1. What Is Acute Gout?
Acute gout occurs when the body experiences a disorder in uric acid metabolism, leading to the formation and deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints, bones, synovial membranes, and even the kidneys.
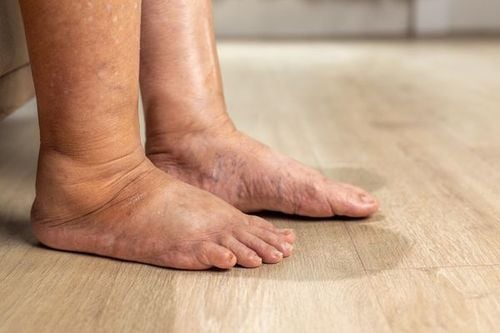
This condition causes intense pain in joints such as the fingers, toes, wrists, elbows, and ankles. Acute gout is characterized by a sudden and severe onset of symptoms. It requires early detection and prompt management to prevent chronic progression and serious complications.
2. Symptoms of Acute Gout
Typical symptoms of acute gout include pain and swelling in the affected joint. Gout attacks often occur unexpectedly at night, with pain so intense that it can cause insomnia. In addition, the patient may experience:
- Joints most commonly affected include the big toe, ankle, and instep.
- The skin over the affected joint becomes tight, red, and warm, with severe tenderness at the site.
- The synovial membranes surrounding the joints may also be affected.
Mild to moderate fever may accompany joint pain. - Symptoms usually last 5–7 days, after which swelling and pain gradually subside.
- Acute gout attacks tend to recur, often becoming more severe with each episode.
3. Causes and Triggers of Acute Gout
Gout primarily results from a disturbance in uric acid metabolism. One of the most common contributing factors is a diet high in purines, found in protein-rich foods.
Normally, uric acid is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
However, when blood uric acid levels become excessively high, uric acid crystallizes into urate deposits in joints, bones, and synovial membranes — and sometimes in the renal parenchyma — causing inflammation and pain. Elevated uric acid levels in the blood are the direct cause of gout development.
In addition to this main mechanism, several factors may trigger acute gout attacks, including:
- Unbalanced diet: Consuming large amounts of seafood, red meat, alcohol, and sugary beverages increases uric acid levels.
- Obesity and being overweight: These conditions raise the risk of metabolic disorders, diabetes, and diseases of the liver and kidneys.
- Family history: People with relatives who have gout have a higher likelihood of developing acute gout.
- Certain medications: Diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and low-dose aspirin may increase uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks.
- Gender and health status: Men and individuals who have recently suffered trauma or undergone surgery face a higher risk.
- Cold weather: Low temperatures can affect joint blood circulation and precipitate acute gout episodes.

To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.