Esophageal stricture, cardia in children
Children with esophageal stenosis, achalasia in children all have symptoms of difficulty swallowing, choking, painful swallowing or vomiting. Dilation of the esophagus and cardia is an effective treatment for these diseases.
1. What is the technique of dilatation of the esophagus and cardia?
Esophageal stenosis is caused by congenital anomalies or acquired pathology, thickening of the esophageal wall and proliferation of fibrous tissue. The disease causes malnutrition in children, slow weight gain, food blockage, aspiration syndrome. Causes of esophageal stricture may be:
Surgery to atrophy the esophagus to narrow the acquired anastomosis; Ingestion of corrosive substances such as acids, ... Gastroesophageal reflux, cardiac spasm. Cardiac spasm is an esophageal motility disorder of unknown etiology. Characterized by incomplete relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter and loss of esophageal motility.
Children with esophageal stricture, spasm of the heart all have symptoms of difficulty swallowing, choking, painful swallowing, or vomiting. Diagnosis of the disease is based on X-ray and esophageal endoscopy to determine the location of the stricture, the length of the stricture, the condition of the diverticulum, and the esophageal fistula.
Esophageal stricture dilation is a mechanical technique to tear the fibromuscular or fibrous organizations in the esophagus and cardia. Applied in the treatment of spasms of the heart, narrowing of the esophagus.

Trẻ bị co thắt tâm vị, hẹp thực quản có biểu hiện nuốt khó, nuốt nghẹn, nuốt đau, hay nôn trớ
2. Indications for esophageal stricture, cardia in children in which case? 2.1 Indications Indications for esophageal stricture dilation in children in the following cases:
esophageal stricture after surgery may be caused by swallowing acid by mistake, erosive therapy, radiation therapy, congenital esophageal stricture. Cardiac spasm dilation (indicated for treatment in children 10 years of age and older). 2.2 Contraindications Cases that are contraindicated for esophageal stricture dilation in children include:
Children with respiratory failure, cardiovascular collapse, peritonitis, intestinal perforation, cervical vertebrae injury, esophageal fistula, trachea, esophageal stricture. Cases of gastrointestinal surgery in the last 1 month or intestinal obstruction, coagulopathy, severely reduced platelet count should be considered.
3. Perform esophagogastric dilatation in children 3.1 Esophageal stricture dilatation Esophageal strictures can use plastic bougie or balloon dilatation. Esophageal stricture dilation with plastic tube includes the following steps:
Step 1: Observe by endoscopic screen, insert the soft end of a 1cm long metal wire through the interventional canal and the stenosis, check the passage into the stomach. thick. Step 2: Keeping the lead in the stomach, withdraw the endoscope, use metal to mark the position of the thoracic stenosis, the distance from the narrow position to the dental arch. Step 3: Push the plastic bougie tube to slide on the metal conductor through the narrow place, if there is moderate resistance or the narrow position is relatively tight or bleeding, do not push the bougie tube. If resistance is moderate, a maximum of 3 consecutive bougies with a diameter of more than 1mm should be used in the same dilation session. Depending on the initial dilation and the progression of esophagitis, the number of dilations will vary. Esophageal stricture with balloon dilation includes the following steps:
Step 1: Determine the location and size of the esophageal stricture by endoscopic examination, check the accompanying lesions. Step 2: Pass the soft end of the conductor through the interference channel. Step 3: Slide the catheter balloon over the guide wire. Step 4: On the endoscopic screen, check the position of the balloon at the esophageal stricture. Inflate the balloon to expand the stenosis with the rule that the diameter of the ball should not be larger than 2mm in diameter and up to 3 times the diameter of the stenosis. The maximum number of dilations in the same session is 3 times. Before hot threading, care should be taken to inject 1-2ml of smooth silicone oil into the intervention channel. Balloon esophageal stricture is a safer method with dilation time (within a few minutes). Highly effective when the balloon is placed in a narrow position under the view of the endoscope and the guide wire.
