The article is consulted with pediatric specialists from the Pediatrics and Neonatology Department at Vinmec International General Hospital, Hai Phong.
Borate glycerin is a therapeutic agent in the otolaryngology category. Therefore, when affected by hand-foot-mouth disease, borate glycerin is commonly prescribed for cleansing the throat in children with lesions such as swelling, ulcers, and vesicles.
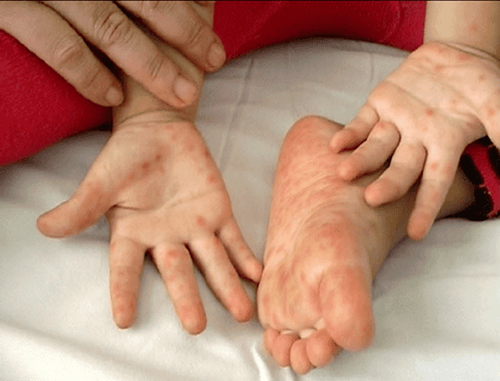
1. Signs of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease in Children
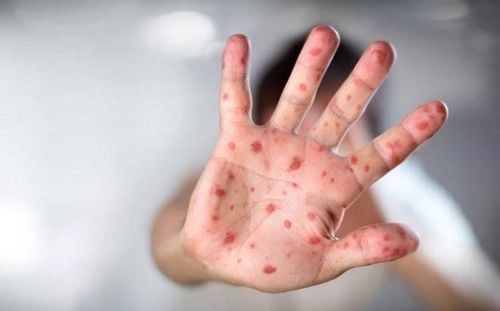
Hand-foot-mouth disease in children has easily recognizable and characteristic signs. Approximately two days after an incubation period, symptoms of hand-foot-mouth disease will manifest as follows:
• Fever: Fever is considered the body's natural response to prevent the invasion of harmful viruses and bacteria.
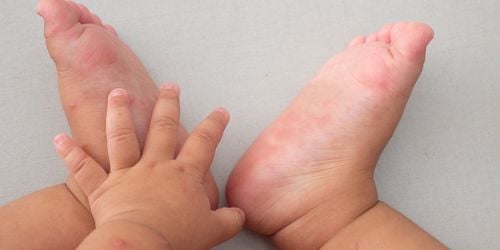
• Skin rash: The child may present lesions such as erythema, vesicles on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, within the oral cavity, and on the tongue. It is important to prevent the child from scratching the vesicles to minimize the risk of secondary infection.
• Fatigue and loss of appetite: Due to the presence of vesicles in the oral cavity, the child may experience oral pain, leading to decreased appetite and overall fatigue.
• Diarrhea: Some children may exhibit diarrhea as a symptom of the infection.
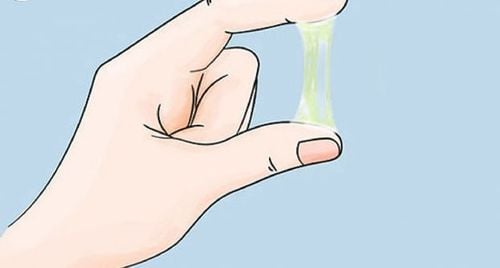
2. How to Use Borate Glycerin Solution for Throat Cleansing in Children with Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease
Borate glycerin serves as a therapeutic agent in the otolaryngology field. Thus, in cases of hand-foot-mouth disease, borate glycerin is often indicated for throat cleansing in children with lesions such as swelling, ulcers, or vesicles.
The procedure for using borate glycerin solution for throat cleansing in children with hand-foot-mouth disease is as follows:
• Have the child sit upright with their mouth wide open.
• Shine a light into the child's throat to adequately illuminate areas of vesicles and ulcers.
• With the right hand, depress the tongue; with the left hand, hold a straight cotton swab, dip it into the solution, and gently apply it to the lesions.
• Clean the child's mouth before and after meals.
3. Other Medications Utilized in Cases of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease in Children
• Antipyretics: If the child has a high fever exceeding 38.5 degrees Celsius, paracetamol should be administered according to the child's weight.
• Oral gels such as: Kamistad, Zyttee also possess antiseptic and analgesic properties to facilitate easier feeding.
• Various antiseptic agents: Lidocaine, benzydamine mouth spray for children over the age of 5, benzydamine mouth rinse for children aged 12 and older, and saline solution with a NaCl concentration of 0.9%.
• Oral rehydration salts: Adequate hydration should be maintained by administering oral rehydration solutions.
Depending on the severity of the hand-foot-mouth disease in children, healthcare providers may prescribe more potent medications for effective treatment, such as:
• Symptoms of meningeal irritation: Treatment in a hospital setting with medications that counteract seizures.
• Bacterial meningitis: Antibiotics combined with close monitoring of respiratory symptoms.
• Complications of encephalitis with paralysis, altered consciousness, and seizures: Administration of neuroprotective agents, anticonvulsants, and prophylactic antibiotics against secondary infections.
• Respiratory failure and cardiovascular collapse: In such cases, special care, shock fluid resuscitation, and prophylactic antibiotics for secondary infections are required.

However, the medications mentioned should not be self-prescribed for children; it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals. Additionally, to reduce the risk of transmitting hand-foot-mouth disease among children, one should:
• Ensure personal hygiene, including that of caregivers, is rigorously maintained.
• Wash hands frequently with soap and clean water.
• Disinfect household surfaces and toys using soap and water, followed by a diluted chlorine solution.
• Avoid contact with infected individuals.
• Consume thoroughly cooked food and ensure safe food hygiene practices. • Do not mouth-feed the child or share personal items.
• If a child exhibits signs of hand-foot-mouth disease, it is advisable to seek immediate medical attention for prompt treatment.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.