Ear eczema is a common skin condition in children caused by various factors, including allergies, pus, or metabolic dysfunction. Although it does not pose immediate health risks, improper treatment can lead to bacterial infections in children.
1. What is ear eczema?
Ear eczema is a form of eczema that appears on the helix, the external auditory canal, and the skin surrounding the ear, characterized by basic but diverse skin lesions.

- It can occur at any age in children and is classified as acute, subacute, or chronic. The specific type of ear eczema depends on the clinical symptoms.
2. Causes of the condition
The exact causes of ear eczema and its physiology are not thoroughly understood currently. Medical experts believe it may be associated with several factors, including:
- Pus: Sticky pus or pus that discharges frequently or accumulates over time. Usually, ear eczema spreads from the ear canal to the outer ear.
- Allergies: Typically, allergy-related ear eczema starts from the head and moves down to the neck, then spreads to the outer ear and canal. Allergy predisposition means external factors can trigger ear eczema.
- Those who suffer from eczema often have an overactive immune system. When irritants are encountered, the immune response can result in various symptoms.
Additionally, another hypothesis suggests that mental health may also contribute to ear eczema. Mental state issues, along with metabolic dysfunction, digestive disorders, neurological disorders, or endocrine system disorders, can cause ear eczema. In such cases, children may be treated with medication and psychological therapies to improve their ear eczema.
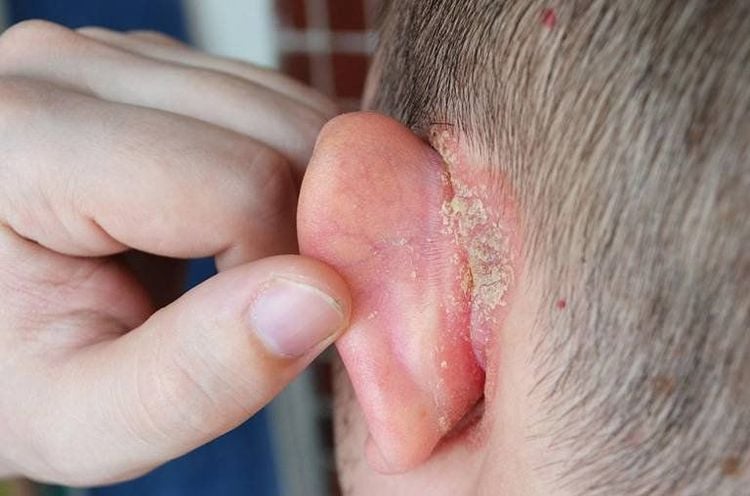
3. Symptoms of the condition
Some symptoms of ear eczema in children include:
- The skin around the outer ear may feel itchy and appear red.
- Small blister-like vesicles that contain clear mucous. These vesicles may rupture, leaving thin, brown, scab-like lesions on the skin surface.
- When the lesion dries, the skin may still feel itchy, red, and thickened.
- Presence of small opaque or gray scales that are easy to peel off.
Ear eczema can cause itching, leading to discomfort and frequent scratching in children, which increases the risk of scratches and potential bacterial infections. Bacterial eczema can easily be recognized by small pus-filled blisters-like vesicles and crusty brown scales on the surface.
In more severe cases, inflammation can spread to other areas, such as the skin behind the ear or the temporal region.
4. Treating ear eczema
Treatment for ear eczema encompasses medication and local care, along with measures to boost the immune system and vitamins supplement. The types of medications include antibiotics, antihistamines, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory drugs:
- For local care, parents should clean the child’s ears and external canals if pus is present, and apply 5% silver nitrate. In cases of bacterial infection, applying methylene blue and using steroid ear drops may be necessary.
- Antibiotics: Options may include Cefuroxime, Cefixime, Levofloxacin, or Augmentin.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Steroid medications such as Methylprednisolone and prednisone (5mg), and enzyme-based drugs like Lysozyme can be used for children.
- Pain relievers: Commonly used remedies include Paracetamol at a dose of 30-40 mg/kg/day.
- Antihistamines: Options include Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, or Chlorpheniramine.
- Supplements: supplements may include Vitamin PP, Calcium C, and B Complex C.
These are some useful tips for caring for children with ear eczema:
- Avoid using water to wash the affected area, especially in children with acute ear eczema. The ear may itch intensely and may have many blisters if scratched. This can lead to increased discharge, spreading the condition to surrounding skin areas. Thus, keeping the wound dry is essential to prevent further spread and infections.
- Do not use warm water or solutions containing irritating substances to clean the affected areas, as this might aggravate the condition.
- Prevent the affected area from coming into contact with known allergens (allergy-inducing substances). These may include certain foods, objects, or animal fur.
- Opt for fragrance-free moisturizers without irritants. Ideally, apply the cream right after bathing the child.
- Protect the ears during cold weather since low temperatures may irritate the skin.
- Use gentle cleansers that are free from irritants; it is best to use cleansers formulated for sensitive skin.
Generally, eczema in children is a common skin condition with various stages and forms. When children exhibit unusual skin symptoms, parents should take them to medical facilities or health centers for professional diagnosis and early treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.