The article is professionally consulted by Vu Huu Thang, M.A, M.D - Intensive Care and Emergency Physician - Department of Intensive Care and Emergency - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
A wound that is suppurating, swollen, and exuding discharge are characteristic signs indicating the risk of infection and necrosis. Therefore, upon observing these signs in an open wound, prompt and accurate management is required, following the guidance of a doctor.
1. The normal healing process of a wound
Normally, when a wound occurs, the body has a self-healing mechanism. The wound healing process is a complex sequence, beginning with inflammation, followed by proliferation (where collagen fibers begin to grow within the wound to help it close faster) and then the maturation phase (scar formation), during which the body produces more collagen to reinforce and remodel the wound.
However, if the wound is not properly cleaned and managed, it may become infected within 24 to 72 hours after injury. If treated promptly, an infected wound will not cause severe complications, but it may leave an unsightly scar.
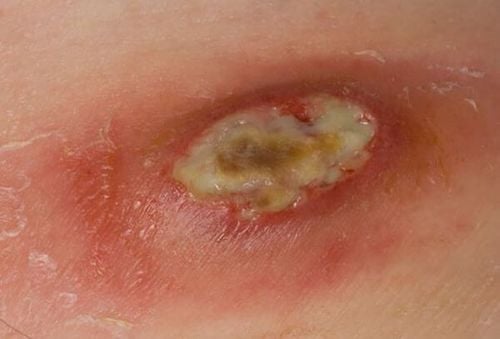
2. Suppurative wounds - a manifestation of an infected wound
Suppurative wounds and swelling are the two most common signs that warn of an infected wound. In addition, wound infections also have many characteristic symptoms such as:
- Swollen wound: This is a common sign that appears immediately after the injury. If the wound becomes infected, swelling typically occurs 4 to 6 days afterward. The red area is approximately 2 to 3 mm around the wound margin or may spread.
- Pus-filled wound: This is the most prominent sign indicating an infected wound. The wound will discharge a colored, foul-smelling exudate, with pus typically appearing 3 to 4 days after the injury.
- Gradually increasing pain in the wound: If the wound is infected, there will be signs of pain that gradually increase over time.
- Fever: Depending on whether the wound is severe or mild, the patient may or may not have a high fever. If the severe wound is infected, the patient shows signs of high fever throughout the body, afternoon fever, fatigue,....
3. Instructions for treating suppurative wounds
Depending on the severity of the wound, its location, and the area affected, the injured person will have different treatment options. In addition, the patient's overall health and the duration of the injury are also two factors that influence the wound treatment process. If the wound has heavy pus, the patient should go to a medical facility for examination.
Below are the instructions for treating infected suppurative wounds:
- Clean the wound: When the wound is infected, it is recommended to use saline solution or an antiseptic solution (such as Betadine, Povidone,...) to clean the wound. While cleaning, you may need to incise part of the wound to thoroughly cleanse it.
- Remove bacteria and necrotic tissue: You need to remove pus, bacteria and necrotic tissue to eliminate the cause of the infection, avoid the infection from spreading.The method is to remove the necrosis (or surgery as prescribed by the doctor) if the necrosis is too large and too deep.
- Use of antibiotics: Patients with suppurative wounds may apply antibiotic gel directly to the wound or take oral antibiotics if the infection is severe. However, when using anti-inflammatory medications or antibiotics, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions.
- Dressing the wound: For minor wounds, you may not need to apply a bandage but can use a spray dressing such as Nacurgo, which forms a Polyesteramide biological membrane over the wound to promote healing or use Urgo personal bandages or a thin sterile gauze to cover the wound and prevent friction. For surgical wounds, during hospitalization, healthcare staff will change the dressing. After discharge, the patient can leave the surgical wound exposed to air, but it should remain clean and protected to prevent infection, with the use of a Polyesteramide biological membrane. If the wound is more severe, the patient should spray Nacurgo onto the wound before applying a bandage to help speed up the healing process;

After treating a suppurative wound, you need to avoid strenuous exercise in the wound area, increase nutritional supplements so that the wound heals quickly. Note, take the patient to a medical facility immediately if there are some of the following signs:
- Wounds that cause a lot of pain
- The patient had a high fever with an unclear cause
- Persistent red streaks appear in the wound
- Surface wound infection
- The patient is very weak
To prevent the risk of suppurative wound infection, immediately after the injury, within 10 minutes, you should clean the wound with clean water and a non-irritating soap (to remove dirt and bacteria). Follow the steps for wound care as described above to avoid more severe complications.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.