herpes simplex, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) that spreads through sexual contact in both men and women. The virus can enter the body through breaks in the skin or mucous membranes, leading to a high transmission rate through sexual activity.
If not detected and treated in a timely manner, genital herpes in general and male genital herpes in particular can lead to complications.
The herpes simplex virus responsible for genital herpes has two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2:
- HSV-1 primarily causes genital herpes in areas above the waist, such as the mouth, lips, cheeks, chest, and arms.
- HSV-2 usually causes genital herpes in areas below the waist, such as the buttocks, genital organs, and legs.
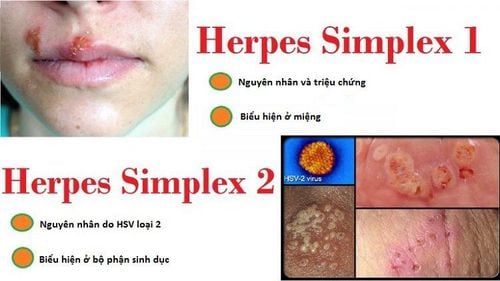
2. Symptoms of Genital Herpes
- In the early stages, genital herpes presents with pain and itching, typically occurring 2 to 7 days after the individual is infected with the virus.
- After a few hours to a few days, blisters or nodules begin to appear on the mucous membranes of the genital area (such as the penis, scrotum in men, or the vagina, cervix in women) or the anus (buttocks, thighs, etc.).
- If these blisters cluster closely together, they may progress into ulcers. These ulcers cause itching, burning sensations, and sharp pain. When the ulcers burst, they may leak fluid or bleed.
- In men, genital herpes can cause pus discharge from the urethra, while in women, there may be increased vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Genital herpes has a very specific cycle.
- The disease can recur annually or monthly; however, most individuals experience infrequent outbreaks. During an outbreak, patients may exhibit flu-like symptoms such as fever, headaches, and swollen lymph nodes in the groin. During the recurrence phase, patients may experience fever, lymphadenopathy, headaches, body aches, and fatigue, leading to poor appetite.
3. Is Genital Herpes Dangerous?
For adults with genital herpes, aside from the skin lesions, the disease does not cause any severe complications. However, individuals will experience discomfort and sharp pain at the lesions until the herpes is completely treated.
Genital herpes causes pain during sexual intercourse, decreases sexual pleasure, and may also affect urination, leading to frequent urges to urinate and painful urination. When the ulcers burst, patients may urinate pus or blood.
Pregnant women with genital herpes risk transmitting the infection to their child during vaginal delivery if the lesions burst. In this case, genital herpes can cause brain damage, vision impairment, or even death in the newborn. Additionally, primary herpes and cervical herpes can lead to miscarriage or premature birth.
During an outbreak, the disease is highly contagious until the affected areas fully heal. Using condoms does not eliminate the risk of transmission if herpes lesions are present in areas surrounding the genitals.
4. Treatment for Genital Herpes
Currently, there is no definitive treatment to completely cure genital herpes, as the virus remains in the body for life. Once infected, there are various treatment options to manage outbreaks, including antiviral medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir. These medications help sores heal more quickly and reduce the frequency of recurrences. They can also be used during or after outbreaks.
For women who have previously had genital herpes and wish to become pregnant, it is essential to inform their doctor about their condition to receive appropriate specialized treatment and avoid the risk of transmission to the baby.
5. Prevention of Genital Herpes

Similar to other sexually transmitted infections, genital herpes can be prevented through measures such as:
- Maintaining personal hygiene, especially before and after sexual intercourse.
- Using condoms for safer sexual practices.
- Being faithful to one partner.
- Taking precautions during oral sex.
- Not sharing needles or any items that may contain bodily fluids, pus, or blood from an infected person.
- If you suspect you have contracted the virus, proactively visit a healthcare provider for diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
- In cases of active infection, it is crucial to prevent transmission by minimizing sexual activity, avoiding contact, and keeping sores clean and dry. Wash your hands thoroughly after touching the sores and wait for the lesions to heal completely before engaging in sexual activity.
When early symptoms of genital herpes are detected, patients should seek medical attention for diagnosis, counseling, and appropriate treatment options.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.