1. Signs of a Sprain in the Ankle or Wrist
1.1. Sprain Severity Levels
Sprains are categorized into three different levels:
- Grade 1 – Mild: The ligament is slightly stretched.
- Grade 2 – Moderate: The ligament is partially torn.
- Grade 3 – Severe: The ligament is completely ruptured.
1.2. Common Signs of a Sprain
Before learning what to do when you sprain a joint, patients should recognize the signs to distinguish sprains from fractures and apply appropriate management. The typical symptoms of a sprain include:
- Sharp pain at the injured joint: A sharp pain occurs in the affected area, especially when the patient moves or walks. After that, the joint becomes stiff, and the pain temporarily subsides. However, about an hour later, the injured joint becomes painful again, swollen, and bruised due to internal bleeding and vascular disturbances.
- Limited movement and difficulty walking: In cases of ankle, wrist, hand, or foot sprains, the patient may be unable to walk or move the joint.
In most cases, X-rays are required to distinguish sprains from fractures, and ultrasound may be performed to assess ligament damage.

2. The Difference Between a Sprain and a Muscle Strain
Patients often confuse sprains with muscle strains, as both involve soft tissue injuries around or within joints.
Muscle strain occurs when a muscle is overstretched, and in more severe cases, the muscle fibers may tear. The symptoms are similar to those of sprains—pain and swelling in the affected muscle or joint area. Both conditions make movement and joint function difficult.
However, to differentiate them, bruising typically appears around the injured joint in sprains, whereas muscle strains cause muscle spasms without visible bruising.
3. What to Do When You Have a Sprain?
The RICE method summarizes the four key steps in initial injury management, especially for sports-related sprains: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
- Rest: Use a cloth or elastic bandage to immobilize the injured joint. This helps reduce pain and swelling and provides joint support.
- Ice: Apply a cold compress to reduce pain and constrict blood vessels, helping minimize swelling. Cold compresses can be applied 4–8 times a day for 15–20 minutes each time. Do not leave the ice pack on one spot for too long, as it may damage the soft tissues.
- Elevation: Keep the injured joint elevated above heart level to reduce swelling and bruising.
- Avoid putting pressure on the injured area: For wrist or ankle sprains, limit weight-bearing. Use assistive devices if necessary.
- Topical or medication use: For sports-related sprains, ethyl chloride spray can be applied to cool the area and relieve pain. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be used, but aspirin should be avoided as it increases bleeding risk and inhibits platelet aggregation.
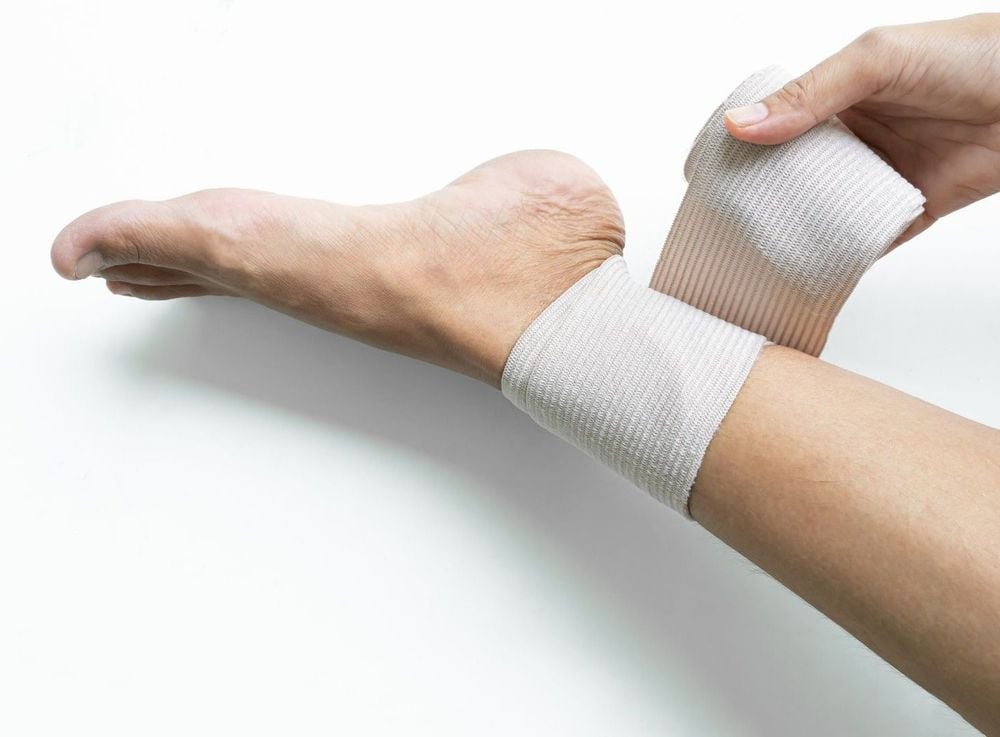
The above measures are suitable for mild sprains where ligaments are stretched or only partially torn. Once pain subsides, gentle joint exercises should be started to promote circulation
For severe sprains, patients should visit a hospital or medical center for evaluation. The doctor may recommend wearing a brace or cast to immobilize the joint for 4–6 weeks. Afterward, the patient can gradually resume movement under medical supervision.
4. Important Precautions When Managing Sprains
Sprains are common injuries, but many people underestimate them and apply improper treatments, which may cause serious complications. Here are important precautions to follow:
- Do not use alcohol, herbal balm, or hot compresses on the injured area, as these may increase internal bleeding.
- Do not inject any medication directly into the sprain site to avoid vasodilation, swelling, or bruising.
- Do not wrap the area too tightly, as it may cause pain and bruising.
Sprains are among the most common injuries and can cause serious consequences if not managed properly. Therefore, patients should understand how to handle sprains and seek medical attention if symptoms are severe or persist even when mild. Doctors can accurately identify the cause and recommend appropriate treatment for the current condition.
Vinmec International General Hospital specializes in examining and treating musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis, degeneration, herniation, and joint or bone pain. At Vinmec, diagnosis and treatment are conducted using advanced medical technologies that not only provide high effectiveness but also minimize recurrence risks. Vinmec’s success is attributed to its modern facilities and a team of highly qualified, experienced doctors, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes for all patients.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.



