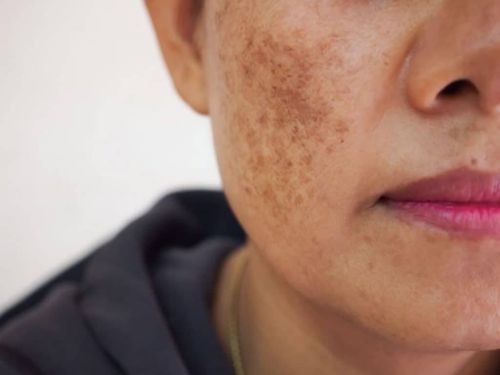
Melasma is a widespread skin condition characterized by the appearance of symmetrical, non-elevated pigmented lesions, ranging from light to dark brown, affecting both males and females. Although melasma is less common in men, it negatively impacts quality of life and aesthetics just as much as it does in women. The causes of melasma are often associated with sun exposure, hormonal influences, and other factors, etc,…
1. Melasma in men
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by the appearance of irregular symmetrical pigmented spots, ranging from light to dark brown, associated with sun-exposed areas, particularly on the face. Although melasma can affect all races and both genders, it is more commonly seen in women. However, melasma negatively impacts the quality of life in men just as much as in women.
There are many detailed studies on melasma in women, while there are very few studies on the clinical pathology and treatment methods in men. Although melasma generally presents similarly in both men and women, there are certain clinical differences, causes, and treatment approaches for melasma in men. Hyperpigmentation in sun-exposed areas such as the face can be a cosmetic concern for patients and may negatively affect their quality of life.

2. Causes of melasma in men
Currently, the exact causes of melasma are still unknown. However, some of the most common factors may include sun exposure, hormonal influences, and genetics. Additionally, it has been observed that melasma is more prevalent in individuals with Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI, particularly those of Asian, Hispanic, and African descent, as well as in men with darker skin tones from Asian, African, and American backgrounds. Furthermore, the increased prevalence of melasma in Indian men may be attributed to their darker skin and the tropical climate of India. Some risk factors that contribute to the development of melasma in men include:
2.1 Frequent sun exposure
Regular exposure to sunlight is a common cause of hyperpigmentation, triggering the production of melanin and leading to melasma. Melanin acts as the skin's natural sunscreen by protecting it from harmful UV rays. Excessive sun exposure can disrupt this process, resulting in increased pigmentation.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation (UVA and UVB) enhances the proliferation and activity of melanocytes, causing epidermal pigmentation, which is more pronounced in sun-exposed areas. This is further supported by findings that melasma often improves in winter and worsens during the summer months. Moreover, there is a higher prevalence in tropical regions and areas at high altitudes.
2.2 Congenital and genetic factors
The hereditary etiology of melasma with a familial predisposition is a notable risk factor. The occurrence of melasma has been documented in twins, indicating a shared genetic component. Additionally, various studies have shown that a family history of melasma is observed among close relatives, such as mothers, siblings, aunts, uncles, and cousins, etc…
However, nowadays, there have been no studies investigating the genetic correlation with melasma. The differences in genetic predisposition across various studies and populations may be due to the multifactorial nature of melasma, suggesting that the development of the condition may be related to the regulation of epigenetic hormones and environmental influences.

2.3 Age
As individuals age, the signs of skin aging become clearer. The number of melanin-producing cells decreases, but the remaining cells increase in size, and their distribution becomes more concentrated in specific areas of the skin. These physiological changes account for the increase in age spots in individuals over 40 years old.
2.4 Hormonal imbalance
The influence of hormones is also a primary cause of skin hyperpigmentation, particularly known as melasma. Two studies have reported low testosterone levels in Indian men with melasma. One of these studies assessing hormone levels in men with melasma found elevated LH and low testosterone levels in approximately 9.7% of the cases.
2.5 Medication use
In addition to endogenous hormonal factors, the use of exogenous hormonal medications or agents that induce melasma has been shown to cause the condition. Some cases of melasma have been reported following hormone therapy. Finasteride is believed to increase testosterone levels, leading to subsequent melasma pigmentation.
The use of cosmetics and the consumption of certain medications with photosensitizing properties are also associated with the development of melasma. An Indian study observed that the use of mustard oil for body and hair massage was more prevalent among men with melasma, accounting for 43.9%. Additionally, a study by Vazquez et al. indicated that the use of cosmetics such as soaps, shaving creams, and perfumes was reported in 92.6% of men with melasma.

2.6 Due to certain disease
Some chronic diseases such as thyroid disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, typhoid fever, etc,... have been identified in men with melasma. Hyperpigmentation is also a symptom of several diseases, including autoimmune disorders, gastrointestinal issues, metabolic disorders, and vitamin deficiencies.
Additionally, conditions such as dermatitis, acne, allergic dermatitis, psoriasis, or following an injury like burns or chemical exposure, etc,… can also lead to increased skin pigmentation. As a result, the skin may become darker and lose color after the wound heals.
In summary, melasma is less common in men than in women; however, it significantly impacts the quality of life of those affected. One of the leading causes of melasma in men is sun exposure, along with potential factors such as genetics, hormonal imbalance, etc,... If melasma persists, it is advisable to visit a healthcare facility specializing in dermatology for evaluation and appropriate treatment options which are suitable for your skin type.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, dermatologytimes.com
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.