Rovamycine is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections and skin infections. Understanding the medication helps ensure effective treatment.
1. Uses of Rovamycine
Rovamycine contains the active ingredient spiramycin and comes in various formulations with different strengths, including 1.5MUI, 3MUI tablets, and 0.375 MUI, 0.750 MUI oral suspension powders.
Spiramycin is a broad-spectrum macrolide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis to suppress bacterial growth. This antibiotic is effective against various bacterial strains such as Streptococcus, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus, Helicobacter pylori, and Campylobacter jejuni.
Due to its bactericidal effect, Rovamycine is indicated for the following cases:
- Infections caused by bacteria sensitive to this class of antibiotics, such as pharyngitis, acute sinusitis, secondary infections in acute bronchitis...
- Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
- Community-acquired pneumonia in individuals without resistance factors, such as recent use of this class of drugs, and no severe clinical signs...
- Pneumonia caused by atypical bacteria.
- Benign skin infections, such as impetigo, impetigo contagiosa, skin and subcutaneous tissue infections (especially erysipelas).
- Oral infections.
- Non-gonococcal genital infections.
- Prevention of meningococcal meningitis: In cases where rifampicin antibiotics are contraindicated. Spiramycin is not used to treat meningococcal meningitis but is indicated for prophylaxis in patients who have previously been treated and recovered, before returning to community activities and preventive treatment for those who have been in contact with the patient within 10 days before hospitalization.
- Prevention of acute rheumatic fever recurrence in patients allergic to penicillin antibiotics.
- Toxoplasmosis in pregnant women.
Rovamycine is contraindicated in the following cases:
- History of allergy to this antibiotic or other macrolide antibiotics.
- Not for use in breastfeeding women.
- Caution is advised for patients with liver dysfunction, G6PD deficiency. Pregnant women may use it, but they should consult a doctor. If generalized skin redness and pustules appear along with a fever while using the medication, treatment should be discontinued, and spiramycin should be contraindicated for future use.
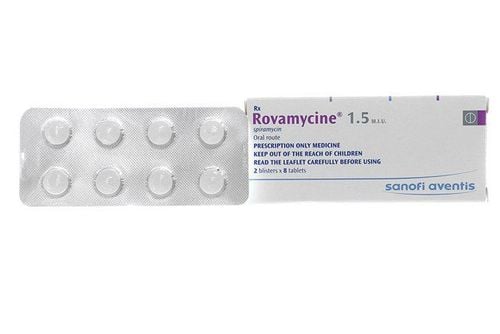
2. Dosage and usage of Rovamycine
Dosage:
- Adults: 2 to 3 tablets of 3 MUI or 4-6 tablets of 1.5 MUI, totaling 6-9 MUI per day, divided into 2 or 3 doses.
- Infants and children: The dosage is 150,000 - 300,000 UI/kg/day, divided into 2 to 3 doses.
Prevention of meningococcal meningitis:
- Adults: 3 MUI every 12 hours for 5 days.
- Children: 75,000 UI/kg every 12 hours for 5 days.
Spiramycin is generally not excreted in an active form through the kidneys, so no dosage adjustment is needed in cases of renal impairment.
Usage:
- For powdered forms: Pour the powder into a glass of water, fill the packet with water, pour it back into the glass, and stir to dissolve.
- For tablets: Swallow directly with water.
3. Some precautions when using Rovamycine
- The medication may cause some side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and possible allergic skin reactions.
- It may interact with levodopa. The absorption of carbidopa is inhibited, reducing the plasma concentration of levodopa. Therefore, clinical monitoring and appropriate adjustment of the levodopa dosage are necessary when both medications are used concurrently.
- Before use, you should inform your doctor if you have a history of allergies to the drug, its ingredients, or any other allergies. Inform your doctor about all the medications you are currently taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
- Pregnant women can use it if necessary and should consult a specialist doctor.
- Nursing women should discontinue the medication while breastfeeding, as the drug can be excreted into breast milk.
- Storage: Store the medication at room temperature, away from moisture and direct light. Do not store it in a high humidity bathroom or in the freezer.
Hoping this article has helped you understand what Rovamycine is used for, its dosage, and the special precautions when using it. Rovamycine should be used under the prescription of a doctor, so do not use it on your own.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.