This article is professionally consulted by Nguyen Thi My Linh, Specialist level I, M.D, Pediatrics and Neonatology Department, Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang. She has 12 years of experience in diagnosing and treating pediatric diseases, particularly in neonatal resuscitation and the treatment of neonatal diseases. In addition, she has expertise in breastfeeding counseling as well as pediatric nutrition counseling and intervention.
Preterm infants require careful monitoring of their weight. Normally, the weight gain standard is at least 5 grams per day for extremely preterm infants, or 20 grams per day for very preterm infants.
1. How do preterm infants develop?
The principle of development for preterm infants is that one month of extrauterine support is equivalent to one month of normal intrauterine is satisfactory, and if the growth is greater than that, it is considered good.
If the infant gains weight at only one-third of the required rate, this indicates that the preterm infant is failing to thrive, the mother needs support from skilled healthcare staff .
Generally, preterm infants need to be carefully monitored regarding weight before being discharged, typically a preterm infant must weigh at least 2 kg before being ready to leave the incubator and the weight gain standard is at least 5 grams per day for extremely preterm infants, or 20 grams per day for very preterm infants. And in any case, newborns also need to gain 15 grams per day.

2. Standard weight chart for preterm infants under 5 years old
The standard weight chart for preterm infants is typically compared with the general height and weight charts for children of the same age and sex to assess whether the child is developing normally. However, since each child develops individually, parents need not be overly concerned if their child is developing steadily and showing proportional measurements over time. Below is the weight chart for Vietnamese newborns in 2018 (from 0 to 6 months old, in kg). The chart is based on the growth standards of the WHO 2007 and is currently being applied to Vietnamese infants.
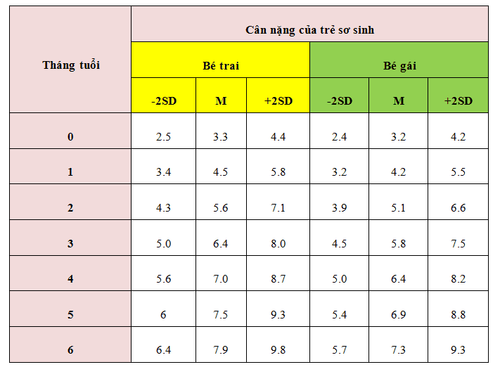
SD stands for standard deviation. In addition to the standard level (M), the WHO marks deviation levels from 1 to 3, with a minus (-) indicating underweight and a plus (+) indicating overweight.
However, the range from -1SD to +1SD is considered normal growth, -2SD and +2SD is the risk of underweight or overweight, -3SD and +3SD is malnutrition or obesity, which require intervention.
Due to fragile health and sensitive constitution, many preterm infants face serious health issues such as heart disease, brain hemorrhage, kidney failure, jaundice, anemia and problems related to the lungs, vision, hearing, motor development. Therefore, mothers should monitor their child’s physical symptoms. If any abnormalities occur, they should promptly take the child to a pediatrician for timely treatment.
In addition to the daily nutrition regimen for preterm infants, parents should supplement their child’s diet with supportive products containing lysine, essential minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins to meet the full nutritional needs of the child. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help the child eat well, and promote overall development.
Please access the website Vinmec.com regularly and stay updated with useful information to care for the baby and the whole family.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.