This article is advised by Trần Văn Trọng, Specialist II, MD - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang.
Colon polyps in children are a fairly common condition that parents need to pay more attention to. In the early stages of the disease, colon polyps often develop silently with few clear symptoms, making diagnosis and detection difficult.
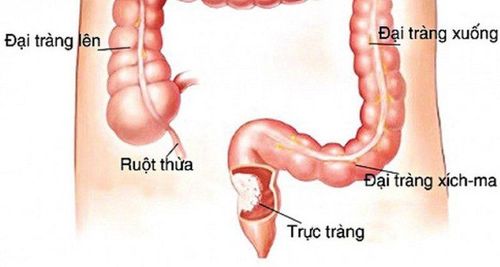
1. What are colon polyps in children?
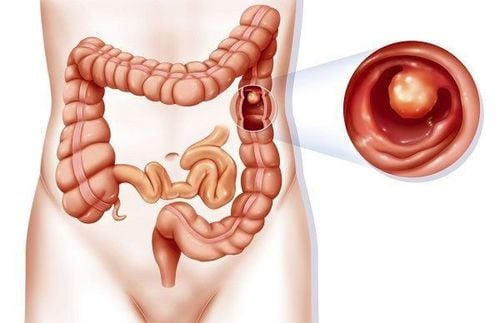
Colon polyps are benign tumors that develop on the lining of the colon (large intestine). Most of these polyps are harmless, but certain types like tubular adenomas and villous adenomas have the potential to progress into cancer. Polyps can occur singly or as multiple polyp formations along the colon. Most often, polyps do not cause any symptoms and are usually discovered incidentally during X-rays, colonoscopies, or through blood tests looking for occult blood in feces.
Many factors can increase the risk of developing colon polyps in children, including diet, infections, genetic factors, and the child's constitution. Children typically present with colon polyps between the ages of 4 and 7, although children as young as 1 or 2 years old can also be affected, albeit at a lower rate. Colon polyps are also more common in boys than in girls.

2. Symptoms of colon polyps in children
The symptoms of colon polyps in children can vary widely, including:
- Passing fresh blood or detecting blood mixed with stool even if the child is not constipated.
- Large colon polyps can cause severe abdominal pain, sometimes leading to intestinal obstruction.
- Larger polyps with small villous projections may secrete salt and water, resulting in diarrhea and significant fluid loss, leading to hypokalemia.
- Continuous blood loss from polyps can cause anemia, manifesting as pale skin, pale palms, and mucous membranes.
- Long rectal polyps may prolapse out of the anus.
3. Common types of colon polyps in children
• The most common polyps found in children are solitary, pedunculated polyps approximately 0.5 to 1 cm in size. However, cases of children with multiple polyps or a large polyp measuring 2 to 3 cm in the colon are not uncommon.
• Familial adenomatous polyposis is more commonly seen in older children and is less common in younger children or in infants still breastfeeding. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, dark-colored blood in stool, and anemia. Children with this type of polyp commonly have multiple polyps scattered throughout the colon and rectum.
• Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a hereditary disease caused by a mutation in the STK11 gene, increasing a child's risk of colorectal and other cancers. Children with this syndrome have pigmented spots on their lips, around the mouth, oral mucosa, eyes, nose, palate, and palms and soles. Polyps associated with this syndrome frequently lead to intussusception in the small intestine and rarely become malignant.
• Gardner syndrome is a genetic disorder associated with multiple organ involvement, characterized by multiple colon polyps, osteomas, and soft tissue tumors. In this case, hundreds or thousands of tubular adenomas in the colon have a nearly 100% chance of developing into cancer if left untreated. Therefore, children are often recommended to undergo preventive colectomy to mitigate this risk.
4. Are colon polyps in children dangerous?
Most colon polyps in children are benign and not immediately concerning. However, if not detected and treated promptly, polyps can grow larger, leading to issues such as weight loss and malnutrition, which can affect the child's normal development.
Additionally, if left unattended, colon polyps can result in more severe issues such as digestive disorders, gastrointestinal bleeding, and the risk of developing cancer. Research indicates that the likelihood of colon polyps transforming into cancer increases with the child's age. This risk usually occurs after 10 years from the initial detection of polyps and depends on the type and size of the polyps. Polyps such as tubular adenomas and villous adenomas, particularly those measuring between 1 and 1.5 cm, have a high risk of developing into cancer.
5. Diagnosis and treatment of colon polyps in children
Early detection and treatment of colon polyps in children are vital to preventing complications such as intestinal obstruction or cancer. If children exhibit signs such as abdominal pain, digestive disorders, changes in bowel habits, or blood in the stool, parents should take them to the doctor for examination. Diagnostic methods include gathering medical history, clinical examination, barium contrast imaging of the colon, and a complete colonoscopy, which will be performed.
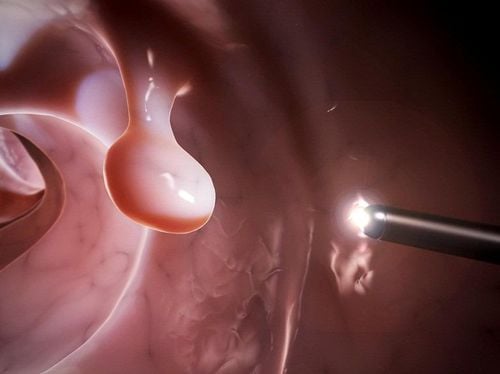
Regarding treatment, the endoscopic polypectomy is a quite common method for both children and adults. This procedure involves the doctor examining the area where the polyp appears and removing it using electrocautery. During a single session, the doctor can remove between 50 to 60 polyps. This procedure is considered safe, and most patients can be discharged right after the surgery. However, in some cases where there are difficulties in controlling bleeding, patients will need to be monitored further.
In children, due to good development conditions, the recurrence of colorectal polyps after removal is quite rare, except in cases of familial polyposis. In such situations, the doctor must closely monitor the patient after the endoscopic polypectomy to prevent possible complications. Additionally, to assess the effectiveness of the treatment, patients need to visit for a follow-up and undergo a colonoscopy six months after the surgery.

In summary, colorectal polyps in children are a health issue that requires careful attention and monitoring. Although most cases of polyps are benign, they can cause uncomfortable symptoms and complications if not addressed promptly. Parents should pay attention by taking their children for regular check-ups and consulting medical specialists to detect and manage colorectal polyps effectively.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.