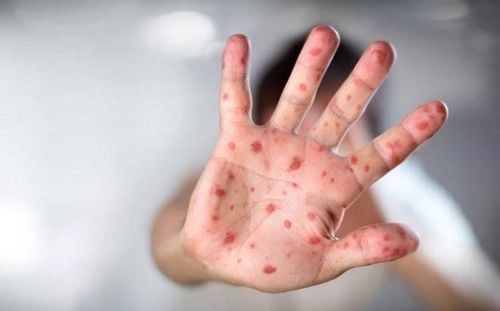
Hand, foot, and mouth disease - a mild, contagious viral infection in young children - is characterized by mouth ulcers and rashes on the hands and feet. Sometimes, hand, foot, and mouth disease symptoms are easily confused with foot and mouth disease. This article will help us understand more about these two diseases.
1. What is hand, foot and mouth disease?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is an acute viral infectious disease that can be transmitted through the digestive tract. It is commonly found in young children and can cause large epidemics.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is common in Asian countries and is becoming a public health concern in Vietnam.
2. Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease
The typical signs of hand, foot, and mouth disease are high fever, ulcers in the mouth, and rashes and blisters on the hands, feet, and buttocks.
There are some common symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease, including:
- High fever.
- Sore throat.
- The patient feels uncomfortable and tired.
- The tongue, gums, and inside the cheeks are painful, red, and have blisters.
- Children feel uncomfortable and irritable.
- Loss of appetite.
- Rashes appear, not itchy, but sometimes blisters appear on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and buttocks.
It usually takes 3 to 6 days from infection until you start to have signs and symptoms of the disease. Fever is often the first sign of hand, foot, and mouth disease, followed by a sore throat, loss of appetite, and general malaise.
A day or two after the fever, painful sores may appear in the front of the mouth or throat. A rash may appear on the hands, feet, and buttocks, lasting a day or two.
Ulcers that develop in the back of the mouth and throat may suggest that your child has a viral illness called herpangina. Distinctive features of herpangina include a sudden high fever and, in some cases, seizures. Ulcers that appear on the hands, feet, or other parts of the body are rare.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is usually a mild illness that causes only a few days of fever with mild signs and symptoms. Contact your doctor if mouth sores or a sore throat prevent your child from drinking fluids. Seek medical attention if your child's signs and symptoms worsen after a few days.
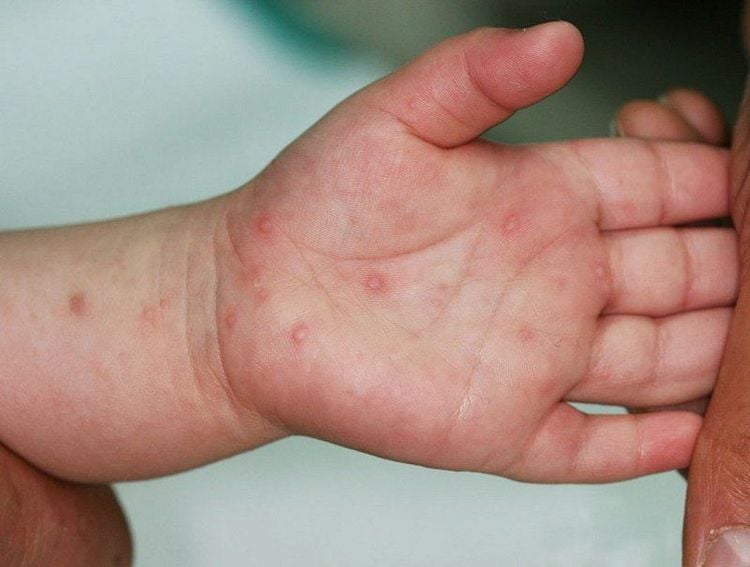
3. Causes of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
The most common cause of hand, foot, and mouth disease is infection with coxsackievirus A16. Coxsackievirus belongs to a group of viruses called nonovio enteroviruses. Other types of enteroviruses sometimes cause hand, foot, and mouth disease.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is spread through person-to-person contact with an infected person:
- Nasal secretions or throat secretions
- Saliva
- Fluid from blisters
- Contact when an infected person sneezes or coughs
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is most common in children, especially in childcare settings, because of frequent diaper changes and potty training and because young children often put their hands in their mouths.
Although your child is most contagious with hand, foot, and mouth disease during the first week of illness, the virus can remain in the body for weeks after the signs and symptoms are gone, which means your child can still infect others.
Some people, especially adults, can spread the virus without showing any signs or symptoms of the disease.
4. Distinguishing between hand, foot, and mouth disease and foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease and foot and mouth disease are not related. Foot and mouth disease is a contagious viral disease found in animals.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease are caused by enteroviruses, while foot and mouth disease is caused by the Foot and Mouth Disease Virus.
The epidemiology of the two diseases is also different. Hand, foot, and mouth disease occurs in humans, while foot and mouth disease occurs only in cloven-hoofed animals such as buffalo, cows, pigs, goats, sheep, deer, etc. There is no information showing that foot and mouth disease occurs in humans.
5. Risk of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease

Hand, foot, and mouth disease mainly affects children under 10 years of age, usually those under 5. Children in child care centers are particularly susceptible to outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease because the infection is spread through person-to-person contact, and young children are most susceptible.
Children usually develop immunity to hand, foot, and mouth disease as they get older by making antibodies after being exposed to the virus that causes it. However, adolescents and adults can get the disease.
6. Complications of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
The most common hand, foot, and mouth disease complication is dehydration. The disease can cause sores in the mouth and throat, making swallowing painful and difficult.
Watch closely to make sure your child drinks fluids regularly throughout the illness. If dehydration is severe, intravenous (IV) fluids may be needed.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is usually a mild illness that causes only a few days of fever and relatively mild signs and symptoms. A rare and sometimes severe form of coxsackievirus can involve the brain and cause other complications:
- Meningitis: This is a rare infection and inflammation of the membranes (meninges) and cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Encephalitis: This serious and potentially life-threatening illness involves brain inflammation caused by a virus. Encephalitis is rare.
Washing hands properly with antibacterial soap, maintaining environmental hygiene, limiting contact with infected people... are some preventive measures that can help reduce the risk of hand, foot and mouth disease infection.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.