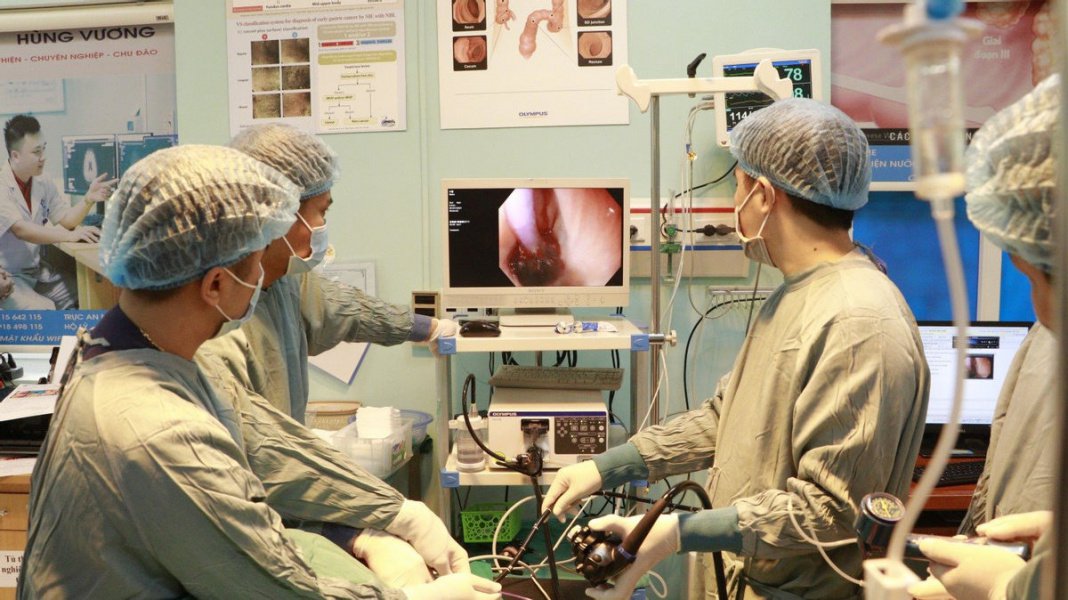
Nong hẹp thực quản đạt hiệu quả cao hơn dưới sự quan sát của nội soi và dây dẫn
3.2 Cardiocentesis Cardiac angioplasty includes the following steps:
Step 1: Insert the soft end of the wire into the intervention channel to enter the cardia. Step 2: Mark the center position with metal. Step 3: Keeping the lead intact, withdraw the endoscope, push the balloon to slide on the lead to the cardia. Check the position of the balloon at the cardia. Step 4: Treatment of achalasia with cardiac dilatation technique should pay attention to inflate the balloon slowly and gently pull the balloon to make sure the balloon is fixed in the correct position when the balloon is inflated. Under the light, the balloon is observed to have a sand-shaped shape, the pressure measured at the waist of the ball fluctuates in the range of 7 - 12psi. With a 30mm ball, pump only once for 45s for 12 year olds, for older children, pump 30mm for 30s, 35mm for 15s. Step 5: Withdraw the balloon, then inject a small amount of contrast dye into the esophagus to check the esophagus for tear or leak. Cardiac dilatation needs to be done 2-3 times.
Step 1: Insert the soft end of the wire into the intervention channel to enter the cardia. Step 2: Mark the center position with metal. Step 3: Keeping the lead intact, withdraw the endoscope, push the balloon to slide on the lead to the cardia. Check the position of the balloon at the cardia. Step 4: Treatment of achalasia with cardiac dilatation technique should pay attention to inflate the balloon slowly and gently pull the balloon to make sure the balloon is fixed in the correct position when the balloon is inflated. Under the light, the balloon is observed to have a sand-shaped shape, the pressure measured at the waist of the ball fluctuates in the range of 7 - 12psi. With a 30mm ball, pump only once for 45s for 12 year olds, for older children, pump 30mm for 30s, 35mm for 15s. Step 5: Withdraw the balloon, then inject a small amount of contrast dye into the esophagus to check the esophagus for tear or leak. Cardiac dilatation needs to be done 2-3 times.
4. Monitoring and management during and after the treatment of esophageal stricture, cardia in children During the process of esophageal stricture, the heart needs to monitor the child for fever, cough, wheezing, and ventilation status. Pneumothorax, subcutaneous emphysema, vomiting, anemia, respiratory failure. If there are no signs of complications, the child can be fed after 24 hours.
Some complications that may occur when performing esophageal stricture, cardia and management are as follows:
Suspicion of esophageal perforation: Appears when the patient has pneumomediastinum or pleural effusion, bleeding massively, as determined by chest radiograph. At that time, external consultation is required and the patient is treated and resuscitated. Esophageal perforation during cardiac dilatation: Usually appearing in the first 5 hours, the patient needs immediate surgery to repair the tear and open the pericardial muscle. In summary, dilation of the esophagus and the cardia is a common treatment for children with congenital or acquired esophageal spasm and esophageal stricture. To be safe and have the highest effectiveness, this technique needs to be performed in hospitals with modern equipment systems and a team of good doctors. Currently, the Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital is trusted by many parents to examine the diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to. Vinmec brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts by:
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: Including leading experts with high professional qualifications ( professor, associate professor, doctorate, master), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. The doctors are well-trained, professional, have a heart - a vision. Understanding young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. Advanced techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to play comfortably and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.






